- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In

Definition of thesis
Did you know.
In high school, college, or graduate school, students often have to write a thesis on a topic in their major field of study. In many fields, a final thesis is the biggest challenge involved in getting a master's degree, and the same is true for students studying for a Ph.D. (a Ph.D. thesis is often called a dissertation ). But a thesis may also be an idea; so in the course of the paper the student may put forth several theses (notice the plural form) and attempt to prove them.
Examples of thesis in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'thesis.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
in sense 3, Middle English, lowering of the voice, from Late Latin & Greek; Late Latin, from Greek, downbeat, more important part of a foot, literally, act of laying down; in other senses, Latin, from Greek, literally, act of laying down, from tithenai to put, lay down — more at do
14th century, in the meaning defined at sense 3a(1)
Dictionary Entries Near thesis
the sins of the fathers are visited upon the children
thesis novel
Cite this Entry
“Thesis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/thesis. Accessed 28 Jun. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of thesis, more from merriam-webster on thesis.
Nglish: Translation of thesis for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of thesis for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about thesis
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, flower etymologies for your spring garden, 12 star wars words, 'swash', 'praya', and 12 more beachy words, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, games & quizzes.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 28, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Boosting Citations: A Comparative Analysis of Graphical Abstract vs. Video Abstract

The Impact of Visual Abstracts on Boosting Citations

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of thesis in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- I wrote my thesis on literacy strategies for boys .
- Her main thesis is that children need a lot of verbal stimulation .
- boilerplate
- composition
- corresponding author
- dissertation
- essay question
- peer review
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
thesis | Intermediate English
Examples of thesis, collocations with thesis.
These are words often used in combination with thesis .
Click on a collocation to see more examples of it.
Translations of thesis
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
at the coalface
doing the work involved in a job, in real working conditions, rather than planning or talking about it

Fakes and forgeries (Things that are not what they seem to be)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- Intermediate Noun
- Collocations
- Translations
- All translations
To add thesis to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add thesis to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write a Thesis
I. What is a Thesis?
The thesis (pronounced thee -seez), also known as a thesis statement, is the sentence that introduces the main argument or point of view of a composition (formal essay, nonfiction piece, or narrative). It is the main claim that the author is making about that topic and serves to summarize and introduce that writing that will be discussed throughout the entire piece. For this reason, the thesis is typically found within the first introduction paragraph.
II. Examples of Theses
Here are a few examples of theses which may be found in the introductions of a variety of essays :
In “The Mending Wall,” Robert Frost uses imagery, metaphor, and dialogue to argue against the use of fences between neighbors.
In this example, the thesis introduces the main subject (Frost’s poem “The Mending Wall”), aspects of the subject which will be examined (imagery, metaphor, and dialogue) and the writer’s argument (fences should not be used).
While Facebook connects some, overall, the social networking site is negative in that it isolates users, causes jealousy, and becomes an addiction.
This thesis introduces an argumentative essay which argues against the use of Facebook due to three of its negative effects.
During the college application process, I discovered my willingness to work hard to achieve my dreams and just what those dreams were.
In this more personal example, the thesis statement introduces a narrative essay which will focus on personal development in realizing one’s goals and how to achieve them.
III. The Importance of Using a Thesis
Theses are absolutely necessary components in essays because they introduce what an essay will be about. Without a thesis, the essay lacks clear organization and direction. Theses allow writers to organize their ideas by clearly stating them, and they allow readers to be aware from the beginning of a composition’s subject, argument, and course. Thesis statements must precisely express an argument within the introductory paragraph of the piece in order to guide the reader from the very beginning.
IV. Examples of Theses in Literature
For examples of theses in literature, consider these thesis statements from essays about topics in literature:
In William Shakespeare’s “ Sonnet 46,” both physicality and emotion together form powerful romantic love.
This thesis statement clearly states the work and its author as well as the main argument: physicality and emotion create romantic love.
In The Scarlet Letter, Nathaniel Hawthorne symbolically shows Hester Prynne’s developing identity through the use of the letter A: she moves from adulteress to able community member to angel.
In this example, the work and author are introduced as well as the main argument and supporting points: Prynne’s identity is shown through the letter A in three ways: adulteress, able community member, and angel.
John Keats’ poem “To Autumn” utilizes rhythm, rhyme, and imagery to examine autumn’s simultaneous birth and decay.
This thesis statement introduces the poem and its author along with an argument about the nature of autumn. This argument will be supported by an examination of rhythm, rhyme, and imagery.
V. Examples of Theses in Pop Culture
Sometimes, pop culture attempts to make arguments similar to those of research papers and essays. Here are a few examples of theses in pop culture:

America’s food industry is making a killing and it’s making us sick, but you have the power to turn the tables.
The documentary Food Inc. examines this thesis with evidence throughout the film including video evidence, interviews with experts, and scientific research.

Orca whales should not be kept in captivity, as it is psychologically traumatizing and has caused them to kill their own trainers.
Blackfish uses footage, interviews, and history to argue for the thesis that orca whales should not be held in captivity.
VI. Related Terms
Just as a thesis is introduced in the beginning of a composition, the hypothesis is considered a starting point as well. Whereas a thesis introduces the main point of an essay, the hypothesis introduces a proposed explanation which is being investigated through scientific or mathematical research. Thesis statements present arguments based on evidence which is presented throughout the paper, whereas hypotheses are being tested by scientists and mathematicians who may disprove or prove them through experimentation. Here is an example of a hypothesis versus a thesis:
Hypothesis:
Students skip school more often as summer vacation approaches.
This hypothesis could be tested by examining attendance records and interviewing students. It may or may not be true.
Students skip school due to sickness, boredom with classes, and the urge to rebel.
This thesis presents an argument which will be examined and supported in the paper with detailed evidence and research.
Introduction
A paper’s introduction is its first paragraph which is used to introduce the paper’s main aim and points used to support that aim throughout the paper. The thesis statement is the most important part of the introduction which states all of this information in one concise statement. Typically, introduction paragraphs require a thesis statement which ties together the entire introduction and introduces the rest of the paper.
VII. Conclusion
Theses are necessary components of well-organized and convincing essays, nonfiction pieces, narratives , and documentaries. They allow writers to organize and support arguments to be developed throughout a composition, and they allow readers to understand from the beginning what the aim of the composition is.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.

When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.
Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Think of yourself as a member of a jury, listening to a lawyer who is presenting an opening argument. You'll want to know very soon whether the lawyer believes the accused to be guilty or not guilty, and how the lawyer plans to convince you. Readers of academic essays are like jury members: before they have read too far, they want to know what the essay argues as well as how the writer plans to make the argument. After reading your thesis statement, the reader should think, "This essay is going to try to convince me of something. I'm not convinced yet, but I'm interested to see how I might be."
An effective thesis cannot be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." A thesis is not a topic; nor is it a fact; nor is it an opinion. "Reasons for the fall of communism" is a topic. "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" is a fact known by educated people. "The fall of communism is the best thing that ever happened in Europe" is an opinion. (Superlatives like "the best" almost always lead to trouble. It's impossible to weigh every "thing" that ever happened in Europe. And what about the fall of Hitler? Couldn't that be "the best thing"?)
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay.
Steps in Constructing a Thesis
First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication. Does the author contradict himself or herself? Is a point made and later reversed? What are the deeper implications of the author's argument? Figuring out the why to one or more of these questions, or to related questions, will put you on the path to developing a working thesis. (Without the why, you probably have only come up with an observation—that there are, for instance, many different metaphors in such-and-such a poem—which is not a thesis.)
Once you have a working thesis, write it down. There is nothing as frustrating as hitting on a great idea for a thesis, then forgetting it when you lose concentration. And by writing down your thesis you will be forced to think of it clearly, logically, and concisely. You probably will not be able to write out a final-draft version of your thesis the first time you try, but you'll get yourself on the right track by writing down what you have.
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction. Although this is not required in all academic essays, it is a good rule of thumb.
Anticipate the counterarguments. Once you have a working thesis, you should think about what might be said against it. This will help you to refine your thesis, and it will also make you think of the arguments that you'll need to refute later on in your essay. (Every argument has a counterargument. If yours doesn't, then it's not an argument—it may be a fact, or an opinion, but it is not an argument.)
This statement is on its way to being a thesis. However, it is too easy to imagine possible counterarguments. For example, a political observer might believe that Dukakis lost because he suffered from a "soft-on-crime" image. If you complicate your thesis by anticipating the counterargument, you'll strengthen your argument, as shown in the sentence below.
Some Caveats and Some Examples
A thesis is never a question. Readers of academic essays expect to have questions discussed, explored, or even answered. A question ("Why did communism collapse in Eastern Europe?") is not an argument, and without an argument, a thesis is dead in the water.
A thesis is never a list. "For political, economic, social and cultural reasons, communism collapsed in Eastern Europe" does a good job of "telegraphing" the reader what to expect in the essay—a section about political reasons, a section about economic reasons, a section about social reasons, and a section about cultural reasons. However, political, economic, social and cultural reasons are pretty much the only possible reasons why communism could collapse. This sentence lacks tension and doesn't advance an argument. Everyone knows that politics, economics, and culture are important.
A thesis should never be vague, combative or confrontational. An ineffective thesis would be, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because communism is evil." This is hard to argue (evil from whose perspective? what does evil mean?) and it is likely to mark you as moralistic and judgmental rather than rational and thorough. It also may spark a defensive reaction from readers sympathetic to communism. If readers strongly disagree with you right off the bat, they may stop reading.
An effective thesis has a definable, arguable claim. "While cultural forces contributed to the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe, the disintegration of economies played the key role in driving its decline" is an effective thesis sentence that "telegraphs," so that the reader expects the essay to have a section about cultural forces and another about the disintegration of economies. This thesis makes a definite, arguable claim: that the disintegration of economies played a more important role than cultural forces in defeating communism in Eastern Europe. The reader would react to this statement by thinking, "Perhaps what the author says is true, but I am not convinced. I want to read further to see how the author argues this claim."
A thesis should be as clear and specific as possible. Avoid overused, general terms and abstractions. For example, "Communism collapsed in Eastern Europe because of the ruling elite's inability to address the economic concerns of the people" is more powerful than "Communism collapsed due to societal discontent."
Copyright 1999, Maxine Rodburg and The Tutors of the Writing Center at Harvard University

What is a Thesis? Definition, Examples of Theses in Literature
Home » The Writer’s Dictionary » What is a Thesis? Definition, Examples of Theses in Literature
Thesis definition: A thesis is a statement in which the writer conveys his position regarding a topic.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis statement refers to part of an essay where the writer establishes his position regarding a topic. This is the position that the writer will further explore throughout his paper.
Example of Thesis
- Topic : religious freedom.
- Thesis : All citizens of the United States should be allowed to exercise the religion of their choice freely without interference from government.
- Explanation : In this thesis statement, the writer has taken the position that all citizens should be free to worship and practice their religion as they see fit. The government should not pressure citizens into any religion, and it should not persecute members of any faith community.
The Importance of a Thesis Statement
Thesis statements are important in order to establish the writer’s position regarding a topic or idea. They help to introduce the essay and set a focus for the reader.
Narrative thesis statements are found in narrative essays or in literature. They set the scene for the lesson that will be explored or taught through the piece.
Famous opening lines that exemplify a narrative thesis:
- The following narrative thesis is found in A Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens:
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair.”
The Function of Thesis in Literature
Narrative thesis statements are important in literature in order to establish the purpose for the work or introduce the lesson that the novel will attempt to teach. This allows the reader to have a focus when beginning the novel in order to effectively engage them into the story.
Examples of Theses in Literature
In the memoir, I am Malala by Malala Yousafzai, a thesis statement can be found in the beginning pages of her story.
- “One year ago I left my home for school and never returned. I was shot by a Taliban bullet and was flown out of Pakistan unconscious. Some people say I will never return home, but I believe firmly in my heart that I will. To be torn from the country that you love is not something to wish on anyone.”
In this thesis statement, Yousafzai establishes the basis of her memoir, which is to tell the story of how she was forced to leave her home.
In Vladmir Nabokov’s Lolita , a thesis can be seen in the line, “Lolita, light of my life, the fire of my loins”.
Here the narrator establishes the identity of the young nymph that he is unhealthily obsessed with in the story. Lolita is a young child while he is a grown man; therefore, this statement creates the uneasy feeling about him that continues throughout the novel.
Summary: What Are Theses?
Define thesis in literature: In summation, a thesis statement establishes a purpose in the piece of writing. It may establish the lesson or story to be told, or in an essay it may establish the position the writer assumes when exploring a topic.
Either way, it is important for the thesis to be clear in order to effectively convey the writer’s message.
Final Example:
In Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Cask of Amontillado,” the thesis statement can be found in the first line of the short story. Montresor immediately states his purpose, “the thousand injuries of Fortunato I had borne as best I could, but when he ventured upon insult I vowed revenge.”
In this statement, Montresor states that he will be seeking revenge after being treated wrongly by Fortunato. By beginning the story with the narrative thesis establishes the purpose for the remainder of the piece.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
What is a thesis statement? [with example]

What is a thesis statement?
Purpose of a thesis statement, how to write the best thesis statement, thesis statement example, frequently asked questions about thesis statements, related articles.
A thesis statement is a concise description of the goal of your work. This element is one of the most essential components of academic writing , as it tells your readers what they can expect in your paper.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
If you find yourself in the process of writing a a paper, but you don't know how to create a thesis statement , you've come to the right place. In the next paragraphs, you will learn about the most important elements of a thesis statement and how to come up with one.
A thesis statement highlights the main topic, shows how it will evolve, and conveys clearly the aim of your work. It does not only share the topic but it conveys the conclusion you came up with.
A good thesis statement provides directions for the development of the topic throughout the paper. In sum, this element of academic writing is crucial to sound research .
You can create a great thesis statement by following the format we outlined in our guide How to write a thesis statement .
In general, you should adhere to the following tips to write the best thesis statement:
- Focus the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Write the answer to the main question of your topic.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic.
- Do not state the obvious. Give a disputable stance that requires evidence.
Tip: To check if your thesis is clear, explain it to a peer or colleague. If they are confused, then you likely need to re-write it.
Here's an example of a thesis statement:
In what follows, I will explore Fiorina’s position in more depth, focusing especially on her claim that technology is "a great tool for democratization." Ultimately, I argue that the primary problem with Fiorina’s stance lies in her laissez-faire understanding of technology. By granting technology a kind of independent existence apart from human motivation and intent—by positing that "technology permits anybody to play," as if it possesses an autonomy all its own—Fiorina unwittingly opens the way for the very kind of discriminatory and undemocratic mechanisms that her position seemingly rejects.
Tip: Once you finish your paper, return to your thesis statement to make sure that it reflects what you actually wrote.
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. It really depends on your academic and expertise level. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements, for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Yes. Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have an extremely elaborate statement. A couple of clear sentences indicating the aim of your essay will be more than enough.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .

- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
thesis statement
[ thee -sis steyt-m uh nt ]
- a short statement, usually one sentence, that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, etc., and is developed, supported, and explained in the text by means of examples and evidence.
Discover More
Word history and origins.
Origin of thesis statement 1
More About Thesis Statement
What is a thesis statement .
In academic writing, a thesis statement is generally a sentence or two that summarizes the main point that an essay, research paper, or speech is making. It is typically located at the end of the introductory paragraph(s).
Thesis statements are kind of like roadmaps, laying out for the reader/listener where the writer/speaker is headed (argument) and how they are going to get there (evidence).
The thesis statement is widely taught in the humanities, especially in English classes in high school and college, to teach students how to make persuasive arguments that cite and analyze evidence and examples researched from literary, historical, or other texts.
Why is a thesis statement important in an essay?
Thesis comes from a Greek word that literally means “a setting down.” In the 300s BC, Aristotle defined thesis as when a philosopher puts forth a new idea that conflicts with general opinion.
Fast forward to today, when we use thesis to mean a “proposition” or “argument” one formally presents and defends. In academic settings, a thesis can be short for a thesis statement (our focus here) in an essay or shorter research paper. It can also be used for those much, much longer dissertations graduate students research, write, and defend for their degree (e.g., master’s thesis or doctoral thesis ).
Let’s look at statement real quick. It is a declaration or assertion. Sound redundant? The idea is that a thesis statement is the point in a paper or presentation that explicitly states the thesis. Usually in a sentence or two, the thesis statement summarizes the argument that’s going to be developed in the evidence and examples to come.
So, a thesis statement is just a sentence that gets the main point across. But, learning how to write these ain’t easy. That’s why educators, especially in English classes in high school and college, spend a lot of time teaching students how to craft effective thesis statements.
Why? Because in school, work, and life, we have to persuade people of our ideas and our point of view. These ideas might concern an analysis of literature or history, like a play by Shakespeare or a moment in the Civil Rights Movement. Or, these ideas might be a call to action, such as eating a certain diet or pursuing a business strategy.
How to write a thesis statement
There are many ways to make an effective thesis statement , but here are some general tips to follow.
So, let’s say you read a text, Shakespeare’s Twelfth Night , or researched a topic, the health benefits of kale. Then you formed an opinion about it—a claim you want to make about it and why others should care. You found evidence—quotes, examples, facts, statistics—in your resources that you think back up your argument. Your thesis statement brings all these together: point of view , evidence , and significance . It lays out where the entire paper or presentation is going, which is why educators often liken it to a roadmap .
Here’s an example:
Kale is good for you because it is nutrient-dense, cancer-fighting, and loaded with antioxidants.
The argument here—which a first-year high-schooler might make in a persuasive essay—is that “kale is good for you” (despite how some think it tastes). The claims it’s using to back up this assertion are that it’s 1) “nutrient-dense”; 2) “cancer-fighting”; and 3) “loaded with antioxidants.” The reader can expect that the rest of the essay will develop these claims, that is, cite and analyze evidence for them.
Here’s a thesis statement for a literary analysis of Shakespeare’s Twelfth Night. This resembles more of a college-level example:
Shakespeare’s Twelfth Night suggests that, when women do not reciprocate a man’s love, they are unjustly made out to be sexually deviant. This is illustrated in how the character Olivia is condemned as asexual because of her rejection of Duke Orsino.
Note how this thesis statement makes its claim in two sentences. Its argument centers on how women characters are vilified when they reject a man, and its evidence will be interactions between characters in Shakespeare’s play.
What are real-life examples of thesis statement ?
The term thesis statement is generally used by teachers and students in junior high, high school, and college, especially in English, Social Studies, and other classes in the humanities.
Okay so I rewrote my thesis statement! It’s a wee bit more vague but still a good direction a think. It’s more open so I can talk about more things and add more evidence. Wrote out an in-depth plan and then my brain crapped out. So I’m going to bed! Tomorrow is the day! — 🎃Unpaid Bills🎃 //Chaela (@Cierafire) August 14, 2019
Writing an explanatory essay in phases: thesis statement, body paragraph, concluding statement. Peer conversations to identify text evidence to support our thesis. pic.twitter.com/b6fdgx8rkD — Cheyenne England (@MsEnglandReads) August 7, 2019
The thesis statement is taught in what’s called the five-paragraph essay (or theme). This essay has an introduction which “funnels into” the thesis statement, including three reasons backing up the main argument. The next three paragraphs develop each of these claims, respectively, citing evidence and examples, such as literary texts, historical documents, or scientific reports. The final paragraph, the conclusion, restates the thesis statement and summarizes the paper and its broader significance.
Opentextbc.ca
Even after we are no longer in the classroom, people continue to reference thesis statements. While “real-life” thesis statements may not be as formal as the ones seen in five-paragraph essays, having a thesis statement —a point, a position, or a theory of the case—is considered informative, persuasive, and valuable in work, in the community, and in our personal lives.
The thesis statement is so widely taught and familiar that sometimes people joke about them. On social media, for instance, people may humorously end a post with “In this essay, I will …” when expressing a deeply felt but ultimately low-stakes opinion on some popular topic. The phrase In this essay, I will alludes to the signposting language some people use in their thesis statements.
pumpkin spice has nothing to do with pumpkins but with covering up pumpkin taste, it's a way to disassociate from the world rather than experience it, which mirrors late capitalism; in this essay I will — rachel syme (@rachsyme) August 15, 2019
Look up a word, learn it forever.
Other forms: theses
A thesis is the most important or foundational idea of an argument. If the thesis of your paper is that chocolate ice cream is better than vanilla, you'll need to back that up with plenty of sundae-based research.
The noun thesis has more than one important sense to it. One definition of thesis is that it is the most important or foundational idea of an argument, presentation, or piece of writing. But it can also mean a large work of art, criticism, or scientific research that represents original research and is generally the final requirement for an academic degree.
- noun an unproved statement put forward as a premise in an argument see more see less type of: assumption , premise , premiss a statement that is assumed to be true and from which a conclusion can be drawn
- noun a treatise advancing a new point of view resulting from research; usually a requirement for an advanced academic degree synonyms: dissertation see more see less type of: tractate , treatise a formal exposition
Vocabulary lists containing thesis
A thorough survey of various textbooks, assignments, content area standards, and examinations yields the following list of words compiled by Jim Burke . You cannot expect to succeed on assignments if you do not understand the directions.
Persuade yourself to study this list of words related to argumentative writing. You'll learn all about making claims, supporting arguments with evidence, and maintaining an objective tone. It's no fallacy that reviewing these words will improve your credibility as a writer.
To improve your fluency in English Language Arts and Reading (ELAR), learn this academic vocabulary list that includes words selected from the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) state standards.
Sign up now (it’s free!)
Whether you’re a teacher or a learner, vocabulary.com can put you or your class on the path to systematic vocabulary improvement..
What Exactly Is A Dissertation (Or Thesis)?
If you’ve landed on this article, chances are you’ve got a dissertation or thesis project coming up (hopefully it’s not due next week!), and you’re now asking yourself the classic question, “what the #%#%^ is a dissertation?”…
In this post, I’ll break down the basics of exactly what a dissertation is, in plain language. No ivory tower academia.
So, let’s get to the pressing question – what is a dissertation?
A dissertation (or thesis) = a research project
Simply put, a dissertation (or thesis – depending on which country you’re studying in) is a research project . In other words, your task is to ask a research question (or set of questions) and then set about finding the answer(s). Simple enough, right?
Well, the catch is that you’ve got to undertake this research project in an academic fashion , and there’s a wealth of academic language that makes it all (look) rather confusing (thanks, academia). However, at its core, a dissertation is about undertaking research (investigating something). This is really important to understand, because the key skill that your university is trying to develop in you (and will be testing you on) is your ability to undertake research in a well-structured structured, critical and academically rigorous way.
This research-centric focus is significantly different from assignments or essays, where the main concern is whether you can understand and apply the prescribed module theory. I’ll explain some other key differences between dissertations or theses and assignments a bit later in this article, but for now, let’s dig a little deeper into what a dissertation is.
A dissertation (or thesis) is a process.
Okay, so now that you understand that a dissertation is a research project (which is testing your ability to undertake quality research), let’s go a little deeper into what that means in practical terms.
The best way to understand a dissertation is to view it as a process – more specifically a research process (it is a research project, after all). This process involves four essential steps, which I’ll discuss below.

Step 1 – You identify a worthy research question
The very first step of the research process is to find a meaningful research question, or a set of questions. In other words, you need to find a suitable topic for investigation. Since a dissertation is all about research, identifying the key question(s) is the critical first step. Here’s an example of a well-defined research question:
“Which factors cultivate or erode customer trust in UK-based life insurance brokers?”
This clearly defined question sets the direction of the research . From the question alone, you can understand exactly what the outcome of the research might look like – i.e. a set of findings about which factors help brokers develop customer trust, and which factors negatively impact trust.
But how on earth do I find a suitable research question, you ask? Don’t worry about this right now – when you’re ready, you can read our article about finding a dissertation topic . However, right now, the important thing to understand is that the first step in the dissertation process is identifying the key research question(s). Without a clear question, you cannot move forward.
Step 2 – You review the existing research
Once the research question is clearly established, the next step is to review the existing research/literature (both academic and professional/industry) to understand what has already been said with regard to the question. In academic speak, this is called a literature review .
This step is critically important as, in all likelihood, someone else has asked a similar question to yours, and therefore you can build on the work of others . Good academic research is not about reinventing the wheel or starting from scratch – it’s about familiarising yourself with the current state of knowledge, and then using that as your basis for further research.
Simply put, the first step to answering your research question is to look at what other researchers have to say about it. Sometimes this will lead you to change your research question or direction slightly (for example, if the existing research already provides a comprehensive answer). Don’t stress – this is completely acceptable and a normal part of the research process.
Step 3 – You carry out your own research
Once you’ve got a decent understanding of the existing state of knowledge, you will carry out your own research by collecting and analysing the relevant data. This could take to form of primary research (collecting your own fresh data), secondary research (synthesising existing data) or both, depending on the nature of your degree, research question(s) and even your university’s specific requirements.
Exactly what data you collect and how you go about analysing it depends largely on the research question(s) you are asking, but very often you will take either a qualitative approach (e.g. interviews or focus groups) or a quantitative approach (e.g. online surveys). In other words, your research approach can be words-based, numbers-based, or both . Don’t let the terminology scare you and don’t worry about these technical details for now – we’ll explain research methodology in later posts .
Step 4 – You develop answers to your research question(s)
Combining your understanding of the existing research (Step 2) with the findings from your own original research (Step 3), you then (attempt to) answer your original research question (s). The process of asking, investigating and then answering has gone full circle.

Of course, your research won’t always provide rock-solid answers to your original questions, and indeed you might find that your findings spur new questions altogether. Don’t worry – this is completely acceptable and is a natural part of the research process.
So, to recap, a dissertation is best understood as a research process, where you are:
- Ask a meaningful research question(s)
- Carry out the research (both existing research and your own)
- Analyse the results to develop an answer to your original research question(s).

Depending on your specific degree and the way your university designs its coursework, you might be asking yourself “but isn’t this just a longer version of a normal assignment?”. Well, it’s quite possible that your previous assignments required a similar research process, but there are some key differences you need to be aware of, which I’ll explain next.
Same same, but different…
While there are, naturally, similarities between dissertations/theses and assignments, its important to understand the differences so that you approach your dissertation with the right mindset and focus your energy on the right things. Here, I’ll discuss four ways in which writing a dissertation differs substantially from assignments and essays, and why this matters.
Difference #1 – You must decide (and live with) the direction.
Unlike assignments or essays, where the general topic is determined for you, for your dissertation, you will (typically) be the one who decides on your research questions and overall direction. This means that you will need to:
- Find a suitable research question (or set of questions)
- Justify why its worth investigating (in the form of a research proposal )
- Find all the relevant existing research and familiarise yourself with the theory
This is very different from assignments, where the theory is given to you on a platter, and the direction is largely pre-defined. Therefore, before you start the dissertation process, you need to understand the basics of academic research, how to find a suitable research topic and how to source the relevant literature.

Difference #2 – It’s a long project, and you’re on your own.
A dissertation is a long journey, at least compared to assignments. Typically, you will spend 3 – 6 months writing around 15,000 – 25,000 words (for Masters-level, much more for PhD) on just one subject. Therefore, successfully completing your dissertation requires a substantial amount of stamina .
To make it even more challenging, your classmates will not be researching the same thing as you are, so you have limited support, other than your supervisor (who may be very busy). This can make it quite a lonely journey . Therefore, you need a lot of self-discipline and self-direction in order to see it through to the end. You should also try to build a support network of people who can help you through the process (perhaps alumni, faculty or a private coach ).
Difference #3 – They’re testing research skills.
We touched on this earlier. Unlike assignments or essays, where the markers are assessing your ability to understand and apply the theories, models and frameworks that they provide you with, your dissertation will be is assessing your ability to undertake high-quality research in an academically rigorous manner.
Of course, your ability to understand the relevant theory (i.e. within your literature review) is still very important, but this is only one piece of the research skills puzzle. You need to demonstrate the full spectrum of research skills.
It’s important to note that your research does not need to be ground-breaking, revolutionary or world-changing – that is not what the markers are assessing. They are assessing whether you can apply well-established research principles and skills to a worthwhile topic of enquiry. Don’t feel like you need to solve the world’s major problems. It’s simply not going to happen (you’re a first-time researcher, after all) – and doesn’t need to happen in order to earn good marks.
Difference #4 – Your focus needs to be narrow and deep.
In your assignments, you were likely encouraged to take a broad, interconnected, high-level view of the theory and connect as many different ideas and concepts as possible. In your dissertation, however, you typically need to narrow your focus and go deep into one particular topic. Think about the research question we looked at earlier:
The focus is intentionally very narrow – specifically the focus is on:
- The UK only – no other countries are being considered.
- Life insurance brokers only – not financial services, not vehicle insurance, not medical insurance, etc.
- Customer trust only – not reputation, not customer loyalty, not employee trust, supplier trust, etc.
By keeping the focus narrow, you enable yourself to deeply probe whichever topic you choose – and this depth is essential for earning good marks. Importantly, ringfencing your focus doesn’t mean ignoring the connections to other topics – you should still acknowledge all the linkages, but don’t get distracted – stay focused on the research question(s).

So, as you can see, a dissertation is more than just an extended assignment or essay. It’s a unique research project that you (and only you) must lead from start to finish. The good news is that, if done right, completing your dissertation will equip you with strong research skills, which you will most certainly use in the future, regardless of whether you follow an academic or professional path.
Wrapping up
Hopefully in this post, I’ve answered your key question, “what is a dissertation?”, at least at a big picture-level. To recap on the key points:
- A dissertation is simply a structured research project .
- It’s useful to view a dissertation as a process involving asking a question, undertaking research and then answering that question.
- First and foremost, your marker(s) will be assessing your research skills , so its essential that you focus on producing a rigorous, academically sound piece of work (as opposed to changing the world or making a scientific breakthrough).
- While there are similarities, a dissertation is different from assignments and essays in multiple ways. It’s important to understand these differences if you want to produce a quality dissertation.
In this post, I’ve gently touched on some of the intricacies of the dissertation, including research questions, data types and research methodologies. Be sure to check out the Grad Coach Blog for more detailed discussion of these areas.
You Might Also Like:

34 Comments
Hello Derek
Yes, I struggle with literature review and am highly frustrated (with myself).
Thank you for the guide that you have sent, especially the apps. I am working through the guide and busy with the implementation of it.
Hope to hear from you again!
Regards Micheal
Great to hear that, Michael. All the best with your research!
Thank you. That was quite something to move forward with. Despite the fact that I was lost. I will now be able to do something with the information given.
That’s great, Pheladi. Good luck!
Thank you so much for your videos and writing research proposal and dissertation. These videos are useful. I was struggling, but now I am starting to write. I hope to watch your more videos to learn more about the dissertation.
Before this post, I didn’t know where to start my research, today I have some light and do certain % of my research. I may need for direction on literature review. Big thanks to you.
Very very good Derek
Thanks immensely Derek
You’re welcome 🙂 Good luck with your dissertation/thesis.
Thank you Derek for widening my scope on research, this can be likened to a blind man whose eyes can now see.
Remain bless sir🙏
You guys are doing really great… I am extremely grateful for your help… Keep going.. Please activate that research help for indian students as well I couldn’t access it being an indian.
Hello Derek,
I got stuck in the concept paper because I changed my topic. Now I don’t know where to pick up the pieces again. How can I focus and stay on track. I am getting scared.
Thank you so much Derek, I am a new comer, learning for the first time how to write a good research. These in information’s to me is a mind opener, I hope to learn more from you in the future, Thanks and God bless.
Thanks Guys this means so much to me
A pretty good and insightful piece for beginners like me. Looking forward to more helpful hints and guide. Thanks to Derek.
This is so helpful…really appreciate your work.
Great to hear that
On cybersecurity Analytics research to banking transactions
This was of great help to me and quite informative .
Thank you so much GradCoach,
This is like a light at the end of the tunnel. You are a lifesaver. Thank you once again.
hello, I’m so grateful for such great information. It appears basic, but it is so relevant in understanding the research process.
Your website is very helpful for writing thesis. A big well done to the team. Do you have a website for paper writing and academic publishing or how to publish my thesis, how to land a fully funded PhD, etc. Just the general upward trajectory in the academia. Thank you
I have learned a lot from the lectures, it was beneficial and helped me a lot in my research journey. Thank you very much
Thank you for your gifts of enlightenment to a person like me who’s always a student. May your ‘well’not dry out.
It’s quite a fun and superb, now I have come to believe that the way one teach can have an impact in understanding and can change one’s assumption and position about a subject or a problem, before I came here and learn I consider research methodology a hard thing because, I wasn’t taught by a mentor like this one. Thanks so much who ever have make this effort to make this something easy and engaging
I can’t imagine that world has achieved major aspects of every field of study
Thank you very much for all the valuable, wonderful and comprehensive amount of information… I highly appreciate your support, 100% I recommend you
This topic is intended for my MPhil. Work (The perception of parents on Technical and Vocational Education, the impact on educational policy). May you consider the suitability of the topic for me and refine if the need be. Thank you,
Hello here…
i have gone through the notes and it is interesting. All i need now is a pdf file that contain a whole dissertation writing inclusive of chapter 1 to 5 on motivation as a topic… thanks
Remarkable!!! You made it sound so simple
I got stuck in my writing because I need to change my topic. I am getting scared as I have a semester left 🙁
Thanks for such an educational opportunity and support
Thanks for your educational opportunity and support
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Thesis: Definition and Examples in Composition
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A thesis ( THEE-ses ) is the main (or controlling) idea of an essay , report , speech , or research paper , sometimes written as a single declarative sentence known as a thesis statement . A thesis may be implied rather than stated directly. Plural: theses . It's also known as a thesis statement, thesis sentence, controlling idea.
In the classical rhetorical exercises known as the progymnasmata , the thesis is an exercise that requires a student to argue a case for one side or the other.
Etymology From the Greek, "to put"
Examples and Observations (Definition #1)
- "My thesis is simple: in the next century mankind must harness the nuclear genie if our energy needs are to be met and our security preserved." (John B. Ritch, "Nuclear Green," Prospect Magazine , March 1999)
- "We watch baseball: it's what we have always imagined life should be like. We play softball. It's sloppy--the way life really is." (from the introduction to Watching Baseball, Playing Softball)
- "Through Mansfield's skillful handling of point of view, characterization, and plot development, Miss Brill comes across as a convincing character who evokes our sympathy." (thesis statement in Miss Brill's Fragile Fantasy )
- "Suppose there were no critics to tell us how to react to a picture, a play, or a new composition of music. Suppose we wandered innocent as the dawn into an art exhibition of unsigned paintings. By what standards, by what values would we decide whether they were good or bad, talented or untalented, success or failures? How can we ever know that what we think is right?" (Marya Mannes, "How Do You Know It's Good?")
- "I think people are disturbed by the discovery that no longer is a small town autonomous--it is a creature of the state and of the Federal Government. We have accepted money for our schools, our libraries, our hospitals, our winter roads. Now we face the inevitable consequence: the benefactor wants to call the turns." (E.B. White, "Letter from the East")
- "It is possible to stop most drug addiction in the United States within a very short time. Simply make all drugs available and sell them at cost." (Gore Vidal, "Drugs")
- The Two Parts of an Effective Thesis "An effective thesis is generally composed of two parts: a topic and the writer's attitude or opinion about or reaction to that topic." (William J. Kelly, Strategy and Structure . Allyn and Bacon, 1996)
- Drafting and Revising a Thesis "It's a good idea to formulate a thesis early in the writing process , perhaps by jotting it on scratch paper, by putting it at the head of a rough outline , or by attempting to write an introductory paragraph that includes the thesis. Your tentative thesis will probably be less graceful than the thesis you include in the final version of your essay. Here, for example, is one student's early effort: Although they both play percussion instruments, drummers and percussionists are very different. The thesis that appeared in the final draft of the student's paper was more polished: Two types of musicians play percussion instruments--drummers and percussionists--and they are as different as Quiet Riot and the New York Philharmonic. Don't worry too soon about the exact wording of your thesis, however, because your main point may change as you refine your ideas." (Diana Hacker, The Bedford Handbook , 6th ed. Bedford/St. Martin's, 2002)
- A Good Thesis - "A good thesis tells the audience exactly what you want them to know, understand, and remember when your speech is done. Write it as a simple, declarative sentence (or two) that restates the speech purpose and states the main points that support the purpose. Although you may formulate a thesis statement early in the speech development process, you may revise and reword it as you research your topic.' (Sherwyn P. Morreale, Brian H. Spitzberg, and J. Kevin Barge, Human Communication: Motivation, Knowledge, and Skills , 2nd ed. Thomson Higher Education, 2007) - "An effective thesis statement singles out some aspect of a subject for attention and clearly defines your approach to it." (David Blakesley and Jeffrey L. Hoogeveen, Writing: A Manual for the Digital Age . Wadsworth, 2011)
Examples and Observations (Definition #2)
" Thesis . This advanced exercise [one of the progymnasmata] asks the student to write an answer to a 'general question' ( quaestio infina )--that is, a question not involving individuals. . . . Quintilian . . . notes that a general question can be made into a persuasive subject if names are added (II.4.25). That is, a Thesis would pose a general question such as 'Should a man marry?' or 'Should one fortify a city?' (A Special Question on the other hand would be 'Should Marcus marry Livia?' or 'Should Athens spend money to build a defensive wall?')" (James J. Murphy, A Short History of Writing Instruction: From Ancient Greece to Modern America , 2nd ed. Lawrence Erlbaum, 2001)
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- What an Essay Is and How to Write One
- Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- Revising a Paper
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- Understanding Organization in Composition and Speech
- What Is a Written Summary?
- An Essay Revision Checklist
- Focusing in Composition
Inside Out 2 and the Deeper Meaning Behind the Pixar Movie, Explained

Your changes have been saved
Email Is sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Quick Links
Bigger emotions in inside out 2, growing up means feeling less joy, capturing the feeling of childhood, anxiety is an overwhelming emotion, inside out 2 teaches audiences to live with their emotions.
- Inside Out 2 is a box office hit, resonating with audiences thanks to its relatable exploration of complex emotions.
- New characters like Anxiety add depth to the film, showcasing the overwhelming nature of growing up and conflicting feelings.
- The movie teaches valuable lessons about living with emotions, finding balance, and embracing the complexities of life.
Inside Out 2 is a box office hit. Not only did it mark the first $100+ opening weekend of the year and helped turn around the doom and gloom of the summer box office, but it has also been a hit with critics and audiences as it has a 91% on Rotten Tomatoes and scored an A CinemaScore. With $155 million, it is the second highest-grossing film for an animated movie, behind only Incredibles 2 , and opening above sequels to juggernaut hits like Frozen 2 , Finding Dory , and Toy Story 4 . With good word of mouth and a light summer in terms of competition, this might be not only one of the biggest films of the season but the whole year, as word of mouth will likely support it.
Like the first film, Inside Out 2 looks at the complex emotions that drive humans and makes it easily accessible to both a young audience encountering these thoughts for the first time and adults who might have lived with this for years but never quite knew how to explain it. The core five emotions of Joy (Amy Poehler), Sadness (Phyllis Smith), Anger (Lewis Black), Fear (Tony Hale), and Disgust (Liza Lapira) from the first film are joined by Envy (Ayo Edebiri), Ennui (Adèle Exarchopoulos), Embarrassment (Paul Walter Hauser), a brief role for Nostalgia (June Squibb), and the main newcomer, Anxiety (Maya Hawke). Inside Out 2 delivers an important message about the complex, conflicting emotions we feel growing up and how our emotions do not define who we are but guide us.

Inside Out 2
Read Our Review
The main plot of Inside Out 2 kicks into gear when Riley's (Kensington Tallman) puberty alarm goes off , much to the shock of the core five emotions. Their new console is extremely sensitive, making every one of Riley's emotions even bigger despite them barely touching the console. Everyone who has been a teenager can relate to this, as the emotions one feels are heightened. Many people encounter new emotions for the first time, and they feel larger, almost world-ending. This is why high school dramas and romances have been popular in film, as they feel so relatable. Everyone at some point remembers when it felt like the world ended for something so minor because the emotions were bigger.

Does Inside Out 2 Have a Post-Credits Scene?
...and what does it all mean for the future of the series?
This also sets the stage for new emotions to take control . In the film, Anxiety tells the core five that Riley's life requires more sophisticated emotions, and in many ways, the new emotions are more complex feelings of four of them. Anxiety herself compares herself to Fear, where Fear keeps her worried about what she can see; Anxiety keeps her concerned about what she can't see and is looking to the future.
She later weaponizes Riley's imagination to create stressful scenarios in her mind, in what she thinks is preparing her but instead is keeping her up at night. Envy is the inverse of Disgust, while embarrassment is another form of Sadness (these two emotions later share a bond). Ennui, or as she describes herself, Boredom, is the opposite of Anger. Where Anger feels emotions very passionately, Ennui is resigned to everything. The only exception is Joy, which ties into one of Inside Out 2 's more devastating sequences .
Joy has been the emotion in control for most of Riley's life . When Inside Out 2 begins, she has learned her lesson from the first film and sees the value in all of Riley's emotions, even Sadness. So when Anxiety and new emotions arrive , Joy welcomes them but also wants to maintain a sense of control. She is used to calling the shots until Anxiety takes over, where she and the other five get repressed. Joy tries her best to keep everything together, staying positive and thinking to herself. All she needs to do is find Riley's sense of self, which will make everything better.
Yet when the tube to headquarters is shut down, and it seems like Joy can't help Riley, she has a moment to think. She looks down on all the negative emotions and memories she has repressed for Riley and is shocked at just how many there are. Defeated, she says, "I can't stop Anxiety. Maybe this is what happens when you grow up. You feel less joy.”
This line obviously will hit a lot of people very hard, particularly older audiences. It is hard to argue that when you grow up, sometimes the weight of various problems in life can become overwhelming. It feels harder to be happy, and people tend to look back on how joyful they were in their youth with less care in the world.
Sometimes, the things that make us happy no longer do; they are just part of growing up and dealing with more complex emotions. It is hard to return to that joy of childlike wonder. One could even say much of the negative criticism from certain fans of properties like Star Wars and even Pixar is from audiences who have grown up and are upset less with the individual projects but that they don't make them feel the joy they did as a kid.
Inside Out 2 , like the Toy Story sequels and Monsters University , might be an animated movie aimed at families. Still, it also acknowledges the passage of time and realizes the kids who saw the original film are older. This is likely an emotion they have been feeling, and in 2024, it feels like it is a sentiment everyone shares. Between inflation, rising global conflicts, and various other issues going on in the world, it feels like finding joy in anything is becoming harder. Luckily, Inside Out 2 shows that even though Joy never goes away .
One of Inside Out 2 's most clever bits of writing is the characterization of Anxiety. She is the antagonist of the movie, but she is not an evil villain like The Prospector from Toy Story 2 or Syndrome in The Incredibles . Anxiety is doing what she thinks is best for Riley to help protect her. Every action she does is not out of her own selfish interest but in service of helping Riley as she sees fit. As is the case with anyone who has anxiety, it can be a very powerful emotion. In the film, Anxiety quickly takes control of Riley's mind, suppressing the main five emotions and making big changes, creating a new sense of self while tossing the old one away.
In the film's climax, Anxiety's efforts to give Riley a new sense of self backfires , with Riley believing she isn't good enough. Anxiety tries everything to fix it but begins to overwhelm Riley's systems, giving her an anxiety attack. Anxiety begins to move in a whirlwind around Riley's console, where not even the other emotions can stop her. Envy even tells her, "You are putting too much pressure on her." When the main five emotions get back to headquarters, they, along with Ennui, Embarrassment, and Envy, try pulling the new sense of self out of Riley and replacing it with the old one, but it doesn't work.

Pixar: How the Animation Studio Has Changed Over Time
How the shape of Pixar's groundbreaking footprint on the animation industry has evolved over the years.
Joy enters Anxiety's storm, and while she initially tries to yell at Anxiety to stop, Joy notices something. Despite Anxiety moving around the console, she is also frozen, stuck in place, and overwhelmed, much like somebody having a panic attack . Joy tells her it is okay to let go, and she understands she is doing what is best for Riley. Joy also realizes she is making a similar mistake to Anxiety. Earlier in the film, Joy had been shoving the awful thoughts that would weigh on Riley to the back of her mind. Both Joy and Anxiety tried to control Riley instead of letting her be who she was. Anxiety lets go, and Joy's actions earlier in the movie of riding the negative thoughts back to headquarters begin to take form in Riley's sense of self.
This new sense of self is a complex web of conflicting thoughts . Joy and positive emotions mixed with Anxiety, as well as a whole host of others. Riley is growing up, which means her worldview and her own identity is not so simple. She can have conflicting ideas about herself because that is what growing up is like. Riley can be both a good person and sometimes a bad friend, and it is important to recognize those contradicting notions.
This settles Riley down, and she apologizes to her friends as she had been ignoring them for most of the movie due to Anxiety and wanting to prioritize future friends in high school so Riley wouldn't be alone. Like the first film's climax, Riley has a heart-to-heart with the people she loves. Yet in the inverse of the first film, where Joy needs to let Sadness take control, saying, "Riley needs you," Sadness gets to tell Joy that Riley needs her. It is a reminder that Joy always has a way of coming back if we just let it into our lives.
By the film's conclusion, all nine main emotions have found a balance in Riley's head . Even Anxiety has a place there. There are healthy and unhealthy anxieties, just like with all emotions. Joy is a valuable tool, but it can also create toxic positivity. As with all the emotions, she deserves a necessary function; it is all just in degrees. It is also worth noting that emotions do not make Riley who she is. They can guide her, but in the end, Riley is the culmination of her life choices, of which emotions are part. All of these aspects of Riley are an important part of growing up.
Inside Out 2 will hopefully be a helpful tool for young kids encountering these emotions for the first time. It will help them explain these difficult concepts while also acknowledging the good and bad parts of all their conflicting emotions. As for older audiences, they will likely relate deeply to the film's concepts and wish they had it when they were younger, but they can be grateful that future generations will have it to look to when they need help understanding their feelings. Inside Out 2 is playing in theaters now.
Volatility Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It
Your writing, at its best
Compose bold, clear, mistake-free, writing with Grammarly's AI-powered writing assistant
Volatility is a critical concept to understand in the stock market. Volatility refers to how much the price of a security varies over time. It is one of the primary factors that can influence your investment strategy. Understanding this concept will help you make better trading decisions, whether you’re buying or selling stock — or even just thinking about whether to buy or sell at all.
This is everything you need to know about what volatility is, how it works in the modern world, and why it is essential to understand!
What Is Volatility?
Volatility is a measure of the amount of uncertainty in the stock market. Market volatility can be evaluated through standard deviation, which measures the variation in a data set from its average value over a period of time. The higher the standard deviation or volatility, the greater the chance that prices will fall or rise sharply compared to previous price changes.
The word volatility is derived from the Latin word volatilis , which means “that can fly.” The present meaning of volatility as a measure of price variation is a relatively new development in its history.
Standard deviation is essential to understand when analyzing stocks or other investments because it helps you determine how risky investment might be based on historical price changes and identifies periods where stocks may have been overvalued or undervalued.
Historically there has been no direct correlation between high volatility and poor performance over a long period (e.g., five years or more). Still, low historical volatility does not guarantee future returns either — it indicates only that returns and losses are likely less extreme than they were during periods with higher historical volatility levels.
Price volatility can be measured using different ranges or bins — tools used to identify and quantify price movements in an organized way. A bin is basically a range of prices that share similar characteristics (for example, they could be all within $10). The higher the number of bins on the x-axis (or horizontal axis), the more detailed your analysis will be.
Synonyms
Some popular synonyms for the word volatility include:
- Fluctuations
- Unpredictability
Can Volatility Be Measured?
The definition of volatility is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security or market index. In other words, it measures how much prices can change over time.
Stock market volatility can be measured in many ways. The most common measure is the standard deviation which measures the dispersion of a set of data from its mean. In other words, it measures how spread the data points are around their average value. This can be calculated for any given number (e.g., stock prices over three months).
Because of this, measures of volatility can be used in some trading strategies. It’s a measure of how much the price of an asset fluctuates over time. It’s usually expressed either as a percentage or an implied probability.
The primary value of vo l atility is when trading can help predict future market movements. For example, suppose you see that the price of an asset tends to rise or fall wildly from one day to the next.
In that case, there’s probably going to be another significant change in its value soon — and you might want to invest based on what seems like impending volatility (or sell off your current holdings).
What Is the Volatility Index?
The Cboe Volatility Index or VIX is a measure of the implied volatility of the stock market. A low VIX means that investors are feeling calm right now, but a high VIX can indicate fear in the market. The current value of the VIX depends on two things: how much time has passed since its last update and how volatile stocks have been lately.
The VIX considers data from all stocks in the S&P 500 index and provides a way to quantify investor sentiment at any given time. It’s calculated using options contracts on those companies’ stocks and their implied volatility — or how volatile those options are thought to be over time.
Using the volatility index can help you make accurate estimations about the future volatility of a stock option in a volatile market, whether in the long or short term. The market price of stocks can occasionally be riskier than others, so ensure you’re well educated and don’t lose money to dramatic decreases in value. This can significantly help with asset allocation when the stock market is reaching a boiling point.
Why Does Volatility Matter?
Volatility is a measure of risk. The more volatile something is, the greater its risk. Volatility can be used to determine future prices and also predicts future price movements. High volatility is generally considered bad for investment, while low volatility is considered to be prime investing time.
Because of this, knowing how to use volatility in your investing strategy can give you an edge in protecting your portfolio during times of market turmoil or making sure it grows as fast as possible during more stable periods.
Our blog here at The Word Counter aims to provide people with practical tips and tools for expanding their communication skills. Think of our articles as an extension of the service we provide through our website — an opportunity for deeper exploration into improving your language skills!
We hope that our blog can help you in your journey of increasing your communication capabilities. And don’t forget: we’re always glad to help personally if you need some aid along the way! Check out our latest articles , and see where that knowledge can take you in your life!
Sources:
Volatile Definition & Meaning | Dictionary.com
VOLATILITY | Cambridge English Dictionary
Volatility From the Investor’s Point of View | Investopedia
Kevin Miller is a growth marketer with an extensive background in Search Engine Optimization, paid acquisition and email marketing. He is also an online editor and writer based out of Los Angeles, CA. He studied at Georgetown University, worked at Google and became infatuated with English Grammar and for years has been diving into the language, demystifying the do's and don'ts for all who share the same passion! He can be found online here.
Recent Posts

Marxist Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Ideal Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It

Thesis Meaning: Here’s What It Means and How To Use It
Exxon Mobil: The Permian Printing Press
- Exxon Mobil Corporation completes largest shale patch merger with Pioneer Natural Resources.
- Analysts have mixed opinions on Exxon's future performance post-merger.
- Exxon's relentless commitment to cost control and potential for long-term growth make it a solid investment opportunity.
- We rate Exxon as a strong buy at current levels.
- Looking for more investing ideas like this one? Get them exclusively at The Daily Drilling Report. Learn More »

Introduction
The ink is now drying on the biggest shale patch merger of all time. In case memory escapes you, I am referring to Exxon Mobil Corporation's ( NYSE: XOM ) purchase of Pioneer Natural Resources- formerly PXD . As of May 3rd, 2024, the two oil giants are now one shale colossus. We were supportive of the merger in the context of what we see developing in shale's future, and discussed why in a public article last fall. Our updated shale thesis was in another public article if you would like more depth on this topic.
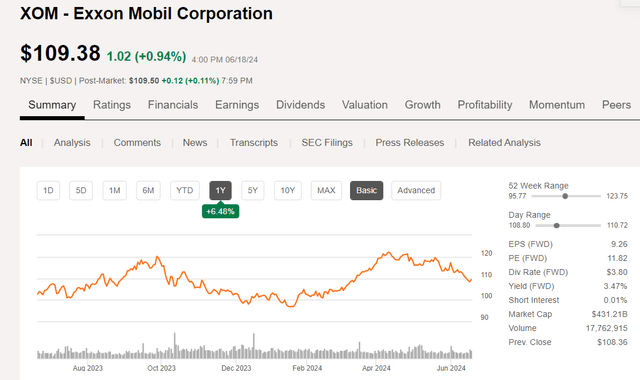
XOM price chart (Seeking Alpha)
We remain bullish on XOM, and think that the value obtained in the merger is not yet reflected in the stock, making the current level a solid entry point or basis for adding.
The analyst community is a little tepid at current levels, ranking XOM as an Overweight . Price targets range from $114-$152, with a median of $131.50. Even if that median figure is correct over the short haul, it represents a decent gain from one of the largest industrial corporations on Earth. And, when packaged with the capital returns that are in the pipeline in the coming decades, investors should carefully consider if XOM meets their investment profile.
XOM has recently gotten a downgrade from Truist's Neal Dingman . Citing concerns about cash flow yield below peers-(XOM has peers?!?!?), driven by capex allocation to lower performing sustainable businesses, he's reduced his target from $146 to $124.00. Tipranks has him at 144 out of over 8000 ranked analysts with a success rating of 68%. I think he's stretched out a bit over his skis on this one, as energy companies are dialing back on some of this "sustainable" stuff. We shall see.
On a technical basis, the stock is still above long-term support at $102, and right on its 200-day SMA. With the turn, we have seen in crude oil prompted by a bullish call by Standard Chartered and the market figuring out what OPEC+ really meant by scaling up production, any thought of XOM hitting the long-term support line in the near term is starting to look pretty iffy. People who want in should probably take the jump, at least with a little bite.
The thesis for XOM now that they have eaten PXD
In this article, we are going to assume you know about Guyana and not discuss it much except to say that it hasn't peaked yet. It also has breakeven costs in the mid-upper $20's and can expect Brent pricing. Guyana is a cash flow monster. Ok, that out of the way, let's review why everybody and their Uncle Eddie is soaking up all the Permian acreage that they can.
The company also participates in other business, refining, chemicals, and dabbles in various sustainable and carbon sequestration businesses. None of those have the impact that upstream E&P operations do, hence the focus of this article.
The shale shell game
Once I completely got my arms around shale, maybe eight years ago, I formulated a set of attributes that would describe the ultimate winners in the shale shell game. Here they are again.
Rock quality- Tier I acreage in the key Wolfcamp A, Bone Spring, Spraberry and Avalon plays. This also drives the top-tier drilling locations the company brags about.
Scale -typified by vast swathes of acreage and lowers unit costs. In the end, low cost of supply trumps everything else as fields mature.
Connectedness -enabling longer lateral sections
Logistics -resources in basin, primarily sand and water
Technology -I initially underestimated the role this would play in leveraging higher and higher well recoveries. Tech-AI led improvements in reservoir description, well designs, and completion intensity, have helped to flatten the trajectory longer than I thought would be the case. Showing that even grizzled, old Fluidsdoc can be surprised occasionally.
Export to marketing hubs - if you can't move toward refining and processing, there is no value added.
What do I mean by "Shell Game?" By virtual of its high natural declines 30% annually in good rock-Tier I, over 50% in less good rock-Tiers II, III, IV, production is a roller coaster. To maintain output levels, you must constantly drill to replace legacy declines. Some of this effect has been masked recently by the incredible technological and efficiency gains the industry has pulled off combined with DUC withdrawal. But as I have noted, the buffer created by tech and DUCs has about run its course, and the pace of drilling presently will soon result in a bending of the production curve.
The industry knows this and has been on a frantic drive to mop up and aggregate Tier I drilling locations through the M&A frenzy of the last couple of years. One by one, the mighty have devoured tasty, smaller morsels in the hope of being one of the shale winners. M&A will grind out cost for the survivors. We're seeing it already in the reduced rig count , down nearly 200 rigs since late 2022. I don't want to get too Lord'sy of the Ring'sy here, but eventually, there will be one Permian shale driller to rule them all, and it will be ExxonMobil.
What does the PXD deal mean for XOM?
It shouldn't take much further description to understand the Industrial Logic behind the merger. Without PXD's footprint, XOM was missing on four out of six of my shale survivor bullet points. The Midland also brings a higher "oil-cut" than the Delaware typically, and XOM's acreage there is not as good as some we have reviewed. The PXD footprint in the Midland-almost a million acres connects prior XOM acreage making it far more useful, ticking 6 out of 6 boxes on the Fluidsdoc list of attributes.
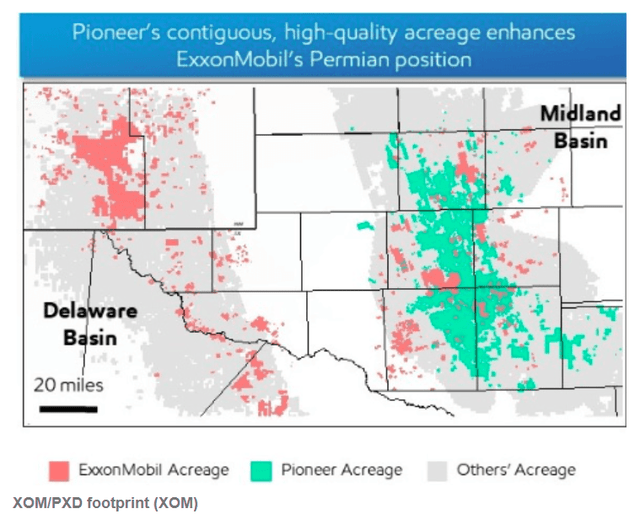
XOM/PXD merger logic (XOM)
Here's a quote that gives us an unusually good look into what management's plan is-
The transaction is a unique opportunity to deliver leading capital efficiency and cost performance as well as increase production by combining Pioneer’s large-scale, contiguous, high-quality undeveloped Midland acreage with ExxonMobil’s demonstrated industry-leading Permian resource development approach. The unique, complementary fit of Pioneer’s contiguous acreage will allow ExxonMobil to drill long, best-in-class laterals -- up to four miles -- which will result in fewer wells and a smaller surface footprint. The company also expects to enhance field digitalization and automation that will optimize production throughput and cost.
PXD's acreage takes a disconnected position with some good chunks that are widely dispersed, and transforms it into a massive block where if the company wanted to...they could drill 5-6 mile laterals. I can almost see your jaws dropping. 5–6 miles, you say!!!! That's unheard of.
No, it's not. Not for XOM. On Sakhalin island, before they pulled out of Russia, XOM was routinely drilling 5–6 miles and sometimes as much as 9-miles. Now, let's understand the Sakhalin wel ls bear little relationship to Permian wells. We are talking standalone screen completions in a sandstone reservoir vs. frac-packs in a shale reservoir. Sandstone reservoirs and shale reservoirs are two entirely different "breeds of cat." That said, there is nothing about shale-fracking that would preclude a nine-mile completion, except perhaps diminishing returns from the toe section of the well. If you have the dirt, the pumps, the water and the sand, it can be done. Resulting, as they note, in fewer wells. Whether it makes sense is another story.
The Permian Play is middle-aged, but XOM drank from the Fountain of Youth
Nothing lasts forever, right? The Permian has been roaring for the last decade. Ten years ago, it was producing 1.4 mm BOPD and 5-BCF/D of gas. Today it's grinding out 6.1 mm BOPD and 25 BCF/D of gas. The air is coming out of the balloon. There's a lot left, but it's price-dependent and in a decade or so, production will fall. Precipitously. It may be entering a shallow decline already, as we have noted. These are the salad days for the Permian, but at the current extraction rate of 2.2 bn BPY there is an end point hanging out there. Probably in the mid-2030's for most operators.
Exxon Mobil with Pioneer now has 12,000 Tier I and II drilling locations . If they POP 500 per year, they stay busy grinding out a couple of million barrels a day for the next 22 years. Way longer than anyone else in this space.
The XOM that I know
I have worked with XOM on a number of projects over my time in the oilfield. From California in the '80s on Platform's Hondo and Habitat, to Wildcat's in Brazil, to the Jansz-lo field in Australia in 2014... I could go on... wait, I almost forgot my GoM field work with XOM in the Grand Isle area. Ok, I'll stop. Wait...there's Beryl Alpha in the North Sea on the Mobil side in the '90s. Now I'll really stop.
One thing that stands out pretty clearly in all of those experiences, is their relentless commitment to cost control. If you did something for X on one well, the XOM supervisors would insist you do for X-10% on the next well. I am not talking necessarily about unit costs, although that was certainly a component. What I mean is figuring out ways to minimize your time on critical path, reduce waste, and enhance safe operations. Safety pays! And, that mindset is made to order for fields in which you will be drilling hundreds of wells per year. It's a repetitive task, why redesign every one? There isn't a reason.
Figuratively speaking, if company X is Simul-fracking-frac 3, and wirelining 3, XOM will Quadro-frac-frac 4 wireline 4. If company Y is drilling 15,000' laterals, XOM will drill 30,000' laterals. This will drive hundreds of thousands in cost per, well, out of the total cost. I am not necessarily saying these exact numbers will play out, but XOM will do whatever it takes to be the low-cost producer. The best breakevens I've seen for the Permian are in the low $30's. XOM has forecast costs of $35 per barrel in the announcement. There is no reason, with the scale with which XOM will be operating, this doesn't get into the $20's. Maybe the low $20's.
Key parts of the deal
XOM shelled out $59 bn for PXD. For that, they got P-2 reserves of 2.2 bn BOIP, and production that more than doubled their standalone output, and brought their daily output to 1.3 mm BOEPD. PXD was running EBITDA between $10-12 bn a year, so with that revenue consolidated to the balance sheet, and at $75-80 WTI, for Q-2, 2024, XOM should add another $2.5-3.0 bn per quarter, depending on oil prices.
The merger was a stock swap which created no new debt, and in the grand scheme of things only minor dilution to existing shareholders. Essentially, 233 mm shares added to their existing float of 3.99 bn common shares outstanding. Meh.
Risks to the thesis
Admittedly, as strong as XOM is, they are not OPEC+, pumping ~38 mm BOPD, and eager to reclaim some lost market share in 2025. I think they will be cautious about, as Brent is right where they want it. But you never know with those fun-loving sheikhs. They have flooded the market before, and if 4-5 mm BOPD came on the market in a short period of time, XOM shares would suffer. That's a risk that's difficult to quantify, though, so you should just be aware of it.
If WTI sags back into the $70's, for any extended period of time due to inventories rising, shares of XOM could stagnate or decline. I don't see them going much below the 200-day SMA, but you know the oil market....
They could screw it up. Despite the generally high opinion I hold of XOM and its operations skills, there is always the possibility they miss the target in the Permian, or extraneous factors come into play to derail their anticipated success. Murphy is alive and well. Stuff happens.
Your takeaway
Not every big deal works out. Some just take time. XOM was pilloried in the market, and perhaps rightly so, for the XTO deal in late 2009. Who knew then, that in 2010 gas would drop from $8.00 MCF to $2.00 MCF, and sometime sub-zero at WAHA occasionally? In the fullness of time, XTO may still shine as LNG and AI sop up more and more gas.
I think the PXD deal was and is a winner for XOM, and its shares do not reflect the full value of the transaction. In an $80 WTI environment at worst case, XOM has a field margin of $45 per BOE. That's $21 bn per year at current rates, and potentially higher if production rises toward 2.0 mm BOE per day. Higher oil prices? Perhaps or perhaps not, as we've noted that's somewhat out of their control.
But, we don't need higher prices for XOM to absolutely rain cash in the coming decades. Over the last year, where oil prices fluctuated between the upper $60's and $90, that XOM covered capex, debt, the dividend, and share buybacks. That's a business on a solid footing in any category. We expect more of the same in 2024.
I think XOM is a buy at current levels and if WTI remains above $80, shares should certainly rally from current levels toward the mid-range of analyst estimates. I think the company is a strong buy for investors looking for long-term growth and rising income for as far as the eye can see.

The Daily Drilling Report
This article was written by
Fluidsdoc is an international oil industry veteran with 40 years of experience having worked on six continents and in over twenty countries around the world. He is an expert in the upstream oilpatch and an energy sector specialist.
He is the leader of the investing group The Daily Drilling Report where he provides investment analysis for the oil and gas industry. Features of the group include: a model portfolio that covers all segments of upstream oilfield activity with weekly updates, ideas for both U.S and international energy companies, coverage from shale to deepwater drillers, technical analysis to identify catalysts, and more. Learn More .
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, but may initiate a beneficial Long position through a purchase of the stock, or the purchase of call options or similar derivatives in XOM over the next 72 hours. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article. This is not advice to buy or sell this stock or ETF in spite of the particular rating I am required to select in the SA template. I am not an accountant or CPA or CFA. This article is intended to provide information to interested parties and is in no way a recommendation to buy or sell the securities mentioned. As I have no knowledge of individual investor circumstances, goals, and/or portfolio concentration or diversification, readers are expected to do their own due diligence before investing their hard-earned cash.
Seeking Alpha's Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
Recommended For You
About xom stock.
| Symbol | Last Price | % Chg |
|---|
More on XOM
Related stocks.
| Symbol | Last Price | % Chg |
|---|---|---|
| XOM | - | - |
| XOM:CA | - | - |
Trending Analysis
Trending news.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn the meaning of thesis as a dissertation, a proposition, or a part of a foot or a measure. See synonyms, examples, word history, and related entries of thesis.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. Learn how to structure, write, and defend your thesis with this comprehensive guide and examples.
A thesis is a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially for a college or university degree, or the main idea, opinion, or theory of a person, group, or speech. Learn more about the meaning, usage, and examples of thesis from Cambridge Dictionary.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay. Learn how to write a clear, concise, and contentious thesis statement by following four simple steps and see examples for different types of essays.
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. Learn how to write a thesis statement, different types of thesis statements, and the structure of a thesis document.
A thesis is a long piece of writing on a particular subject, especially for a college or university degree, or the main idea, opinion, or theory of a person, group, or speech. Learn more about the meaning, usage, and examples of thesis from Cambridge Dictionary.
Thesis definition: a proposition stated or put forward for consideration, especially one to be discussed and proved or to be maintained against objections. See examples of THESIS used in a sentence.
A thesis statement is a sentence that summarizes the argument of an essay and answers the question asked by the assignment. Learn how to create, evaluate, and revise a thesis statement with examples and tips.
Learn how to write a strong thesis for an academic essay, based on analysis of evidence and argument. Find out the difference between descriptive, analytical, and normative claims, and how to frame a question or problem for your readers.
A thesis is the main claim that the author makes about a topic and summarizes the essay's argument. Learn how to write a thesis, see examples from literature and pop culture, and understand the difference between a thesis and a hypothesis.
A thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student's original research and findings on a particular topic or question. Learn about the history, structure, and writing process of a thesis, with an example template and tips.
Etymology. The term thesis comes from the Greek word θέσις, meaning "something put forth", and refers to an intellectual proposition. Dissertation comes from the Latin dissertātiō, meaning "discussion". Aristotle was the first philosopher to define the term thesis.. A 'thesis' is a supposition of some eminent philosopher that conflicts with the general opinion...for to take notice when ...
A good thesis statement needs to do the following: Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences. Answer your project's main research question. Clearly state your position in relation to the topic. Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
Thesis statement. A thesis statement is a statement of one's core argument, the main idea (s), and/or a concise summary of an essay, research paper, etc. [1] It is usually expressed in one or two sentences near the beginning of a paper, and may be reiterated elsewhere, such as in the conclusion. In some contexts, such as in the British ...
A thesis is a statement that conveys the writer's position or the purpose of a piece of writing. Learn how to write a thesis statement for an essay or a narrative, and see examples from literature and famous works.
A thesis statement is a concise description of the goal of your work. This element is one of the most essential components of academic writing, as it tells your readers what they can expect in your paper. Definition. A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis. If you find yourself in the process of writing a a paper, but ...
Thesis statement definition: a short statement, usually one sentence, that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, etc., and is developed, supported, and explained in the text by means of examples and evidence.. See examples of THESIS STATEMENT used in a sentence.
thesis: 1 n an unproved statement put forward as a premise in an argument Type of: assumption , premise , premiss a statement that is assumed to be true and from which a conclusion can be drawn n a treatise advancing a new point of view resulting from research; usually a requirement for an advanced academic degree Synonyms: dissertation Type ...
A dissertation (or thesis) is a process. Okay, so now that you understand that a dissertation is a research project (which is testing your ability to undertake quality research), let's go a little deeper into what that means in practical terms. The best way to understand a dissertation is to view it as a process - more specifically a ...
A thesis ( THEE-ses ) is the main (or controlling) idea of an essay, report, speech, or research paper, sometimes written as a single declarative sentence known as a thesis statement. A thesis may be implied rather than stated directly. Plural: theses. It's also known as a thesis statement, thesis sentence, controlling idea.
Inside Out 2 is a box office hit, resonating with audiences thanks to its relatable exploration of complex emotions.; New characters like Anxiety add depth to the film, showcasing the overwhelming ...
The definition of volatility is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security or market index. In other words, it measures how much prices can change over time. Stock market volatility can be measured in many ways. The most common measure is the standard deviation which measures the dispersion of a set of data from its ...
Exxon Mobil Corporation's merger with Pioneer Natural Resources sparks analyst debate on future performance. Read more on XOM update and a look at the oil markets.