
200+ Research Title Ideas To Explore In 2024

Choosing a compelling research title is a critical step in the research process, as it serves as the gateway to capturing the attention of readers and potential collaborators. A well-crafted research title not only encapsulates the essence of your study but also entices readers to delve deeper into your work.
In this blog post, we will explore the significance of research title ideas, the characteristics of an effective title, strategies for generating compelling titles, examples of successful titles, common pitfalls to avoid, the importance of iterative refinement, and ethical considerations in title creation.
Characteristics of a Good Research Title
Table of Contents
Clarity and Precision
A good research title should communicate the core idea of your study clearly and precisely. Avoid vague or overly complex language that might confuse readers.
Relevance to the Research Topic
Ensure that your title accurately reflects the content and focus of your research. It should provide a clear indication of what readers can expect from your study.
Conciseness and Avoidance of Ambiguity
Keep your title concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary words or phrases that may add ambiguity. Aim for clarity and directness to make your title more impactful.
Use of Keywords
Incorporating relevant keywords in your title can enhance its visibility and accessibility. Consider the terms that researchers in your field are likely to search for and integrate them into your title.
Reflecting the Research Methodology or Approach
If your research employs a specific methodology or approach, consider incorporating that information into your title. This helps set expectations for readers and indicates the uniqueness of your study.
What are the Strategies for Generating Research Title Ideas?
- Brainstorming
- Individual Brainstorming: Set aside time to generate title ideas on your own. Consider different angles, perspectives, and aspects of your research.
- Group Brainstorming: Collaborate with peers or mentors to gather diverse perspectives and insights. Group brainstorming can lead to innovative and multidimensional title ideas.
- Keyword Analysis
- Identifying Key Terms and Concepts: Break down your research into key terms and concepts. These will form the foundation of your title.
- Exploring Synonyms and Related Terms: Expand your search by exploring synonyms and related terms. This can help you discover alternative ways to express your research focus.
- Literature Review
- Examining Existing Titles in the Field: Review titles of relevant studies in your field to identify common patterns and effective strategies.
- Analyzing Successful Titles for Inspiration: Analyze successful research titles to understand what makes them stand out. Look for elements that resonate with your own research.
- Consultation with Peers and Mentors
- Seek feedback from peers and mentors during the title creation process. External perspectives can offer valuable insights and help refine your ideas.
- Use of Online Tools and Title Generators
- Explore online tools and title generators designed to aid in the generation of creative and relevant research titles. While these tools can be helpful, exercise discretion and ensure the generated titles align with the essence of your research.
200+ Research Title Ideas: Category-Wise
Technology and computer science.
- “Cybersecurity Measures in the Age of Quantum Computing”
- “Machine Learning Applications for Predictive Maintenance”
- “The Impact of Augmented Reality on Learning Outcomes”
- “Blockchain Technology: Enhancing Supply Chain Transparency”
- “Human-Computer Interaction in Virtual Reality Environments”
Environmental Science and Sustainability
- “Evaluating the Efficacy of Green Infrastructure in Urban Areas”
- “Climate Change Resilience Strategies for Coastal Communities”
- “Biodiversity Conservation in Tropical Rainforests”
- “Renewable Energy Adoption in Developing Economies”
- “Assessing the Environmental Impact of Plastic Alternatives”
Health and Medicine
- “Precision Medicine Approaches in Cancer Treatment”
- “Mental Health Interventions for Youth in Urban Settings”
- “Telemedicine: Bridging Gaps in Rural Healthcare Access”
- “The Role of Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Disorders”
- “Ethical Considerations in Genetic Editing Technologies”
Social Sciences and Psychology
- “Social Media Influence on Body Image Perception”
- “Impact of Cultural Diversity on Team Performance”
- “Psychological Resilience in the Face of Global Crises”
- “Parental Involvement and Academic Achievement in Adolescents”
- “Exploring the Dynamics of Online Communities and Identity”
Business and Economics
- “Sustainable Business Practices and Consumer Behavior”
- “The Role of Big Data in Financial Decision-Making”
- “Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Emerging Markets”
- “Corporate Social Responsibility and Brand Loyalty”
- “Economic Implications of Remote Work Adoption”
Education and Pedagogy
- “Inclusive Education Models for Diverse Learning Needs”
- “Gamification in STEM Education: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Online Learning Effectiveness in Higher Education”
- “Teacher Training for Integrating Technology in Classrooms”
- “Assessment Strategies for Measuring Critical Thinking Skills”
Psychology and Behavior
- “The Influence of Social Media on Adolescent Well-being”
- “Cognitive Biases in Decision-Making: A Cross-Cultural Study”
- “The Role of Empathy in Conflict Resolution”
- “Positive Psychology Interventions for Workplace Satisfaction”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Sleep Patterns and Mental Health”
Biology and Genetics
- “Genetic Markers for Predisposition to Neurodegenerative Diseases”
- “CRISPR-Cas9 Technology: Ethical Implications and Future Prospects”
- “Evolutionary Adaptations in Response to Environmental Changes”
- “Understanding the Microbiome’s Impact on Immune System Function”
- “Epigenetic Modifications and Their Role in Disease Development”
Urban Planning and Architecture
- “Smart Cities: Balancing Technological Innovation and Privacy”
- “Revitalizing Urban Spaces: Community Engagement in Design”
- “Sustainable Architecture: Integrating Nature into Urban Designs”
- “Transit-Oriented Development and Its Impact on City Dynamics”
- “Assessing the Cultural Significance of Urban Landscapes”
Linguistics and Communication
- “The Influence of Language on Cross-Cultural Communication”
- “Language Development in Multilingual Environments”
- “The Impact of Nonverbal Communication on Interpersonal Relationships”
- “Digital Communication and the Evolution of Language”
- “Language Processing in Bilingual Individuals: A Neuroscientific Approach”
Political Science and International Relations
- “The Role of Social Media in Political Mobilization”
- “Global Governance in the Era of Transnational Challenges”
- “Human Rights and the Ethics of Intervention in International Affairs”
- “Political Polarization: Causes and Consequences”
- “Climate Change Diplomacy: Assessing International Agreements”
Physics and Astronomy
- “Dark Matter: Unraveling the Mysteries of the Universe”
- “Quantum Entanglement and Its Potential Applications”
- “The Search for Exoplanets in Habitable Zones”
- “Astrophysical Phenomena: Exploring Black Holes and Neutron Stars”
- “Advancements in Quantum Computing Algorithms”
Education Technology (EdTech)
- “Adaptive Learning Platforms: Personalizing Education for Every Student”
- “The Impact of Virtual Reality Simulations on STEM Education”
- “E-Learning Accessibility for Students with Disabilities”
- “Gamified Learning: Enhancing Student Engagement and Retention”
- “Digital Literacy Education: Navigating the Information Age”
Sociology and Anthropology
- “Cultural Shifts in Modern Society: An Anthropological Exploration”
- “Social Movements in the Digital Age: Activism and Connectivity”
- “Gender Roles and Equality: A Cross-Cultural Perspective”
- “Urbanization and Its Effects on Traditional Societal Structures”
- “Cultural Appropriation: Understanding Boundaries and Respect”
Materials Science and Engineering
- “Nanostructured Materials: Innovations in Manufacturing and Applications”
- “Biodegradable Polymers: Towards Sustainable Packaging Solutions”
- “Materials for Energy Storage: Advancements and Challenges”
- “Smart Materials in Healthcare: From Diagnosis to Treatment”
- “Robust Coatings for Extreme Environments: Applications in Aerospace”
History and Archaeology
- “Digital Reconstruction of Historical Sites: Preserving the Past”
- “Trade Routes in Ancient Civilizations: A Comparative Study”
- “Archaeogenetics: Unraveling Human Migrations Through DNA Analysis”
- “Historical Linguistics: Tracing Language Evolution Over Millennia”
- “The Archaeology of Conflict: Studying War through Artifacts”
Marketing and Consumer Behavior
- “Influencer Marketing: Impact on Consumer Trust and Purchasing Decisions”
- “The Role of Brand Storytelling in Consumer Engagement”
- “E-commerce Personalization Strategies: Balancing Customization and Privacy”
- “Cross-Cultural Marketing: Adapting Campaigns for Global Audiences”
- “Consumer Perceptions of Sustainable Products: A Market Analysis”
Neuroscience and Cognitive Science
- “Neuroplasticity and Cognitive Rehabilitation: Implications for Therapy”
- “The Neuroscience of Decision-Making: Insights from Brain Imaging”
- “Cognitive Aging: Understanding Memory Decline and Cognitive Resilience”
- “The Role of Neurotransmitters in Emotional Regulation”
- “Neuroethical Considerations in Brain-Computer Interface Technologies”
Public Health and Epidemiology
- “Epidemiological Trends in Infectious Diseases: Lessons from Global Outbreaks”
- “Public Health Interventions for Reducing Non-Communicable Diseases”
- “Health Disparities Among Marginalized Communities: Addressing the Gaps”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Vector-Borne Diseases”
- “Community-Based Approaches to Promoting Health Equity”
Robotics and Automation
- “Human-Robot Collaboration in Manufacturing: Enhancing Productivity and Safety”
- “Autonomous Vehicles: Navigating the Path to Mainstream Adoption”
- “Soft Robotics: Engineering Flexibility for Real-World Applications”
- “Ethical Considerations in the Development of AI-powered Robotics”
- “Bio-Inspired Robotics: Learning from Nature to Enhance Machine Intelligence”
Literature and Literary Criticism
- “Postcolonial Narratives: Deconstructing Power Structures in Literature”
- “Digital Storytelling Platforms: Changing the Landscape of Narrative Arts”
- “Literature and Cultural Identity: Exploring Representations in Global Contexts”
- “Eco-Critical Perspectives in Contemporary Literature”
- “Feminist Literary Criticism: Reinterpreting Classic Texts Through a New Lens”
Chemistry and Chemical Engineering
- “Green Chemistry: Sustainable Approaches to Chemical Synthesis”
- “Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery: Innovations in Biomedical Applications”
- “Chemical Process Optimization: Towards Energy-Efficient Production”
- “The Chemistry of Taste: Molecular Insights into Food Flavors”
- “Catalytic Converters: Advancements in Pollution Control Technologies”
Cultural Studies and Media
- “Media Representations of Social Movements: Framing and Impact”
- “Pop Culture and Identity: Exploring Trends in a Globalized World”
- “The Influence of Social Media on Political Discourse”
- “Reality Television and Perceptions of Reality: A Cultural Analysis”
- “Media Literacy Education: Navigating the Digital Information Age”
Astronomy and Astrophysics
- “Gravitational Waves: Probing the Cosmos for New Discoveries”
- “The Life Cycle of Stars: From Birth to Supernova”
- “Astrobiology: Searching for Extraterrestrial Life in the Universe”
- “Dark Energy and the Accelerating Expansion of the Universe”
- “Cosmic Microwave Background: Insights into the Early Universe”
Social Work and Community Development
- “Community-Based Mental Health Interventions: A Social Work Perspective”
- “Youth Empowerment Programs: Fostering Resilience in Vulnerable Communities”
- “Social Justice Advocacy in Contemporary Social Work Practice”
- “Intersectionality in Social Work: Addressing the Complex Needs of Individuals”
- “The Role of Technology in Enhancing Social Services Delivery”
Artificial Intelligence and Ethics
- “Ethical Considerations in AI Decision-Making: Balancing Autonomy and Accountability”
- “Bias and Fairness in Machine Learning Algorithms: A Critical Examination”
- “Explainable AI: Bridging the Gap Between Complexity and Transparency”
- “The Social Implications of AI-Generated Content: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “AI and Personal Privacy: Navigating the Ethical Dimensions of Data Usage”
Linguistics and Computational Linguistics
- “Natural Language Processing: Advancements in Understanding Human Communication”
- “Multilingualism in the Digital Age: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “Cognitive Linguistics: Exploring the Relationship Between Language and Thought”
- “Speech Recognition Technologies: Applications in Everyday Life”
- “Syntax and Semantics: Unraveling the Structure of Language”
Geology and Earth Sciences
- “Geological Hazards Assessment in Urban Planning: A Case Study”
- “Paleoclimatology: Reconstructing Past Climate Patterns for Future Predictions”
- “Geomorphological Processes in Coastal Landscapes: Implications for Conservation”
- “Volcanic Activity Monitoring: Early Warning Systems and Mitigation Strategies”
- “The Impact of Human Activities on Soil Erosion: An Ecological Perspective”
Political Economy and Global Governance
- “Global Trade Agreements: Assessing Economic Impacts and Equity”
- “Political Economy of Energy Transition: Policies and Socioeconomic Effects”
- “The Role of International Organizations in Global Governance”
- “Financial Inclusion and Economic Development: A Comparative Analysis”
- “The Political Economy of Pandemics: Governance and Crisis Response”
Food Science and Nutrition
- “Nutrigenomics: Personalized Nutrition for Optimal Health”
- “Functional Foods: Exploring Health Benefits Beyond Basic Nutrition”
- “Sustainable Food Production: Innovations in Agriculture and Aquaculture”
- “Dietary Patterns and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Review”
- “Food Allergies and Sensitivities: Mechanisms and Management Strategies”
Sociology and Technology
- “Digital Inequalities: Examining Access and Usage Patterns Across Demographics”
- “The Impact of Social Media on Social Capital and Community Building”
- “Technological Surveillance and Privacy Concerns: A Sociological Analysis”
- “Virtual Communities: An Exploration of Identity Formation in Online Spaces”
- “The Social Dynamics of Online Activism: Mobilization and Participation”
Materials Science and Nanotechnology
- “Nanomaterials for Biomedical Imaging: Enhancing Diagnostic Precision”
- “Self-Healing Materials: Advances in Sustainable and Resilient Infrastructure”
- “Smart Textiles: Integrating Nanotechnology for Enhanced Functionality”
- “Multifunctional Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery: Targeted Therapies and Beyond”
- “Nanocomposites for Energy Storage: Engineering Efficient Capacitors”
Communication and Media Studies
- “Media Convergence: The Evolution of Content Delivery in the Digital Age”
- “The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Consumer Behavior”
- “Crisis Communication in a Hyperconnected World: Lessons from Global Events”
- “Media Framing of Environmental Issues: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Digital Detox: Understanding Media Consumption Patterns and Well-being”
Developmental Psychology
- “Early Childhood Attachment and Its Long-Term Impact on Adult Relationships”
- “Cognitive Development in Adolescence: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “Parenting Styles and Academic Achievement: A Cross-Cultural Perspective”
- “Identity Formation in Emerging Adulthood: The Role of Social Influences”
- “Interventions for Promoting Resilience in At-Risk Youth Populations”
Aerospace Engineering
- “Advancements in Aerodynamics: Redefining Flight Efficiency”
- “Space Debris Management: Mitigating Risks in Earth’s Orbit”
- “Aerodynamic Design Optimization for Supersonic Flight”
- “Hypersonic Propulsion Technologies: Pushing the Boundaries of Speed”
- “Materials for Space Exploration: Engineering Solutions for Harsh Environments”
Political Psychology
- “Political Polarization and Public Opinion: Exploring Cognitive Biases”
- “Leadership Styles and Public Perception: A Psychological Analysis”
- “Nationalism and Identity: Psychological Factors Shaping Political Beliefs”
- “The Influence of Emotional Appeals in Political Communication”
- “Crisis Leadership: The Psychological Dynamics of Decision-Making in Times of Uncertainty”
Marine Biology and Conservation
- “Coral Reef Restoration: Strategies for Biodiversity Conservation”
- “Ocean Plastic Pollution: Assessing Impacts on Marine Ecosystems”
- “Marine Mammal Communication: Insights from Bioacoustics”
- “Sustainable Fisheries Management: Balancing Ecological and Economic Concerns”
- “The Role of Mangrove Ecosystems in Coastal Resilience”
Artificial Intelligence and Creativity
- “Generative AI in Creative Industries: Challenges and Innovations”
- “AI-Enhanced Creativity Tools: Empowering Artists and Designers”
- “Machine Learning for Music Composition: Bridging Art and Technology”
- “Creative AI in Film and Entertainment: Transforming Storytelling”
- “Ethical Considerations in AI-Generated Art and Content”
Cultural Anthropology
- “Cultural Relativism in Anthropological Research: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “Rituals and Symbolism: Unraveling Cultural Practices Across Societies”
- “Migration and Cultural Identity: An Ethnographic Exploration”
- “Material Culture Studies: Understanding Societies through Objects”
- “Indigenous Knowledge Systems: Preserving and Promoting Cultural Heritage”
Quantum Computing and Information Science
- “Quantum Information Processing: Algorithms and Applications”
- “Quantum Cryptography: Securing Communication in the Quantum Era”
- “Quantum Machine Learning: Enhancing AI through Quantum Computing”
- “Quantum Computing in Finance: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “Quantum Internet: Building the Next Generation of Information Networks”
Public Policy and Urban Planning
- “Smart Cities and Inclusive Urban Development: A Policy Perspective”
- “Public-Private Partnerships in Infrastructure Development: Lessons Learned”
- “The Impact of Transportation Policies on Urban Mobility Patterns”
- “Housing Affordability: Policy Approaches to Addressing Urban Challenges”
- “Data-Driven Decision-Making in Urban Governance: Opportunities and Risks”
Gerontology and Aging Studies
- “Healthy Aging Interventions: Promoting Quality of Life in Older Adults”
- “Social Isolation and Mental Health in Aging Populations: Interventions and Support”
- “Technology Adoption Among Older Adults: Bridging the Digital Divide”
- “End-of-Life Decision-Making: Ethical Considerations and Legal Frameworks”
- “Cognitive Resilience in Aging: Strategies for Maintaining Mental Sharpness”
Examples of Effective Research Titles
Illustrative Examples from Various Disciplines
Here are examples of effective research titles from different disciplines:
- “Unlocking the Mysteries of Neural Plasticity: A Multidisciplinary Approach”
- “Sustainable Urban Development: Integrating Environmental and Social Perspectives”
- “Quantum Computing: Navigating the Path to Practical Applications”
Analysis of What Makes Each Title Effective
- Clear indication of the research focus.
- Inclusion of key terms relevant to the field.
- Incorporation of a multidisciplinary or integrated approach where applicable.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Research Title Creation
A. Vagueness and Ambiguity
Vague or ambiguous titles can deter readers from engaging with your research. Ensure your title is straightforward and leaves no room for misinterpretation.
B. Overuse of Jargon
While technical terms are essential, excessive jargon can alienate readers who may not be familiar with the specific terminology. Strike a balance between precision and accessibility.
C. Lack of Alignment with Research Objectives
Your title should align seamlessly with the objectives and findings of your research. Avoid creating titles that misrepresent the core contributions of your study.
D. Lengthy and Complicated Titles
Lengthy titles can be overwhelming and may not effectively convey the essence of your research. Aim for brevity while maintaining clarity and informativeness.
E. Lack of Creativity and Engagement
A bland title may not capture the interest of potential readers. Inject creativity where appropriate and strive to create a title that sparks curiosity.
Ethical Considerations in Research Title Creation
- Avoiding Sensationalism and Misleading Titles
Ensure that your title accurately represents the content of your research. Avoid sensationalism or misleading language that may compromise the integrity of your work.
- Ensuring Accuracy and Integrity in Representing Research Content
Your title should uphold the principles of accuracy and integrity. Any claims or implications in the title should be supported by the actual findings of your research.
Crafting a captivating research title is a nuanced process that requires careful consideration of various factors. From clarity and relevance to creativity and ethical considerations, each element plays a crucial role in the success of your title.
By following the outlined strategies and avoiding common pitfalls for research title ideas, researchers can enhance the visibility and impact of their work, contributing to the broader scholarly conversation. Remember, your research title is the first impression readers have of your work, so make it count.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
How to Start a Research Title? Examples from 105,975 Titles
I analyzed a random sample of 105,975 full-text research papers, uploaded to PubMed Central between the years 2016 and 2021, in order to explore common ways to start a research title.
I used the BioC API to download the data (see the References section below).
Common ways to start a title
The most common 3-word phrases to start a title, the most common 2-word phrases to start a title, the most common words to start a title, can a title start with “how”.
In our sample, 289 titles out of 105,975 (0.27%) started with the word “How”.
Here are some examples:
How Useful are Systematic Reviews for Informing Palliative Care Practice? Survey of 25 Cochrane Systematic Reviews Link to the article on PubMed
How the Leopard Hides Its Spots: ASIP Mutations and Melanism in Wild Cats Link to the article on PubMed
How Do Red Blood Cells Know When to Die? Link to the article on PubMed
Can a title start with “Why”?
In our sample, 68 titles out of 105,975 (0.06%) started with the word “Why”.
Why Don’t All Infants Have Bifidobacteria in Their Stool? Link to the article on PubMed
Why Women Bleed and How They Are Saved: A Cross-Sectional Study of Caesarean Section Near-Miss Morbidity Link to the article on PubMed
Why Most Published Research Findings Are False Link to the article on PLOS MEDICINE
- Comeau DC, Wei CH, Islamaj Doğan R, and Lu Z. PMC text mining subset in BioC: about 3 million full text articles and growing, Bioinformatics , btz070, 2019.
Further reading
- How to Write & Publish a Research Paper: Step-by-Step Guide
- Can a Research Title Be a Question? Real-World Examples
- How Long Should a Research Title Be? Data from 104,161 Examples
- How Long Should a Research Paper Be? Data from 61,519 Examples
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Choosing a Title
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The title summarizes the main idea or ideas of your study. A good title contains the fewest possible words needed to adequately describe the content and/or purpose of your research paper.
Importance of Choosing a Good Title
The title is the part of a paper that is read the most, and it is usually read first . It is, therefore, the most important element that defines the research study. With this in mind, avoid the following when creating a title:
- If the title is too long, this usually indicates there are too many unnecessary words. Avoid language, such as, "A Study to Investigate the...," or "An Examination of the...." These phrases are obvious and generally superfluous unless they are necessary to covey the scope, intent, or type of a study.
- On the other hand, a title which is too short often uses words which are too broad and, thus, does not tell the reader what is being studied. For example, a paper with the title, "African Politics" is so non-specific the title could be the title of a book and so ambiguous that it could refer to anything associated with politics in Africa. A good title should provide information about the focus and/or scope of your research study.
- In academic writing, catchy phrases or non-specific language may be used, but only if it's within the context of the study [e.g., "Fair and Impartial Jury--Catch as Catch Can"]. However, in most cases, you should avoid including words or phrases that do not help the reader understand the purpose of your paper.
- Academic writing is a serious and deliberate endeavor. Avoid using humorous or clever journalistic styles of phrasing when creating the title to your paper. Journalistic headlines often use emotional adjectives [e.g., incredible, amazing, effortless] to highlight a problem experienced by the reader or use "trigger words" or interrogative words like how, what, when, or why to persuade people to read the article or click on a link. These approaches are viewed as counter-productive in academic writing. A reader does not need clever or humorous titles to catch their attention because the act of reading research is assumed to be deliberate based on a desire to learn and improve understanding of the problem. In addition, a humorous title can merely detract from the seriousness and authority of your research.
- Unlike everywhere else in a college-level social sciences research paper [except when using direct quotes in the text], titles do not have to adhere to rigid grammatical or stylistic standards. For example, it could be appropriate to begin a title with a coordinating conjunction [i.e., and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet] if it makes sense to do so and does not detract from the purpose of the study [e.g., "Yet Another Look at Mutual Fund Tournaments"] or beginning the title with an inflected form of a verb such as those ending in -ing [e.g., "Assessing the Political Landscape: Structure, Cognition, and Power in Organizations"].
Appiah, Kingsley Richard et al. “Structural Organisation of Research Article Titles: A Comparative Study of Titles of Business, Gynaecology and Law.” Advances in Language and Literary Studies 10 (2019); Hartley James. “To Attract or to Inform: What are Titles for?” Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 35 (2005): 203-213; Jaakkola, Maarit. “Journalistic Writing and Style.” In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication . Jon F. Nussbaum, editor. (New York: Oxford University Press, 2018): https://oxfordre.com/communication.
Structure and Writing Style
The following parameters can be used to help you formulate a suitable research paper title:
- The purpose of the research
- The scope of the research
- The narrative tone of the paper [typically defined by the type of the research]
- The methods used to study the problem
The initial aim of a title is to capture the reader’s attention and to highlight the research problem under investigation.
Create a Working Title Typically, the final title you submit to your professor is created after the research is complete so that the title accurately captures what has been done . The working title should be developed early in the research process because it can help anchor the focus of the study in much the same way the research problem does. Referring back to the working title can help you reorient yourself back to the main purpose of the study if you find yourself drifting off on a tangent while writing. The Final Title Effective titles in research papers have several characteristics that reflect general principles of academic writing.
- Indicate accurately the subject and scope of the study,
- Rarely use abbreviations or acronyms unless they are commonly known,
- Use words that create a positive impression and stimulate reader interest,
- Use current nomenclature from the field of study,
- Identify key variables, both dependent and independent,
- Reveal how the paper will be organized,
- Suggest a relationship between variables which supports the major hypothesis,
- Is limited to 5 to 15 substantive words,
- Does not include redundant phrasing, such as, "A Study of," "An Analysis of" or similar constructions,
- Takes the form of a question or declarative statement,
- If you use a quote as part of the title, the source of the quote is cited [usually using an asterisk and footnote],
- Use correct grammar and capitalization with all first words and last words capitalized, including the first word of a subtitle. All nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs that appear between the first and last words of the title are also capitalized, and
- Rarely uses an exclamation mark at the end of the title.
The Subtitle Subtitles are frequently used in social sciences research papers because it helps the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem. Think about what type of subtitle listed below reflects the overall approach to your study and whether you believe a subtitle is needed to emphasize the investigative parameters of your research.
1. Explains or provides additional context , e.g., "Linguistic Ethnography and the Study of Welfare Institutions as a Flow of Social Practices: The Case of Residential Child Care Institutions as Paradoxical Institutions." [Palomares, Manuel and David Poveda. Text & Talk: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Language, Discourse and Communication Studies 30 (January 2010): 193-212]
2. Adds substance to a literary, provocative, or imaginative title or quote , e.g., "Listen to What I Say, Not How I Vote": Congressional Support for the President in Washington and at Home." [Grose, Christian R. and Keesha M. Middlemass. Social Science Quarterly 91 (March 2010): 143-167]
3. Qualifies the geographic scope of the research , e.g., "The Geopolitics of the Eastern Border of the European Union: The Case of Romania-Moldova-Ukraine." [Marcu, Silvia. Geopolitics 14 (August 2009): 409-432]
4. Qualifies the temporal scope of the research , e.g., "A Comparison of the Progressive Era and the Depression Years: Societal Influences on Predictions of the Future of the Library, 1895-1940." [Grossman, Hal B. Libraries & the Cultural Record 46 (2011): 102-128]
5. Focuses on investigating the ideas, theories, or work of a particular individual , e.g., "A Deliberative Conception of Politics: How Francesco Saverio Merlino Related Anarchy and Democracy." [La Torre, Massimo. Sociologia del Diritto 28 (January 2001): 75 - 98]
6. Identifies the methodology used , e.g. "Student Activism of the 1960s Revisited: A Multivariate Analysis Research Note." [Aron, William S. Social Forces 52 (March 1974): 408-414]
7. Defines the overarching technique for analyzing the research problem , e.g., "Explaining Territorial Change in Federal Democracies: A Comparative Historical Institutionalist Approach." [ Tillin, Louise. Political Studies 63 (August 2015): 626-641.
With these examples in mind, think about what type of subtitle reflects the overall approach to your study. This will help the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem.
Anstey, A. “Writing Style: What's in a Title?” British Journal of Dermatology 170 (May 2014): 1003-1004; Balch, Tucker. How to Compose a Title for Your Research Paper. Augmented Trader blog. School of Interactive Computing, Georgia Tech University; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. “Formulating the Right Title for a Research Article.” Journal of Association of Physicians of India 64 (February 2016); Choosing the Proper Research Paper Titles. AplusReports.com, 2007-2012; Eva, Kevin W. “Titles, Abstracts, and Authors.” In How to Write a Paper . George M. Hall, editor. 5th edition. (Oxford: John Wiley and Sons, 2013), pp. 33-41; Hartley James. “To Attract or to Inform: What are Titles for?” Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 35 (2005): 203-213; General Format. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Kerkut G.A. “Choosing a Title for a Paper.” Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology 74 (1983): 1; “Tempting Titles.” In Stylish Academic Writing . Helen Sword, editor. (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2012), pp. 63-75; Nundy, Samiran, et al. “How to Choose a Title?” In How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries? A Practical Guide . Edited by Samiran Nundy, Atul Kakar, and Zulfiqar A. Bhutta. (Springer Singapore, 2022), pp. 185-192.
- << Previous: Applying Critical Thinking
- Next: Making an Outline >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
View the latest institution tables
View the latest country/territory tables
How to write a good research paper title
“Unread science is lost science .”

Credit: Mykyta Dolmatov/Getty
“Unread science is lost science.”
28 July 2020

Mykyta Dolmatov/Getty
With the influx of publications brought on by the pandemic, it’s become more challenging than ever for researchers to attract attention to their work.
Understanding which elements of a title will attract readers – or turn them away – has been proven to increase a paper’s citations and Altmetric score .
“In the era of information overload, most students and researchers do not have time to browse the entire text of a paper,” says Patrick Pu , a librarian at the National University of Singapore.
“The title of a paper, together with its abstract, become very important to capture and sustain the attention of readers.”
1. A good title avoids technical language
Since the primary audience of a paper is likely to be researchers working in the same field, using technical language in the title seems to make sense.
But this alienates the wider lay audience, which can bring valuable attention to your work . It can also alienate inexperienced researchers, or those who have recently entered the field.
“A good title does not use unnecessary jargon,” says Elisa De Ranieri , editor-in-chief at the Nature Communications journal (published by Springer Nature, which also publishes Nature Index.) “It communicates the main results in the study in a way that is clear and accessible, ideally to non-specialists or researchers new to the field.”
How-to: When crafting a title, says De Ranieri, write down the main result of the manuscript in a short paragraph. Shorten the text to make it more concise, while still remaining descriptive. Repeat this process until you have a title of fewer than 15 words.
2. A good title is easily searchable
Most readers today are accessing e-journals, which are indexed in scholarly databases such as Scopus and Google Scholar.
“Although these databases usually index the full text of papers, retrieval weightage for ‘Title’ is usually higher than other fields, such as ‘Results’,” Pu explains.
At the National University of Singapore, Pu and his colleagues run information literacy programmes for editors and authors. They give advice for publishing best practice, such as how to identify the most commonly used keywords in literature searches in a given field.
“A professor once told us how he discovered that industry experts were using a different term or keyword to describe his research area,” says Pu.
“He had written a seminal paper that did not include this ‘industry keyword’. He believes his paper, which was highly cited by academics, would have a higher citation count if he had included this keyword in the title. As librarians, we try to highlight this example to our students so that they will consider all possible keywords to use in their searches and paper titles.”
How-to: Authors should speak to an academic librarian at their institution to gain an understanding of keyword and search trends in their field of research. This should inform how the paper title is written.
3. A good title is substantiated by data
Authors should be cautious to not make any claims in the title that can’t be backed up by evidence.
“For instance, if you make a discovery with potential therapeutic relevance, the title should specify whether it was tested or studied in animals or humans/human samples,” says Irene Jarchum , senior editor at the journal Nature Biotechnology (also published by Springer Nature, which publishes the Nature Index.)
Jarchum adds that titles can be contentious because different authors have different views on the use of specific words, such as acronyms, or more fundamentally, what the main message of the title should be.
Some authors may over-interpret the significance of their preliminary findings, and want to reflect this in the title.
How-to: If you know your paper will be contentious within the scientific community, have the data ready to defend your decisions .
4. A good title sparks curiosity
A one-liner that sparks a reader’s interest can be very effective.
“A title has to pique the interest of the person searching for literature in a split-second – enough that they click on the title to read the abstract. Unread science is lost science,” says Christine Mayer , editor-in-chief of the journal Advanced Therapeutics .
Paper titles such as, "White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic" ( 2019 Science ), and “Kids these days: Why the youth of today seem lacking” ( 2019 Science Advances ) are good examples of this principle. Both papers have high Altmetric Attention scores, indicating that they have been widely read and discussed online.
How-to: Take note of the characteristics of paper titles that spark your own interest. Keep a record of these and apply the same principles to your own paper titles.
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write a Great Title

Maximize search-ability and engage your readers from the very beginning
Your title is the first thing anyone who reads your article is going to see, and for many it will be where they stop reading. Learn how to write a title that helps readers find your article, draws your audience in and sets the stage for your research!
How your title impacts the success of your article
Researchers are busy and there will always be more articles to read than time to read them. Good titles help readers find your research, and decide whether to keep reading. Search engines use titles to retrieve relevant articles based on users’ keyword searches. Once readers find your article, they’ll use the title as the first filter to decide whether your research is what they’re looking for. A strong and specific title is the first step toward citations, inclusion in meta-analyses, and influencing your field.
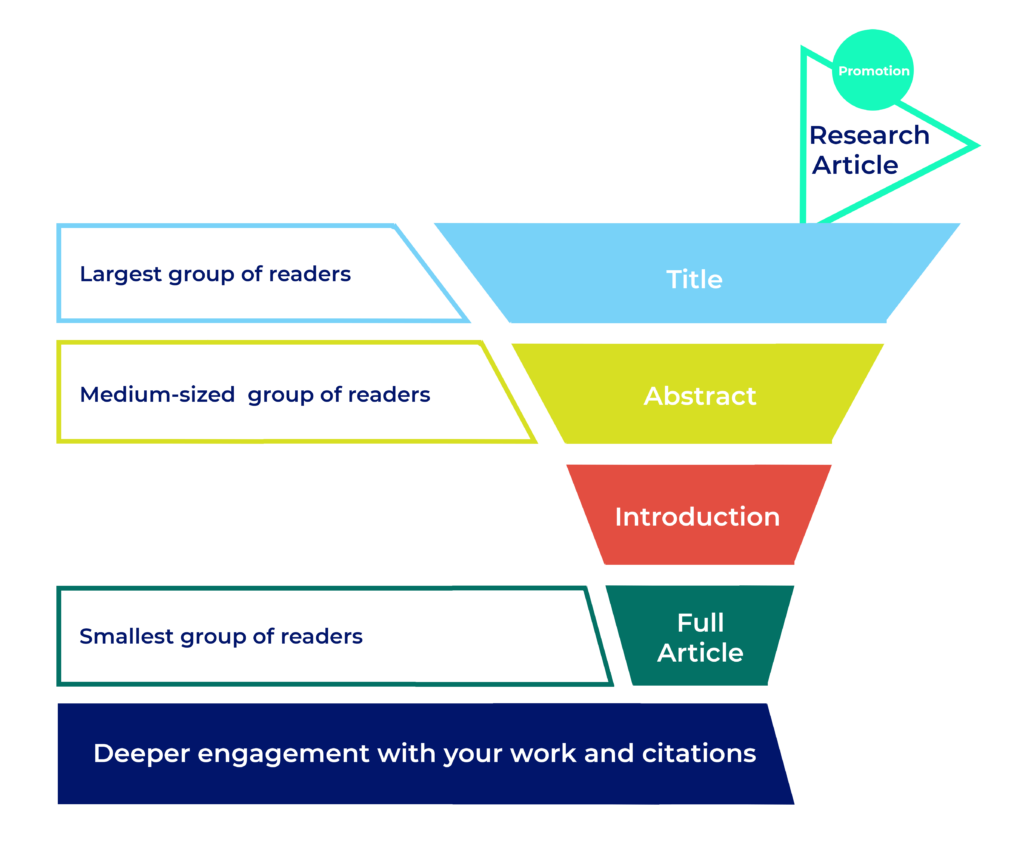
What to include in a title
Include the most important information that will signal to your target audience that they should keep reading.
Key information about the study design
Important keywords
What you discovered
Writing tips
Getting the title right can be more difficult than it seems, and researchers refine their writing skills throughout their career. Some journals even help editors to re-write their titles during the publication process!

- Keep it concise and informative What’s appropriate for titles varies greatly across disciplines. Take a look at some articles published in your field, and check the journal guidelines for character limits. Aim for fewer than 12 words, and check for journal specific word limits.
- Write for your audience Consider who your primary audience is: are they specialists in your specific field, are they cross-disciplinary, are they non-specialists?
- Entice the reader Find a way to pique your readers’ interest, give them enough information to keep them reading.
- Incorporate important keywords Consider what about your article will be most interesting to your audience: Most readers come to an article from a search engine, so take some time and include the important ones in your title!
- Write in sentence case In scientific writing, titles are given in sentence case. Capitalize only the first word of the text, proper nouns, and genus names. See our examples below.

Don’t
- Write your title as a question In most cases, you shouldn’t need to frame your title as a question. You have the answers, you know what you found. Writing your title as a question might draw your readers in, but it’s more likely to put them off.
- Sensationalize your research Be honest with yourself about what you truly discovered. A sensationalized or dramatic title might make a few extra people read a bit further into your article, but you don’t want them disappointed when they get to the results.
Examples…
Format: Prevalence of [disease] in [population] in [location]
Example: Prevalence of tuberculosis in homeless women in San Francisco
Format: Risk factors for [condition] among [population] in [location]
Example: Risk factors for preterm births among low-income women in Mexico City
Format (systematic review/meta-analysis): Effectiveness of [treatment] for [disease] in [population] for [outcome] : A systematic review and meta-analysis
Example: Effectiveness of Hepatitis B treatment in HIV-infected adolescents in the prevention of liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Format (clinical trial): [Intervention] improved [symptoms] of [disease] in [population] : A randomized controlled clinical trial
Example: Using a sleep app lessened insomnia in post-menopausal women in southwest United States: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Format (general molecular studies): Characterization/identification/evaluation of [molecule name] in/from [organism/tissue] (b y [specific biological methods] )
Example: Identification of putative Type-I sex pheromone biosynthesis-related genes expressed in the female pheromone gland of Streltzoviella insularis
Format (general molecular studies): [specific methods/analysis] of organism/tissue reveal insights into [function/role] of [molecule name] in [biological process]
Example: Transcriptome landscape of Rafflesia cantleyi floral buds reveals insights into the roles of transcription factors and phytohormones in flower development
Format (software/method papers): [tool/method/software] for [what purpose] in [what research area]
Example: CRISPR-based tools for targeted transcriptional and epigenetic regulation in plants
Tip: How to edit your work
Editing is challenging, especially if you are acting as both a writer and an editor. Read our guidelines for advice on how to refine your work, including useful tips for setting your intentions, re-review, and consultation with colleagues.
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
Titles in research articles and doctoral dissertations: cross-disciplinary and cross-generic perspectives
- Published: 29 February 2024
- Volume 129 , pages 2285–2307, ( 2024 )
Cite this article

- Jialiang Hao ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0006-5980-4451 1 , 2
228 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
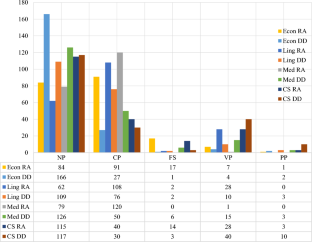
Although titles are often regarded as a minimal aspect of academic discourse, they play a crucial role in knowledge construction across various disciplines and genres. This study examined four features of titles, namely, title length, punctuation usage, structure, and content information, with a corpus comprising 1600 titles of research articles (RAs) from top journals and doctoral dissertations (DDs) from prestigious universities across four soft and hard science disciplines. The results confirm disciplinary and generic variations within the titles of these two critical academic genres. Titles in linguistics and medicine are generally longer than those in economics and computer science (CS). Slightly more titles in hard disciplines contain punctuation than do those in soft disciplines. The average title length of RAs is longer than that of DDs, and more RA titles than DD titles have punctuation in all four disciplines, with no apparent difference in the punctuation variety across the two genres, except for CS titles. Nominal group titles and compound titles are the two most common types, and prepositional phrase titles are the least common in all four disciplines and genres. The content information in titles is different in each discipline and genre. These findings are partially congruent with those of previous studies, indicating the significance of further investigating titles across disciplines and genres.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Balancing AI and academic integrity: what are the positions of academic publishers and universities?

How to design bibliometric research: an overview and a framework proposal

Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice
This paper follows US conventions.
https://www.scimagojr.com/journalrank.php
The impact factor is from the 2022 Journal Citation Reports .
https://www.topuniversities.com/university-rankings/world-university-rankings/2022
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/74/2014/09/guidelines-for-the-PhD-dissertation.pdf
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the american psychological association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association.
Google Scholar
Anthony, L. (2001). Characteristic features of research article titles in computer science. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication, 44 (3), 187–194. https://doi.org/10.1109/47.946464
Article Google Scholar
Bahadoran, Z., Mirmiran, P., Kashfi, K., & Ghasemi, A. (2019). The principles of biomedical scientific writing: Title. International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 17 , e98326. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.98326
Ball, R. (2009). Scholarly communication in transition: The use of question marks in the titles of scientific articles in medicine, life sciences and physics 1966–2005. Scientometrics, 79 (3), 667–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-007-1984-5
Berkenkotter, C., & Huckin, T. N. (1995). News value in scientific journal articles. In C. Berkenkotter & T. N. Huckin (Eds.), Genre knowledge in disciplinary communication: Cognition, culture, power (pp. 27–44). Routledge.
Bramoullé, Y., & Ductor, L. (2018). Title length. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 150 , 311–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2018.01.014
Braticevic, M. N., Babic, I., Abramovic, I., Jokic, A., & Horvat, M. (2020). Title does matter: A cross-sectional study of 30 journals in the medical laboratory technology category. Biochemia Medica, 30 (1), 128–133. https://doi.org/10.11613/bm.2020.010708
Bunton, D. (2002). Generic moves in PhD theses introductions. In J. Flowerdew (Ed.), Academic discourse (pp. 57–75). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315838069
Chapter Google Scholar
Chen, X., & Liu, H. (2023). Academic “click bait”: A diachronic investigation into the use of rhetorical part in pragmatics research article titles. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 66 , 101306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2023.101306
Cheng, S. W., Kuo, C.-W., & Kuo, C.-H. (2012). Research article titles in applied linguistics. Journal of Academic Language and Learning, 6 (1), A1–A14.
Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: looks matter! Indian Pediatrics, 53 (3), 235–241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-016-0827-y
Diao, J. (2021). A lexical and syntactic study of research article titles in library science and scientometrics. Scientometrics, 126 , 6041–6058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-04018-6
El-Dakhs, D. A. S. (2018). Why are abstracts in PhD theses and research articles different? A genre-specific perspective. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 36 , 48–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2018.09.005
Finlay, C. S., Sugimoto, C. R., Li, D., & Russell, T. G. (2012). LIS dissertation titles and abstracts (1930–2009): Where have all the librar* gone? The Library Quarterly, 82 (1), 29–46. https://doi.org/10.1086/662945
Fox, C. W., & Burns, C. S. (2015). The relationship between manuscript title structure and success: Editorial decisions and citation performance for an ecological journal. Ecology and Evolution, 5 , 1970–1980. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1480
Gesuato, S. (2008). Encoding of information in titles: Academic practices across four genres in linguistics. In C. Taylor (Ed.), Ecolingua. The role of E-corpora in translation and language learning (pp. 127–157). EUT Edizioni Università di Trieste.
Gnewuch, M., & Wohlrabe, K. (2017). Title characteristics and citations in economics. Scientometrics, 110 (3), 1573–1578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2216-7
Goodman, R. A., Thacker, S. B., & Siegel, P. Z. (2001). What’s in a title? A descriptive study of article titles in peer-reviewed medical journals. Science Editor, 24 (3), 75–78.
Guo, S., Zhang, G., Ju, Q., Chen, Y., Chen, Q., & Li, L. (2015). The evolution of conceptual diversity in economics titles from 1890 to 2012. Scientometrics, 102 , 2073–2088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-014-1501-6
Habibzadeh, F., & Yadollahie, M. (2010). Are shorter article titles more attractive for citations? Cross-sectional study of 22 scientific journals. Croatian Medical Journal, 51 (2), 165–170. https://doi.org/10.3325/cmj.2010.51.165
Haggan, M. (2004). Research paper titles in literature, linguistics and science: Dimensions of attractions. Journal of Pragmatics, 36 , 293–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-2166(03)00090-0
Hallock, R. M., & Dillner, K. M. (2016). Should title lengths really adhere to the American Psychological Association’s twelve word limit? American Psychologist, 71 (3), 240–242. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0040226
Hartley, J. (2005). To attract or to inform: What are titles for? Journal Technical Writing & Communication, 35 , 203–213. https://doi.org/10.2190/NV6E-FN3N-7NGN-TWQT
Hartley, J. (2007a). Planning that title: Practices and preferences for titles with colons in academic articles. Library & Information Science Research, 29 (4), 553–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2007.05.002
Hartley, J. (2007b). Colonic titles! The Write Stuff, 16 (4), 147–149.
Hyland, K. (2004). Disciplinary interactions: Metadiscourse in L2 postgraduate writing. Journal of Second Language Writing, 13 , 133–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2004.02.001
Hyland, K., & Tse, P. (2005). Hooking the reader: A corpus study of evaluative that in abstracts. English for Specific Purposes, 24 (2), 123–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2004.02.002
Hyland, K., & Zou, H. (2022). Titles in research articles. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 56 , 101094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2022.101094
Jacques, T. S., & Sebire, N. J. (2009). The impact of article titles on citation hits: An analysis of general and specialist medical journals. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine Short Reports, 1 (2), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1258/shorts.2009.100020
Jalilifar, A. (2010). Writing titles in applied linguistics: A comparative study of theses and research articles. Taiwan International ESP Journal, 2 (1), 27–52.
Jalilifar, A., Hayati, A., & Mayahi, N. (2010). An exploration of generic tendencies in Applied Linguistics titles. Journal of Faculty of Letters and Humanities, 5 (16), 35–57.
Jamali, H. R., & Nikzad, M. (2011). Article title type and its relation with the number of downloads and citations. Scientometrics, 88 (2), 653–661. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-011-0412-z
Jiang, F. K., & Hyland, K. (2023). Titles in research articles: Changes across time and discipline. Learned Publishing, 36 , 239–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/leap.1498
Jiang, G. K., & Jiang, Y. (2023). More diversity, more complexity, but more flexibility: Research article titles in TESOL Quarterly , 1967–2022. Scientometrics, 128 , 3959–3980. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-023-04738-x
Kawase, T. (2015). Metadiscourse in the introductions of PhD theses and research articles. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 20 , 114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2015.08.006
Kawase, T. (2018). Rhetorical structure of the introductions of applied linguistics PhD theses. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 31 , 18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2017.12.005
Kerans, M. E., Marshall, J., Murray, A., & Sabaté, S. (2020). Research article title content and form in high-ranked international clinical medicine journals. English for Specific Purposes, 60 , 127–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2020.06.001
Kerans, M. E., Murray, A., & Sabaté, S. (2016). Content and phrasing in titles of original research and review articles in 2015: Range of practice in four clinical journals. Publications, 4 (2), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications4020011
Koutsantoni, D. (2006). Rhetorical strategies in engineering research articles and research theses: Advanced academic literacy and relations of power. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 5 (1), 19–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2005.11.002
Lewison, G., & Hartley, J. (2005). What’s in a title? Numbers of words and the presence of colons. Scientometrics, 63 (2), 341–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-005-0216-0
Li, Z., & Xu, J. (2019). The evolution of research article titles: The case of Journal of Pragmatics 1978–2018. Scientometrics, 121 , 1619–1634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03244-3
Méndez, D. I., ÁngelesAlcaraz, M., & Salager-Meyer, F. (2014). Titles in English-medium Astrophysics research articles. Scientometrics, 98 (3), 2331–2351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-013-1174-6
Milojevic, S. (2017). The length and semantic structure of article titles—evolving disciplinary practices and correlations with impact. Frontiers in Research Metrics and Analysis, 2 , 2. https://doi.org/10.3389/frma.2017.00002
Morales, O. A., Perdomo, B., Cassany, D., Tovar, R. M., & Izarra, É. (2020). Linguistic structures and functions of thesis and dissertation titles in dentistry. Lebende Sprachen, 65 (1), 49–73. https://doi.org/10.1515/les-2020-0003
Moslehi, S., & Kafipour, R. (2022). Syntactic structure and rhetorical combinations of Iranian English research article titles in medicine and applied linguistics: A cross-disciplinary study. Frontiers in Education, 7 , 935274. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.935274
Nagano, R. L. (2015). Research article titles and disciplinary conventions: A corpus study of eight disciplines. Journal of Academic Writing, 5 , 133–144. https://doi.org/10.18552/joaw.v5i1.168
Nair, L. B., & Gibbert, M. (2016). What makes a “good” title and (how) does it matter for citations? A review and general model of article title attributes in management science. Scientometrics, 107 (3), 1331–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-1937-y
Nieuwenhuis, J. (2023). Another article titled “Should I Stay or Should I Go?” or, the mass production of academic research titles. The Information Society, 39 (2), 123–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/01972243.2022.2152916
Paiva, C., Lima, J., & Paiva, B. (2012). Articles with short titles describing the results are cited more often. Clinics, 67 (5), 509–513. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2012(05)17
Paltridge, B. (2002). Thesis and dissertation writing: An examination of published advice and actual practice. English for Specific Purposes, 21 (2), 125–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0889-4906(00)00025-9
Paré, A. (2019). Re-writing the doctorate: New contexts, identities, and genres. Journal of Second Language Writing, 43 , 80–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jslw.2018.08.004
Paré, A., Starke-Meyerring, D., & McAlpine, L. (2009). The dissertation as multi-genre: Many readers, many readings. In C. Bazerman, A. Bonini, & D. Figueiredo (Eds.), Genre in a changing world (pp. 179–193). The WAC Clearinghouse and Parlor Press.
Pearson, W. S. (2020). Research article titles in written feedback on English as a second language writing. Scientometrics, 123 , 997–1019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03388-7
Pearson, W. S. (2021). Quoted speech in linguistics research article titles: Patterns of use and effects on citations. Scientometrics, 126 , 3421–3442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-020-03827-5
Qiu, X., & Ma, X. (2019). Disciplinary enculturation and authorial stance: comparison of stance features among master’s dissertations, doctoral theses, and research articles. Ibérica, 38 , 327–348.
Sahragard, R., & Meihami, H. (2016). A diachronic study on the information provided by the research titles of applied linguistics journals. Scientometrics, 108 , 1315–1331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2049-4
Salager-Meyer, F., Alcaraz-Ariza, M. A., & Briceño, M. L. (2013). Titling and authorship practices in medical case reports: A diachronic study (1840–2009). Communication & Medicine, 10 (1), 63–80. https://doi.org/10.1558/cam.v10i1.63
Soler, V. (2007). Writing titles in science: An exploratory study. English for Specific Purposes, 26 (1), 90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2006.08.001
Soler, V. (2011). Comparative and contrastive observations on scientific titles written in English and Spanish. English for Specific Purposes, 30 (2), 124–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2010.09.002
Soler, V. (2018). Estudio exploratorio de títulos de tesis doctorales redactados en lengua Española [Exploratory study of Ph.D. thesis titles written in Spanish]. Lebende Sprachen, 63 (2), 374–392. https://doi.org/10.1515/les-2018-0022
Swales, J. (1990). Genre analysis: English in academic and research setting . Cambridge University Press.
Swales, J. (2004). Research genres: Explorations and applications. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press . https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139524827
Swales, J., & Feak, C. B. (2012). Academic writing for graduate students . Ann Arbor, MI, The University of Michigan Press.
Book Google Scholar
Taş, E. E. I. (2008). A corpus-based analysis of genre-specific discourse of research: The PhD thesis and the research article in ELT. Doctorate thesis at Middle East Technical University (Turkey) . http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.633.4476&rep=rep1&type=pdf
Thompson, P. (2005). Points of focus and position: Intertextual reference in PhD theses. Journal of English for Academic Purposes, 4 (4), 307–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeap.2005.07.006
Thompson, P. (2013). Thesis and dissertation writing. In B. Paltridge & S. Starfield (Eds.), The handbook of English for specific purposes (pp. 283–299). West Essex.
Wang, Y., & Bai, Y. (2007). A corpus-based syntactic study of medical research article titles. System, 35 , 388–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2007.01.005
Whissell, C. (2012). The trend toward more attractive and informative titles: American psychologist 1946–2010. Psychological Reports, 110 (2), 427–444. https://doi.org/10.2466/17.28.pr0.110.2.427-444
Whissell, C. (2013). Titles in highly ranked multidisciplinary psychology journals 1966–2011: More words and punctuation marks allow for the communication of more information. Psychological Reports, 113 (3), 969–986. https://doi.org/10.2466/28.17.PR0.113x30z5
Xiang, X., & Li, J. (2020). A diachronic comparative study of research article titles in linguistics and literature journals. Scientometrics, 122 , 847–866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-019-03329-z
Xiao, W., & Sun, S. (2020). Dynamic lexical features of PhD theses across disciplines: A text mining approach. Journal of Quantitative Linguistics, 27 (2), 114–133. https://doi.org/10.1080/09296174.2018.1531618
Xie, S. (2020). English research article titles: Cultural and disciplinary perspectives. SAGE Open, 10 (2), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244020933614
Yang, W. (2019). A diachronic keyword analysis in research article titles and cited article titles in applied linguistics from 1990 to 2016. English Text Construction, 12 (1), 84–102. https://doi.org/10.1075/etc.00019.yan
Yitzhaki, M. (2002). Relation of the title length of a journal article to the length of the article. Scientometrics, 54 , 435–447. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016038617639
Zhou, H., & Jiang, F. K. (2023). “The study has clear limitations”: Presentation of limitations in conclusion sections of PhD dissertations and research articles in applied linguistics. English for Specific Purposes, 71 , 34–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esp.2023.02.001
Download references
Acknowledgements
The researcher thanks the handling editor and the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, which significantly contributed to enhancing the quality of the manuscript.
This research was supported and funded by the Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (Program No. 23JK0100).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Xi’an International Studies University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
Jialiang Hao
Weinan Normal University, Weinan, Shaanxi, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jialiang Hao .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author has no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Hao, J. Titles in research articles and doctoral dissertations: cross-disciplinary and cross-generic perspectives. Scientometrics 129 , 2285–2307 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-024-04941-4
Download citation
Received : 10 July 2023
Accepted : 09 January 2024
Published : 29 February 2024
Issue Date : April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-024-04941-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Research articles
- Doctoral dissertations
- Disciplines
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Make a Research Paper Title with Examples
What is a research paper title and why does it matter?
A research paper title summarizes the aim and purpose of your research study. Making a title for your research is one of the most important decisions when writing an article to publish in journals. The research title is the first thing that journal editors and reviewers see when they look at your paper and the only piece of information that fellow researchers will see in a database or search engine query. Good titles that are concise and contain all the relevant terms have been shown to increase citation counts and Altmetric scores .
Therefore, when you title research work, make sure it captures all of the relevant aspects of your study, including the specific topic and problem being investigated. It also should present these elements in a way that is accessible and will captivate readers. Follow these steps to learn how to make a good research title for your work.
How to Make a Research Paper Title in 5 Steps
You might wonder how you are supposed to pick a title from all the content that your manuscript contains—how are you supposed to choose? What will make your research paper title come up in search engines and what will make the people in your field read it?
In a nutshell, your research title should accurately capture what you have done, it should sound interesting to the people who work on the same or a similar topic, and it should contain the important title keywords that other researchers use when looking for literature in databases. To make the title writing process as simple as possible, we have broken it down into 5 simple steps.
Step 1: Answer some key questions about your research paper
What does your paper seek to answer and what does it accomplish? Try to answer these questions as briefly as possible. You can create these questions by going through each section of your paper and finding the MOST relevant information to make a research title.
Step 2: Identify research study keywords
Now that you have answers to your research questions, find the most important parts of these responses and make these your study keywords. Note that you should only choose the most important terms for your keywords–journals usually request anywhere from 3 to 8 keywords maximum.
Step 3: Research title writing: use these keywords
“We employed a case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years to assess how waiting list volume affects the outcomes of liver transplantation in patients; results indicate a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and negative prognosis after the transplant procedure.”
The sentence above is clearly much too long for a research paper title. This is why you will trim and polish your title in the next two steps.
Step 4: Create a working research paper title
To create a working title, remove elements that make it a complete “sentence” but keep everything that is important to what the study is about. Delete all unnecessary and redundant words that are not central to the study or that researchers would most likely not use in a database search.
“ We employed a case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years to assess how the waiting list volume affects the outcome of liver transplantation in patients ; results indicate a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis after transplant procedure ”
Now shift some words around for proper syntax and rephrase it a bit to shorten the length and make it leaner and more natural. What you are left with is:
“A case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcome of transplantation and showing a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis” (Word Count: 38)
This text is getting closer to what we want in a research title, which is just the most important information. But note that the word count for this working title is still 38 words, whereas the average length of published journal article titles is 16 words or fewer. Therefore, we should eliminate some words and phrases that are not essential to this title.
Step 5: Remove any nonessential words and phrases from your title
Because the number of patients studied and the exact outcome are not the most essential parts of this paper, remove these elements first:
“A case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcomes of transplantation and showing a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis” (Word Count: 19)
In addition, the methods used in a study are not usually the most searched-for keywords in databases and represent additional details that you may want to remove to make your title leaner. So what is left is:
“Assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcome and prognosis in liver transplantation patients” (Word Count: 15)
In this final version of the title, one can immediately recognize the subject and what objectives the study aims to achieve. Note that the most important terms appear at the beginning and end of the title: “Assessing,” which is the main action of the study, is placed at the beginning; and “liver transplantation patients,” the specific subject of the study, is placed at the end.
This will aid significantly in your research paper title being found in search engines and database queries, which means that a lot more researchers will be able to locate your article once it is published. In fact, a 2014 review of more than 150,000 papers submitted to the UK’s Research Excellence Framework (REF) database found the style of a paper’s title impacted the number of citations it would typically receive. In most disciplines, articles with shorter, more concise titles yielded more citations.
Adding a Research Paper Subtitle
If your title might require a subtitle to provide more immediate details about your methodology or sample, you can do this by adding this information after a colon:
“ : a case study of US adult patients ages 20-25”
If we abide strictly by our word count rule this may not be necessary or recommended. But every journal has its own standard formatting and style guidelines for research paper titles, so it is a good idea to be aware of the specific journal author instructions , not just when you write the manuscript but also to decide how to create a good title for it.
Research Paper Title Examples
The title examples in the following table illustrate how a title can be interesting but incomplete, complete by uninteresting, complete and interesting but too informal in tone, or some other combination of these. A good research paper title should meet all the requirements in the four columns below.
Tips on Formulating a Good Research Paper Title
In addition to the steps given above, there are a few other important things you want to keep in mind when it comes to how to write a research paper title, regarding formatting, word count, and content:
- Write the title after you’ve written your paper and abstract
- Include all of the essential terms in your paper
- Keep it short and to the point (~16 words or fewer)
- Avoid unnecessary jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords that capture the content of your paper
- Never include a period at the end—your title is NOT a sentence
Research Paper Writing Resources
We hope this article has been helpful in teaching you how to craft your research paper title. But you might still want to dig deeper into different journal title formats and categories that might be more suitable for specific article types or need help with writing a cover letter for your manuscript submission.
In addition to getting English proofreading services , including paper editing services , before submission to journals, be sure to visit our academic resources papers. Here you can find dozens of articles on manuscript writing, from drafting an outline to finding a target journal to submit to.

6 Important Tips on Writing a Research Paper Title
When you are searching for a research study on a particular topic, you probably notice that articles with interesting, descriptive research titles draw you in. By contrast, research paper titles that are not descriptive are usually passed over, even though you may write a good research paper with interesting contents. This shows the importance of coming up with a good title for your research paper when drafting your own manuscript.
Importance of a Research Title
The research title plays a crucial role in the research process, and its importance can be summarized as follows:
Why do Research Titles Matter?
Before we look at how to title a research paper, let’s look at a research title example that illustrates why a good research paper should have a strong title.
Imagine that you are researching meditation and nursing, and you want to find out if any studies have shown that meditation makes nurses better communicators. You conduct a keyword search using the keywords “nursing”, “communication”, and “meditation.” You come up with results that have the following titles:
- Benefits of Meditation for the Nursing Profession: A Quantitative Investigation
- Why Mindful Nurses Make the Best Communicators
- Meditation Gurus
- Nurses on the Move: A Quantitative Report on How Meditation Can Improve Nurse Performance
All four of these research paper titles may describe very similar studies—they could even be titles for the same study! As you can see, they give very different impressions.
- Title 1 describes the topic and the method of the study but is not particularly catchy.
- Title 2 partly describes the topic, but does not give any information about the method of the study—it could simply be a theoretical or opinion piece.
- Title 3 is somewhat catchier but gives almost no information at all about the article.
- Title 4 begins with a catchy main title and is followed by a subtitle that gives information about the content and method of the study.
As we will see, Title 4 has all the characteristics of a good research title.
Characteristics of a Good Research Title
According to rhetoric scholars Hairston and Keene, making a good title for a paper involves ensuring that the title of the research accomplishes four goals as mentioned below:
- It should predict the content of the research paper .
- It should be interesting to the reader .
- It should reflect the tone of the writing .
- It should contain important keywords that will make it easier to be located during a keyword search.
Let’s return to the examples in the previous section to see how to make a research title.
As you can see in the table above, only one of the four example titles fulfills all of the criteria of a suitable research paper title.
Related: You’ve chosen your study topic, but having trouble deciding where to publish it? Here’s a comprehensive course to help you identify the right journal .
Tips for Writing an Effective Research Paper Title
When writing a research title, you can use the four criteria listed above as a guide. Here are a few other tips you can use to make sure your title will be part of the recipe for an effective research paper :
- Make sure your research title describes (a) the topic, (b) the method, (c) the sample, and (d) the results of your study. You can use the following formula:
[ Result ]: A [ method ] study of [ topic ] among [ sample ] Example : Meditation makes nurses perform better: a qualitative study of mindfulness meditation among German nursing students
- Avoid unnecessary words and jargons. Keep the title statement as concise as possible. You want a title that will be comprehensible even to people who are not experts in your field. Check our article for a detailed list of things to avoid when writing an effective research title .
- Make sure your title is between 5 and 15 words in length.
- If you are writing a title for a university assignment or for a particular academic journal, verify that your title conforms to the standards and requirements for that outlet. For example, many journals require that titles fall under a character limit, including spaces. Many universities require that titles take a very specific form, limiting your creativity.
- Use a descriptive phrase to convey the purpose of your research efficiently.
- Most importantly, use critical keywords in the title to increase the discoverability of your article.

Resources for Further Reading
In addition to the tips above, there are many resources online that you can use to help write your research title. Here is a list of links that you may find useful as you work on creating an excellent research title:
- The University of Southern California has a guide specific to social science research papers: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
- The Journal of European Psychology Students has a blog article focusing on APA-compliant research paper titles: http://blog.efpsa.org/2012/09/01/how-to-write-a-good-title-for-journal-articles/
- This article by Kristen Hamlin contains a step-by-step approach to writing titles: http://classroom.synonym.com/choose-title-research-paper-4332.html
Are there any tips or tricks you find useful in crafting research titles? Which tip did you find most useful in this article? Leave a comment to let us know!
- Hairston, M., & Keene, M. 2003. Successful writing . 5th ed. New York: Norton.
- University of Southern California. 2017. Organizing your social sciences research paper: choosing a title . [Online] Available at: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
Thank you so much:) Have a nice day!
Thank you so much, it helped me.. God bless..
Thank you for the excellent article and tips for creating a research work, because I always forget about such an essential element as the keywords when forming topics. In particular, I have found a rapid help with the formation of informative and sound titles that also conforms to the standards and requirements.
I am doing a research work on sales girls or shop girls using qualititative method. Basicly I am from Pakistan and writing on the scenario of mycountry. I am really confused about my research title can you kindly give some suggestions and give me an approperaite tilte

Hi Zubair, Thank you for your question. However, the information you have provided is insufficient for drafting an appropriate title. Information on what exactly you intend to study would be needed in order to draft a meaningful title. Meanwhile, you can try drafting your own title after going through the following articles our website: https://www.enago.com/academy/top-10-tips-on-choosing-an-attractive-research-title/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/writing-a-good-research-title-things-to-avoid/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/write-irresistible-research-paper-title/ We would be happy to give you feedback and suggest changes if required. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
thanks for helping me like this!!
Thank you for this. It helped me improve my research title. I just want to verify to you the title I have just made. “Ensuring the safety: A Quantitative Study of Radio Frequency Identification system among the selected students of ( school’s name ).
(I need your reply asap coz we will be doing the chap. 1 tomorrow. Thank u in advance. 🙂 )
I am actually doing a research paper title. I want to know more further in doing research title. Can you give me some tips on doing a research paper?
Hi Joan, Thank you for your question. We are glad to know that you found our resources useful. Your feedback is very valuable to us. You can try drafting your own title after going through the following articles on our website: https://www.enago.com/academy/top-10-tips-on-choosing-an-attractive-research-title/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/writing-a-good-research-title-things-to-avoid/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/write-irresistible-research-paper-title/
We would be happy to give you feedback and suggest changes if required. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
That really helpful. Thanks alot
Thank you so much. It’s really help me.
Thanks for sharing this tips. Title matters a lot for any article because it contents Keywords of article. It should be eye-catchy. Your article is helpful to select title of any article.
nice blog that you have shared
This blog is very informative for me. Thanks for sharing.
nice information that you have shared
i’m found in selecting my ma thesis title ,so i’m going to do my final research after the proposal approved. Your post help me find good title.
I need help. I need a research title for my study about early mobilization of the mechanically ventilated patients in the ICU. Any suggestions would be highly appreciated.
Thank you for posting your query on the website. When writing manuscripts, too many scholars neglect the research title. This phrase, along with the abstract, is what people will mostly see and read online. Title research of publications shows that the research paper title does matter a lot. Both bibliometrics and altmetrics tracking of citations are now, for better or worse, used to gauge a paper’s “success” for its author(s) and the journal publishing it. Interesting research topics coupled with good or clever yet accurate research titles can draw more attention to your work from peers and the public alike. You can check through the following search results for titles on similar topics: https://www.google.com/search?q=early+mobilization+of+the+mechanically+ventilated+patients+in+the+icu&rlz=1C1GCEU_enIN907IN907&oq=&aqs=chrome.0.69i59.4920093j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 .
We hope this would be helpful in drafting an attractive title for your research paper.
Please let us know in case of any other queries.
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours these days, but I never found any interesting article like yours. It is lovely worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made just right content material as you did, the internet will be much more helpful than ever before.
Wonderful article! We will bee linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say fantastic blog!
In case the topic is new research before you’re writing. And then to stand out, you end up being different.and be inclined to highlight yourself.
There are many free directories, and more paid lists.
To be honest your article is informative. I search many site to know about writing but I didn’t get the information I needed. I saw your site and I read it. I got some new information from here. I think some of your tips can be applied to those too! Thank you so very much for such informative and useful content.
Nice and well written content you have shared with us. thanks a lot!
Thanks for sharing these tips… Rockwide
Its helpful. a person can grab knowledge through it.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, research title examples for students—need inspiration.
I'm finalizing my research project for a class, and I'm really struggling to come up with a good, catchy title that's also informative. Is there a place I can go to browse examples of other students' research titles, or can you guys offer some inspiration or guidance on making mine stand out?
Coming up with a catchy and informative title can definitely be challenging. While it's important for the title to engage the reader, it should also provide a clear idea of what your research project is about. Here are some general tips and examples to help inspire you:
1. Start with a working title while you're researching and drafting, and refine it once your project is complete.
2. Make sure your title is specific, focused, and relevant to your research.
3. Use clear and straightforward language, avoiding jargon and acronyms.
4. Consider using a two-part title, with a catchy or creative part followed by a more descriptive explanation.
Here are some example research titles to give you an idea of what could work for different subjects:
- For a psychology paper: "Digital Detox: Evaluating the Effects of Social Media Abstinence on Mental Health"
- For a biology study: "Unearthing the Secrets: Investigating Soil Microbes and Their Influence on Plant Growth"
- For an economics research: "Trading Places: A Comparative Analysis of Online Retail vs. Brick-and-Mortar Storefronts"
- For a history project: "Stories Behind the Statues: Decoding the Hidden Narratives of Public Monuments"
Remember that every research topic and discipline may call for a slightly different approach. It's a good idea to look at published research articles in your field to get a sense of how others have crafted their titles. Often, academic journals have online archives, providing an excellent source of examples.
Ultimately, allow yourself some flexibility and creative freedom as you craft your research title. Keep it concise, informative, and engaging, and you'll be well on your way to a great title. Good luck!
About CollegeVine’s Expert FAQ
CollegeVine’s Q&A seeks to offer informed perspectives on commonly asked admissions questions. Every answer is refined and validated by our team of admissions experts to ensure it resonates with trusted knowledge in the field.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Eight Recommendations for Writing Titles of Scientific Manuscripts

2010, Public Health Nursing
Related Papers
Learned Publishing
Titles are a crucial feature of research papers and have become increasingly important with changes in publishing practices and the explosion of published research. As a result, novice writers seeking to get their work noticed in international journals might benefit from a clear understanding of the features of research titles and an awareness of the relationship between language and disciplinary context. In this study, we explore this relationship and the impact of changing contexts on titles across the last 60 years on the length, form and content of 36,000 titles from the ten leading journals from six disciplines spread along a soft-hard science continuum. Our results show a considerable increase in the length of titles coupled with more interrogative and compound titles in almost all disciplines. There has also been a growing mention of methods in the titles of hard knowledge papers with more frequent inclusion of results in the softer domains. These diachronic changes can be attributed to different characteristics of the fields and of the changing dynamics of the publishing context. Our findings have important implications for early career academics seeking to publish in English and contribute to studies of diachronic analysis of academic discourse.
Journal of Academic Writing
Robin Nagano
Journal of English for Academic Purposes
Titles are a key part of every academic genre and are particularly important in research papers. Today, online searches are overwhelmingly based on articles rather than journals which means that writers must, more than ever, make their titles both informative and appealing to attract readers who may go on to read, cite and make use of their research. In this paper we explore the key features of 5070 titles in the leading journals of six disciplines in the human and physical sciences to identify their typical structural patterns and content foci. In addition to proposing a model of title patterns, we show there are major disciplinary differences which can be traced to different characteristics of the fields and of the topics of the articles themselves. Our findings have important implications for EAP and ERPP teachers working with early career academic writers.
Journal of Biological Education
Ian Kinchin
Publications
Mary Ellen Kerans
Sara Gesuato
The title of an academic publication names, introduces, metonymically represents and advertises the content it labels, circulating from one text to the next. It is meant to be useful (informative and precise), logical (relevant to the work it names, easily classifiable and storable in databases) and reader-friendly (concise, understandable and appealing; Huth 1987; Swales and Feak 1994; Yitzhaki 1994; Busch-Lauer 2000; Dressler and Eckkramer 2001; Goodman et al. 2001; Yakhontova 2002; Hartley 2005; Lewinson and Hartley 2005; Hartley 2008). Yet, its encoding varies depending on editorial policies, individual authors’ stylistic preferences, and awareness of the role and expected impact of the title on the communicative situation. The following titles, which identify a book, a dissertation, a journal article and a proceedings paper, respectively, illustrate this variation:
Journal of Pragmatics
asha seaforth
Although it is a very small part of the research paper, the title plays an important role as the first point of contact between writer and potential reader and may decide whether or not the paper is read. Research paper titles in the widely differing fields of science, literature and linguistics are studied in detail with a view to showing what researchers from each discipline implicitly feel are important features in the succinct knowledge transmission required in title design. Three basic types of titles in the three disciplines are analyzed: full sentence, compound and a remaining group made up largely of noun phrases with or without postmodification. Very clear-cut differences in frequency and form were found across the three disciplines reflecting fundamental differences in pragmatic intention inherent in the disciplines concerned. Analysis focusses on the role of titles in informing the reader as to what the paper is about and also in attracting him/her to read the paper. Discussion of how these functions are met rests on techniques involved in both information packaging and advertising.
Ecology and Evolution
Charles Fox
Advances in Language and Literary Studies
Since titles are gateways to the heart of research articles (RAs), their organisational structure should be regarded very crucial in appealing to the potential reader. This study aimed to investigate how titles of RAs are presented in three disciplines (Gynaecology/Obstetrics, Business, and Law). After a thorough study of 574 titles, the study revealed that Business titles were averagely longer than those in the other two disciplines. In terms of title style, it was revealed that the Single Unit Title was extensively used in Gynaecology/Obstetrics and Law, while the Compound Unit Title dominated the Business titles. Syntactically, Noun Phrases extremely dominated the Single Unit Titles across the three domains. Detailed examination of the NP modifications showed that nominal titles which were both Pre and Post-modified were highly frequent in all the disciplines, which contrasts what is in the literature. The study also identified the Prepositional Phrase as the commonest structure ...
Mercedes Jaime-Sisó
This paper evidences the progressive adoption of a journalistic approach in title writing in certain scientific fields and suggests the reasons why this evolution has not affected all disciplines. The study is based on an analysis of 8,000 scientific research articles published over the last 25 years. The corpus was carefully selected following the advice of scientific researchers from several university departments. Factors such as the position of the journals in their impact list and the multidisciplinary or specific profile of the publication were considered. The results indicate that anticipating the conclusions in the title has become common practice in experimental works of biomedical research. An analysis of the linguistic characteristics of these conclusive titles is included to identify their basic components. It is suggested that instruction on the use of journalistic strategies is advisable for non-native writers and readers of biomedical research articles in high- rankin...
RELATED PAPERS
Jonathan Lanman
Nicola Lalli
Silvia Mazzoni
Journal of the Neurological Sciences
Helena Buque
CSU毕业证书 查尔斯特大学毕业证
Albert Phillimore
European Neuropsychopharmacology
Dr. István Laszlovszky
2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
Das Reich der Vandalen und …
Alexandra Chavarria Arnau
Protein Expression and Purification
Juan Pedro Luna Arias
Conservation physiology
TRINH NGUYEN
Lloyd Whitman
Electronics Letters
Kwai Man Luk
Medicina Clínica
Pablo Young
The American Journal of Human Genetics
Niels Tommerup
Marciano Adilio Spica
Slavo Radosevic
Revista de Pesquisa e Educação Jurídica
Natan Oliveira
Radiotherapy and Oncology
S. Naccarato
La lámpara de Diógenes
Diego Ulises Alonso Pérez
Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry
Tamara Cifuentes
Classical and Quantum Gravity
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
María Vallet-regí

RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Saudi J Anaesth
- v.13(Suppl 1); 2019 Apr
Writing the title and abstract for a research paper: Being concise, precise, and meticulous is the key
Milind s. tullu.
Department of Pediatrics, Seth G.S. Medical College and KEM Hospital, Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
This article deals with formulating a suitable title and an appropriate abstract for an original research paper. The “title” and the “abstract” are the “initial impressions” of a research article, and hence they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, and meticulously. Often both of these are drafted after the full manuscript is ready. Most readers read only the title and the abstract of a research paper and very few will go on to read the full paper. The title and the abstract are the most important parts of a research paper and should be pleasant to read. The “title” should be descriptive, direct, accurate, appropriate, interesting, concise, precise, unique, and should not be misleading. The “abstract” needs to be simple, specific, clear, unbiased, honest, concise, precise, stand-alone, complete, scholarly, (preferably) structured, and should not be misrepresentative. The abstract should be consistent with the main text of the paper, especially after a revision is made to the paper and should include the key message prominently. It is very important to include the most important words and terms (the “keywords”) in the title and the abstract for appropriate indexing purpose and for retrieval from the search engines and scientific databases. Such keywords should be listed after the abstract. One must adhere to the instructions laid down by the target journal with regard to the style and number of words permitted for the title and the abstract.
Introduction
This article deals with drafting a suitable “title” and an appropriate “abstract” for an original research paper. Because the “title” and the “abstract” are the “initial impressions” or the “face” of a research article, they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, meticulously, and consume time and energy.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ] Often, these are drafted after the complete manuscript draft is ready.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 9 , 10 , 11 ] Most readers will read only the title and the abstract of a published research paper, and very few “interested ones” (especially, if the paper is of use to them) will go on to read the full paper.[ 1 , 2 ] One must remember to adhere to the instructions laid down by the “target journal” (the journal for which the author is writing) regarding the style and number of words permitted for the title and the abstract.[ 2 , 4 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 12 ] Both the title and the abstract are the most important parts of a research paper – for editors (to decide whether to process the paper for further review), for reviewers (to get an initial impression of the paper), and for the readers (as these may be the only parts of the paper available freely and hence, read widely).[ 4 , 8 , 12 ] It may be worth for the novice author to browse through titles and abstracts of several prominent journals (and their target journal as well) to learn more about the wording and styles of the titles and abstracts, as well as the aims and scope of the particular journal.[ 5 , 7 , 9 , 13 ]
The details of the title are discussed under the subheadings of importance, types, drafting, and checklist.
Importance of the title
When a reader browses through the table of contents of a journal issue (hard copy or on website), the title is the “ first detail” or “face” of the paper that is read.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 13 ] Hence, it needs to be simple, direct, accurate, appropriate, specific, functional, interesting, attractive/appealing, concise/brief, precise/focused, unambiguous, memorable, captivating, informative (enough to encourage the reader to read further), unique, catchy, and it should not be misleading.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 9 , 12 ] It should have “just enough details” to arouse the interest and curiosity of the reader so that the reader then goes ahead with studying the abstract and then (if still interested) the full paper.[ 1 , 2 , 4 , 13 ] Journal websites, electronic databases, and search engines use the words in the title and abstract (the “keywords”) to retrieve a particular paper during a search; hence, the importance of these words in accessing the paper by the readers has been emphasized.[ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 12 , 14 ] Such important words (or keywords) should be arranged in appropriate order of importance as per the context of the paper and should be placed at the beginning of the title (rather than the later part of the title, as some search engines like Google may just display only the first six to seven words of the title).[ 3 , 5 , 12 ] Whimsical, amusing, or clever titles, though initially appealing, may be missed or misread by the busy reader and very short titles may miss the essential scientific words (the “keywords”) used by the indexing agencies to catch and categorize the paper.[ 1 , 3 , 4 , 9 ] Also, amusing or hilarious titles may be taken less seriously by the readers and may be cited less often.[ 4 , 15 ] An excessively long or complicated title may put off the readers.[ 3 , 9 ] It may be a good idea to draft the title after the main body of the text and the abstract are drafted.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]
Types of titles
Titles can be descriptive, declarative, or interrogative. They can also be classified as nominal, compound, or full-sentence titles.
Descriptive or neutral title
This has the essential elements of the research theme, that is, the patients/subjects, design, interventions, comparisons/control, and outcome, but does not reveal the main result or the conclusion.[ 3 , 4 , 12 , 16 ] Such a title allows the reader to interpret the findings of the research paper in an impartial manner and with an open mind.[ 3 ] These titles also give complete information about the contents of the article, have several keywords (thus increasing the visibility of the article in search engines), and have increased chances of being read and (then) being cited as well.[ 4 ] Hence, such descriptive titles giving a glimpse of the paper are generally preferred.[ 4 , 16 ]
Declarative title
This title states the main finding of the study in the title itself; it reduces the curiosity of the reader, may point toward a bias on the part of the author, and hence is best avoided.[ 3 , 4 , 12 , 16 ]
Interrogative title
This is the one which has a query or the research question in the title.[ 3 , 4 , 16 ] Though a query in the title has the ability to sensationalize the topic, and has more downloads (but less citations), it can be distracting to the reader and is again best avoided for a research article (but can, at times, be used for a review article).[ 3 , 6 , 16 , 17 ]
From a sentence construct point of view, titles may be nominal (capturing only the main theme of the study), compound (with subtitles to provide additional relevant information such as context, design, location/country, temporal aspect, sample size, importance, and a provocative or a literary; for example, see the title of this review), or full-sentence titles (which are longer and indicate an added degree of certainty of the results).[ 4 , 6 , 9 , 16 ] Any of these constructs may be used depending on the type of article, the key message, and the author's preference or judgement.[ 4 ]
Drafting a suitable title
A stepwise process can be followed to draft the appropriate title. The author should describe the paper in about three sentences, avoiding the results and ensuring that these sentences contain important scientific words/keywords that describe the main contents and subject of the paper.[ 1 , 4 , 6 , 12 ] Then the author should join the sentences to form a single sentence, shorten the length (by removing redundant words or adjectives or phrases), and finally edit the title (thus drafted) to make it more accurate, concise (about 10–15 words), and precise.[ 1 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 9 ] Some journals require that the study design be included in the title, and this may be placed (using a colon) after the primary title.[ 2 , 3 , 4 , 14 ] The title should try to incorporate the Patients, Interventions, Comparisons and Outcome (PICO).[ 3 ] The place of the study may be included in the title (if absolutely necessary), that is, if the patient characteristics (such as study population, socioeconomic conditions, or cultural practices) are expected to vary as per the country (or the place of the study) and have a bearing on the possible outcomes.[ 3 , 6 ] Lengthy titles can be boring and appear unfocused, whereas very short titles may not be representative of the contents of the article; hence, optimum length is required to ensure that the title explains the main theme and content of the manuscript.[ 4 , 5 , 9 ] Abbreviations (except the standard or commonly interpreted ones such as HIV, AIDS, DNA, RNA, CDC, FDA, ECG, and EEG) or acronyms should be avoided in the title, as a reader not familiar with them may skip such an article and nonstandard abbreviations may create problems in indexing the article.[ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 9 , 12 ] Also, too much of technical jargon or chemical formulas in the title may confuse the readers and the article may be skipped by them.[ 4 , 9 ] Numerical values of various parameters (stating study period or sample size) should also be avoided in the titles (unless deemed extremely essential).[ 4 ] It may be worthwhile to take an opinion from a impartial colleague before finalizing the title.[ 4 , 5 , 6 ] Thus, multiple factors (which are, at times, a bit conflicting or contrasting) need to be considered while formulating a title, and hence this should not be done in a hurry.[ 4 , 6 ] Many journals ask the authors to draft a “short title” or “running head” or “running title” for printing in the header or footer of the printed paper.[ 3 , 12 ] This is an abridged version of the main title of up to 40–50 characters, may have standard abbreviations, and helps the reader to navigate through the paper.[ 3 , 12 , 14 ]
Checklist for a good title
Table 1 gives a checklist/useful tips for drafting a good title for a research paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 12 ] Table 2 presents some of the titles used by the author of this article in his earlier research papers, and the appropriateness of the titles has been commented upon. As an individual exercise, the reader may try to improvise upon the titles (further) after reading the corresponding abstract and full paper.
Checklist/useful tips for drafting a good title for a research paper
Some titles used by author of this article in his earlier publications and remark/comment on their appropriateness
The Abstract
The details of the abstract are discussed under the subheadings of importance, types, drafting, and checklist.
Importance of the abstract
The abstract is a summary or synopsis of the full research paper and also needs to have similar characteristics like the title. It needs to be simple, direct, specific, functional, clear, unbiased, honest, concise, precise, self-sufficient, complete, comprehensive, scholarly, balanced, and should not be misleading.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 17 ] Writing an abstract is to extract and summarize (AB – absolutely, STR – straightforward, ACT – actual data presentation and interpretation).[ 17 ] The title and abstracts are the only sections of the research paper that are often freely available to the readers on the journal websites, search engines, and in many abstracting agencies/databases, whereas the full paper may attract a payment per view or a fee for downloading the pdf copy.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 14 ] The abstract is an independent and stand-alone (that is, well understood without reading the full paper) section of the manuscript and is used by the editor to decide the fate of the article and to choose appropriate reviewers.[ 2 , 7 , 10 , 12 , 13 ] Even the reviewers are initially supplied only with the title and the abstract before they agree to review the full manuscript.[ 7 , 13 ] This is the second most commonly read part of the manuscript, and therefore it should reflect the contents of the main text of the paper accurately and thus act as a “real trailer” of the full article.[ 2 , 7 , 11 ] The readers will go through the full paper only if they find the abstract interesting and relevant to their practice; else they may skip the paper if the abstract is unimpressive.[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] The abstract needs to highlight the selling point of the manuscript and succeed in luring the reader to read the complete paper.[ 3 , 7 ] The title and the abstract should be constructed using keywords (key terms/important words) from all the sections of the main text.[ 12 ] Abstracts are also used for submitting research papers to a conference for consideration for presentation (as oral paper or poster).[ 9 , 13 , 17 ] Grammatical and typographic errors reflect poorly on the quality of the abstract, may indicate carelessness/casual attitude on part of the author, and hence should be avoided at all times.[ 9 ]
Types of abstracts
The abstracts can be structured or unstructured. They can also be classified as descriptive or informative abstracts.
Structured and unstructured abstracts
Structured abstracts are followed by most journals, are more informative, and include specific subheadings/subsections under which the abstract needs to be composed.[ 1 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 , 17 , 18 ] These subheadings usually include context/background, objectives, design, setting, participants, interventions, main outcome measures, results, and conclusions.[ 1 ] Some journals stick to the standard IMRAD format for the structure of the abstracts, and the subheadings would include Introduction/Background, Methods, Results, And (instead of Discussion) the Conclusion/s.[ 1 , 2 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 17 , 18 ] Structured abstracts are more elaborate, informative, easy to read, recall, and peer-review, and hence are preferred; however, they consume more space and can have same limitations as an unstructured abstract.[ 7 , 9 , 18 ] The structured abstracts are (possibly) better understood by the reviewers and readers. Anyway, the choice of the type of the abstract and the subheadings of a structured abstract depend on the particular journal style and is not left to the author's wish.[ 7 , 10 , 12 ] Separate subheadings may be necessary for reporting meta-analysis, educational research, quality improvement work, review, or case study.[ 1 ] Clinical trial abstracts need to include the essential items mentioned in the CONSORT (Consolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials) guidelines.[ 7 , 9 , 14 , 19 ] Similar guidelines exist for various other types of studies, including observational studies and for studies of diagnostic accuracy.[ 20 , 21 ] A useful resource for the above guidelines is available at www.equator-network.org (Enhancing the QUAlity and Transparency Of health Research). Unstructured (or non-structured) abstracts are free-flowing, do not have predefined subheadings, and are commonly used for papers that (usually) do not describe original research.[ 1 , 7 , 9 , 10 ]
The four-point structured abstract: This has the following elements which need to be properly balanced with regard to the content/matter under each subheading:[ 9 ]
Background and/or Objectives: This states why the work was undertaken and is usually written in just a couple of sentences.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 ] The hypothesis/study question and the major objectives are also stated under this subheading.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 ]
Methods: This subsection is the longest, states what was done, and gives essential details of the study design, setting, participants, blinding, sample size, sampling method, intervention/s, duration and follow-up, research instruments, main outcome measures, parameters evaluated, and how the outcomes were assessed or analyzed.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
Results/Observations/Findings: This subheading states what was found, is longer, is difficult to draft, and needs to mention important details including the number of study participants, results of analysis (of primary and secondary objectives), and include actual data (numbers, mean, median, standard deviation, “P” values, 95% confidence intervals, effect sizes, relative risks, odds ratio, etc.).[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
Conclusions: The take-home message (the “so what” of the paper) and other significant/important findings should be stated here, considering the interpretation of the research question/hypothesis and results put together (without overinterpreting the findings) and may also include the author's views on the implications of the study.[ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 ]
The eight-point structured abstract: This has the following eight subheadings – Objectives, Study Design, Study Setting, Participants/Patients, Methods/Intervention, Outcome Measures, Results, and Conclusions.[ 3 , 9 , 18 ] The instructions to authors given by the particular journal state whether they use the four- or eight-point abstract or variants thereof.[ 3 , 14 ]
Descriptive and Informative abstracts
Descriptive abstracts are short (75–150 words), only portray what the paper contains without providing any more details; the reader has to read the full paper to know about its contents and are rarely used for original research papers.[ 7 , 10 ] These are used for case reports, reviews, opinions, and so on.[ 7 , 10 ] Informative abstracts (which may be structured or unstructured as described above) give a complete detailed summary of the article contents and truly reflect the actual research done.[ 7 , 10 ]
Drafting a suitable abstract
It is important to religiously stick to the instructions to authors (format, word limit, font size/style, and subheadings) provided by the journal for which the abstract and the paper are being written.[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] Most journals allow 200–300 words for formulating the abstract and it is wise to restrict oneself to this word limit.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 22 ] Though some authors prefer to draft the abstract initially, followed by the main text of the paper, it is recommended to draft the abstract in the end to maintain accuracy and conformity with the main text of the paper (thus maintaining an easy linkage/alignment with title, on one hand, and the introduction section of the main text, on the other hand).[ 2 , 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 ] The authors should check the subheadings (of the structured abstract) permitted by the target journal, use phrases rather than sentences to draft the content of the abstract, and avoid passive voice.[ 1 , 7 , 9 , 12 ] Next, the authors need to get rid of redundant words and edit the abstract (extensively) to the correct word count permitted (every word in the abstract “counts”!).[ 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 13 ] It is important to ensure that the key message, focus, and novelty of the paper are not compromised; the rationale of the study and the basis of the conclusions are clear; and that the abstract is consistent with the main text of the paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 9 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 , 22 ] This is especially important while submitting a revision of the paper (modified after addressing the reviewer's comments), as the changes made in the main (revised) text of the paper need to be reflected in the (revised) abstract as well.[ 2 , 10 , 12 , 14 , 22 ] Abbreviations should be avoided in an abstract, unless they are conventionally accepted or standard; references, tables, or figures should not be cited in the abstract.[ 7 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 13 ] It may be worthwhile not to rush with the abstract and to get an opinion by an impartial colleague on the content of the abstract; and if possible, the full paper (an “informal” peer-review).[ 1 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 11 , 17 ] Appropriate “Keywords” (three to ten words or phrases) should follow the abstract and should be preferably chosen from the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) list of the U.S. National Library of Medicine ( https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/search ) and are used for indexing purposes.[ 2 , 3 , 11 , 12 ] These keywords need to be different from the words in the main title (the title words are automatically used for indexing the article) and can be variants of the terms/phrases used in the title, or words from the abstract and the main text.[ 3 , 12 ] The ICMJE (International Committee of Medical Journal Editors; http://www.icmje.org/ ) also recommends publishing the clinical trial registration number at the end of the abstract.[ 7 , 14 ]
Checklist for a good abstract
Table 3 gives a checklist/useful tips for formulating a good abstract for a research paper.[ 1 , 2 , 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 17 , 22 ]
Checklist/useful tips for formulating a good abstract for a research paper
Concluding Remarks
This review article has given a detailed account of the importance and types of titles and abstracts. It has also attempted to give useful hints for drafting an appropriate title and a complete abstract for a research paper. It is hoped that this review will help the authors in their career in medical writing.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgement
The author thanks Dr. Hemant Deshmukh - Dean, Seth G.S. Medical College & KEM Hospital, for granting permission to publish this manuscript.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example
Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example
Table of Contents

Research Paper Title
Research Paper Title is the name or heading that summarizes the main theme or topic of a research paper . It serves as the first point of contact between the reader and the paper, providing an initial impression of the content, purpose, and scope of the research . A well-crafted research paper title should be concise, informative, and engaging, accurately reflecting the key elements of the study while also capturing the reader’s attention and interest. The title should be clear and easy to understand, and it should accurately convey the main focus and scope of the research paper.
Examples of Research Paper Title
Here are some Good Examples of Research Paper Title:
- “Investigating the Relationship Between Sleep Duration and Academic Performance Among College Students”
- “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment: A Systematic Review”
- “The Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Interventions for Anxiety: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Exploring the Effects of Social Support on Mental Health in Patients with Chronic Illness”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy for Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial”
- “The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Consumer Behavior: A Systematic Review”
- “Investigating the Link Between Personality Traits and Leadership Effectiveness”
- “The Effect of Parental Incarceration on Child Development: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Cultural Intelligence and Cross-Cultural Adaptation: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction for Chronic Pain Management”.
- “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health: A Meta-Analysis”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Global Crop Yields: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Exploring the Relationship between Parental Involvement and Academic Achievement in Elementary School Students”
- “The Ethics of Genetic Editing: A Review of Current Research and Implications for Society”
- “Understanding the Role of Gender in Leadership: A Comparative Study of Male and Female CEOs”
- “The Effect of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial”
- “The Impacts of COVID-19 on Mental Health: A Cross-Cultural Comparison”
- “Assessing the Effectiveness of Online Learning Platforms: A Case Study of Coursera”
- “Exploring the Link between Employee Engagement and Organizational Performance”
- “The Effects of Income Inequality on Social Mobility: A Comparative Analysis of OECD Countries”
- “Exploring the Relationship Between Social Media Use and Mental Health in Adolescents”
- “The Impact of Climate Change on Crop Yield: A Case Study of Maize Production in Sub-Saharan Africa”
- “Examining the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Anxiety Disorders: A Meta-Analysis”
- “An Analysis of the Relationship Between Employee Job Satisfaction and Organizational Commitment”
- “Assessing the Impacts of Wilderness Areas on Local Economies: A Case Study of Yellowstone National Park”
- “The Role of Parental Involvement in Early Childhood Education: A Review of the Literature”
- “Investigating the Effects of Technology on Learning in Higher Education”
- “The Use of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Opportunities and Challenges”
- “A Study of the Relationship Between Personality Traits and Leadership Styles in Business Organizations”.
How to choose Research Paper Title
Choosing a research paper title is an important step in the research process. A good title can attract readers and convey the essence of your research in a concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to choose a research paper title:
- Be clear and concise: A good title should convey the main idea of your research in a clear and concise manner. Avoid using jargon or technical language that may be confusing to readers.
- Use keywords: Including keywords in your title can help readers find your paper when searching for related topics. Use specific, descriptive terms that accurately describe your research.
- Be descriptive: A descriptive title can help readers understand what your research is about. Use adjectives and adverbs to convey the main ideas of your research.
- Consider the audience : Think about the audience for your paper and choose a title that will appeal to them. If your paper is aimed at a specialized audience, you may want to use technical terms or jargon in your title.
- Avoid being too general or too specific : A title that is too general may not convey the specific focus of your research, while a title that is too specific may not be of interest to a broader audience. Strive for a title that accurately reflects the focus of your research without being too narrow or too broad.
- Make it interesting : A title that is interesting or provocative can capture the attention of readers and draw them into your research. Use humor, wordplay, or other creative techniques to make your title stand out.
- Seek feedback: Ask colleagues or advisors for feedback on your title. They may be able to offer suggestions or identify potential problems that you hadn’t considered.
Purpose of Research Paper Title
The research paper title serves several important purposes, including:
- Identifying the subject matter : The title of a research paper should clearly and accurately identify the topic or subject matter that the paper addresses. This helps readers quickly understand what the paper is about.
- Catching the reader’s attention : A well-crafted title can grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in reading the paper. This is particularly important in academic settings where there may be many papers on the same topic.
- Providing context: The title can provide important context for the research paper by indicating the specific area of study, the research methods used, or the key findings.
- Communicating the scope of the paper: A good title can give readers an idea of the scope and depth of the research paper. This can help them decide if the paper is relevant to their interests or research.
- Indicating the research question or hypothesis : The title can often indicate the research question or hypothesis that the paper addresses, which can help readers understand the focus of the research and the main argument or conclusion of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Title
The title of a research paper is an important component that can have several advantages, including:
- Capturing the reader’s attention : A well-crafted research paper title can grab the reader’s attention and encourage them to read further. A captivating title can also increase the visibility of the paper and attract more readers.
- Providing a clear indication of the paper’s focus: A well-written research paper title should clearly convey the main focus and purpose of the study. This helps potential readers quickly determine whether the paper is relevant to their interests.
- Improving discoverability: A descriptive title that includes relevant keywords can improve the discoverability of the research paper in search engines and academic databases, making it easier for other researchers to find and cite.
- Enhancing credibility : A clear and concise title can enhance the credibility of the research and the author. A title that accurately reflects the content of the paper can increase the confidence readers have in the research findings.
- Facilitating communication: A well-written research paper title can facilitate communication among researchers, enabling them to quickly and easily identify relevant studies and engage in discussions related to the topic.
- Making the paper easier to remember : An engaging and memorable research paper title can help readers remember the paper and its findings. This can be especially important in fields where researchers are constantly inundated with new information and need to quickly recall important studies.
- Setting expectations: A good research paper title can set expectations for the reader and help them understand what the paper will cover. This can be especially important for readers who are unfamiliar with the topic or the research area.
- Guiding research: A well-crafted research paper title can also guide future research by highlighting gaps in the current literature or suggesting new areas for investigation.
- Demonstrating creativity: A creative research paper title can demonstrate the author’s creativity and originality, which can be appealing to readers and other researchers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
- Open access
- Published: 10 March 2020
Research and trends in STEM education: a systematic review of journal publications
- Yeping Li 1 ,
- Ke Wang 2 ,
- Yu Xiao 1 &
- Jeffrey E. Froyd 3
International Journal of STEM Education volume 7 , Article number: 11 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
170k Accesses
159 Citations
5 Altmetric
Metrics details
With the rapid increase in the number of scholarly publications on STEM education in recent years, reviews of the status and trends in STEM education research internationally support the development of the field. For this review, we conducted a systematic analysis of 798 articles in STEM education published between 2000 and the end of 2018 in 36 journals to get an overview about developments in STEM education scholarship. We examined those selected journal publications both quantitatively and qualitatively, including the number of articles published, journals in which the articles were published, authorship nationality, and research topic and methods over the years. The results show that research in STEM education is increasing in importance internationally and that the identity of STEM education journals is becoming clearer over time.
Introduction
A recent review of 144 publications in the International Journal of STEM Education ( IJ - STEM ) showed how scholarship in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education developed between August 2014 and the end of 2018 through the lens of one journal (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ). The review of articles published in only one journal over a short period of time prompted the need to review the status and trends in STEM education research internationally by analyzing articles published in a wider range of journals over a longer period of time.
With global recognition of the growing importance of STEM education, we have witnessed the urgent need to support research and scholarship in STEM education (Li, 2014 , 2018a ). Researchers and educators have responded to this on-going call and published their scholarly work through many different publication outlets including journals, books, and conference proceedings. A simple Google search with the term “STEM,” “STEM education,” or “STEM education research” all returned more than 450,000,000 items. Such voluminous information shows the rapidly evolving and vibrant field of STEM education and sheds light on the volume of STEM education research. In any field, it is important to know and understand the status and trends in scholarship for the field to develop and be appropriately supported. This applies to STEM education.
Conducting systematic reviews to explore the status and trends in specific disciplines is common in educational research. For example, researchers surveyed the historical development of research in mathematics education (Kilpatrick, 1992 ) and studied patterns in technology usage in mathematics education (Bray & Tangney, 2017 ; Sokolowski, Li, & Willson, 2015 ). In science education, Tsai and his colleagues have conducted a sequence of reviews of journal articles to synthesize research trends in every 5 years since 1998 (i.e., 1998–2002, 2003–2007, 2008–2012, and 2013–2017), based on publications in three main science education journals including, Science Education , the International Journal of Science Education , and the Journal of Research in Science Teaching (e.g., Lin, Lin, Potvin, & Tsai, 2019 ; Tsai & Wen, 2005 ). Erduran, Ozdem, and Park ( 2015 ) reviewed argumentation in science education research from 1998 to 2014 and Minner, Levy, and Century ( 2010 ) reviewed inquiry-based science instruction between 1984 and 2002. There are also many literature reviews and syntheses in engineering and technology education (e.g., Borrego, Foster, & Froyd, 2015 ; Xu, Williams, Gu, & Zhang, 2019 ). All of these reviews have been well received in different fields of traditional disciplinary education as they critically appraise and summarize the state-of-art of relevant research in a field in general or with a specific focus. Both types of reviews have been conducted with different methods for identifying, collecting, and analyzing relevant publications, and they differ in terms of review aim and topic scope, time period, and ways of literature selection. In this review, we systematically analyze journal publications in STEM education research to overview STEM education scholarship development broadly and globally.
The complexity and ambiguity of examining the status and trends in STEM education research
A review of research development in a field is relatively straight forward, when the field is mature and its scope can be well defined. Unlike discipline-based education research (DBER, National Research Council, 2012 ), STEM education is not a well-defined field. Conducting a comprehensive literature review of STEM education research require careful thought and clearly specified scope to tackle the complexity naturally associated with STEM education. In the following sub-sections, we provide some further discussion.
Diverse perspectives about STEM and STEM education
STEM education as explicated by the term does not have a long history. The interest in helping students learn across STEM fields can be traced back to the 1990s when the US National Science Foundation (NSF) formally included engineering and technology with science and mathematics in undergraduate and K-12 school education (e.g., National Science Foundation, 1998 ). It coined the acronym SMET (science, mathematics, engineering, and technology) that was subsequently used by other agencies including the US Congress (e.g., United States Congress House Committee on Science, 1998 ). NSF also coined the acronym STEM to replace SMET (e.g., Christenson, 2011 ; Chute, 2009 ) and it has become the acronym of choice. However, a consensus has not been reached on the disciplines included within STEM.
To clarify its intent, NSF published a list of approved fields it considered under the umbrella of STEM (see http://bit.ly/2Bk1Yp5 ). The list not only includes disciplines widely considered under the STEM tent (called “core” disciplines, such as physics, chemistry, and materials research), but also includes disciplines in psychology and social sciences (e.g., political science, economics). However, NSF’s list of STEM fields is inconsistent with other federal agencies. Gonzalez and Kuenzi ( 2012 ) noted that at least two US agencies, the Department of Homeland Security and Immigration and Customs Enforcement, use a narrower definition that excludes social sciences. Researchers also view integration across different disciplines of STEM differently using various terms such as, multidisciplinary, interdisciplinary, and transdisciplinary (Vasquez, Sneider, & Comer, 2013 ). These are only two examples of the ambiguity and complexity in describing and specifying what constitutes STEM.
Multiple perspectives about the meaning of STEM education adds further complexity to determining the extent to which scholarly activity can be categorized as STEM education. For example, STEM education can be viewed with a broad and inclusive perspective to include education in the individual disciplines of STEM, i.e., science education, technology education, engineering education, and mathematics education, as well as interdisciplinary or cross-disciplinary combinations of the individual STEM disciplines (English, 2016 ; Li, 2014 ). On the other hand, STEM education can be viewed by others as referring only to interdisciplinary or cross-disciplinary combinations of the individual STEM disciplines (Honey, Pearson, & Schweingruber, 2014 ; Johnson, Peters-Burton, & Moore, 2015 ; Kelley & Knowles, 2016 ; Li, 2018a ). These multiple perspectives allow scholars to publish articles in a vast array and diverse journals, as long as journals are willing to take the position as connected with STEM education. At the same time, however, the situation presents considerable challenges for researchers intending to locate, identify, and classify publications as STEM education research. To tackle such challenges, we tried to find out what we can learn from prior reviews related to STEM education.
Guidance from prior reviews related to STEM education
A search for reviews of STEM education research found multiple reviews that could suggest approaches for identifying publications (e.g., Brown, 2012 ; Henderson, Beach, & Finkelstein, 2011 ; Kim, Sinatra, & Seyranian, 2018 ; Margot & Kettler, 2019 ; Minichiello, Hood, & Harkness, 2018 ; Mizell & Brown, 2016 ; Thibaut et al., 2018 ; Wu & Rau, 2019 ). The review conducted by Brown ( 2012 ) examined the research base of STEM education. He addressed the complexity and ambiguity by confining the review with publications in eight journals, two in each individual discipline, one academic research journal (e.g., the Journal of Research in Science Teaching ) and one practitioner journal (e.g., Science Teacher ). Journals were selected based on suggestions from some faculty members and K-12 teachers. Out of 1100 articles published in these eight journals from January 1, 2007, to October 1, 2010, Brown located 60 articles that authors self-identified as connected to STEM education. He found that the vast majority of these 60 articles focused on issues beyond an individual discipline and there was a research base forming for STEM education. In a follow-up study, Mizell and Brown ( 2016 ) reviewed articles published from January 2013 to October 2015 in the same eight journals plus two additional journals. Mizell and Brown used the same criteria to identify and include articles that authors self-identified as connected to STEM education, i.e., if the authors included STEM in the title or author-supplied keywords. In comparison to Brown’s findings, they found that many more STEM articles were published in a shorter time period and by scholars from many more different academic institutions. Taking together, both Brown ( 2012 ) and Mizell and Brown ( 2016 ) tended to suggest that STEM education mainly consists of interdisciplinary or cross-disciplinary combinations of the individual STEM disciplines, but their approach consisted of selecting a limited number of individual discipline-based journals and then selecting articles that authors self-identified as connected to STEM education.
In contrast to reviews on STEM education, in general, other reviews focused on specific issues in STEM education (e.g., Henderson et al., 2011 ; Kim et al., 2018 ; Margot & Kettler, 2019 ; Minichiello et al., 2018 ; Schreffler, Vasquez III, Chini, & James, 2019 ; Thibaut et al., 2018 ; Wu & Rau, 2019 ). For example, the review by Henderson et al. ( 2011 ) focused on instructional change in undergraduate STEM courses based on 191 conceptual and empirical journal articles published between 1995 and 2008. Margot and Kettler ( 2019 ) focused on what is known about teachers’ values, beliefs, perceived barriers, and needed support related to STEM education based on 25 empirical journal articles published between 2000 and 2016. The focus of these reviews allowed the researchers to limit the number of articles considered, and they typically used keyword searches of selected databases to identify articles on STEM education. Some researchers used this approach to identify publications from journals only (e.g., Henderson et al., 2011 ; Margot & Kettler, 2019 ; Schreffler et al., 2019 ), and others selected and reviewed publications beyond journals (e.g., Minichiello et al., 2018 ; Thibaut et al., 2018 ; Wu & Rau, 2019 ).
The discussion in this section suggests possible reasons contributing to the absence of a general literature review of STEM education research and development: (1) diverse perspectives in existence about STEM and STEM education that contribute to the difficulty of specifying a scope of literature review, (2) its short but rapid development history in comparison to other discipline-based education (e.g., science education), and (3) difficulties in deciding how to establish the scope of the literature review. With respect to the third reason, prior reviews have used one of two approaches to identify and select articles: (a) identifying specific journals first and then searching and selecting specific articles from these journals (e.g., Brown, 2012 ; Erduran et al., 2015 ; Mizell & Brown, 2016 ) and (b) conducting selected database searches with keywords based on a specific focus (e.g., Margot & Kettler, 2019 ; Thibaut et al., 2018 ). However, neither the first approach of selecting a limited number of individual discipline-based journals nor the second approach of selecting a specific focus for the review leads to an approach that provides a general overview of STEM education scholarship development based on existing journal publications.
Current review
Two issues were identified in setting the scope for this review.
What time period should be considered?
What publications will be selected for review?
Time period
We start with the easy one first. As discussed above, the acronym STEM did exist until the early 2000s. Although the existence of the acronym does not generate scholarship on student learning in STEM disciplines, it is symbolic and helps focus attention to efforts in STEM education. Since we want to examine the status and trends in STEM education, it is reasonable to start with the year 2000. Then, we can use the acronym of STEM as an identifier in locating specific research articles in a way as done by others (e.g., Brown, 2012 ; Mizell & Brown, 2016 ). We chose the end of 2018 as the end of the time period for our review that began during 2019.
Focusing on publications beyond individual discipline-based journals
As mentioned before, scholars responded to the call for scholarship development in STEM education with publications that appeared in various outlets and diverse languages, including journals, books, and conference proceedings. However, journal publications are typically credited and valued as one of the most important outlets for research exchange (e.g., Erduran et al., 2015 ; Henderson et al., 2011 ; Lin et al., 2019 ; Xu et al., 2019 ). Thus, in this review, we will also focus on articles published in journals in English.
The discourse above on the complexity and ambiguity regarding STEM education suggests that scholars may publish their research in a wide range of journals beyond individual discipline-based journals. To search and select articles from a wide range of journals, we thought about the approach of searching selected databases with keywords as other scholars used in reviewing STEM education with a specific focus. However, existing journals in STEM education do not have a long history. In fact, IJ-STEM is the first journal in STEM education that has just been accepted into the Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI) (Li, 2019a ). Publications in many STEM education journals are practically not available in several important and popular databases, such as the Web of Science and Scopus. Moreover, some journals in STEM education were not normalized due to a journal’s name change or irregular publication schedule. For example, the Journal of STEM Education was named as Journal of SMET Education when it started in 2000 in a print format, and the journal’s name was not changed until 2003, Vol 4 (3 and 4), and also went fully on-line starting 2004 (Raju & Sankar, 2003 ). A simple Google Scholar search with keywords will not be able to provide accurate information, unless you visit the journal’s website to check all publications over the years. Those added complexities prevented us from taking the database search as a viable approach. Thus, we decided to identify journals first and then search and select articles from these journals. Further details about the approach are provided in the “ Method ” section.
Research questions
Given a broader range of journals and a longer period of time to be covered in this review, we can examine some of the same questions as the IJ-STEM review (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ), but we do not have access to data on readership, articles accessed, or articles cited for the other journals selected for this review. Specifically, we are interested in addressing the following six research questions:
What were the status and trends in STEM education research from 2000 to the end of 2018 based on journal publications?
What were the patterns of publications in STEM education research across different journals?
Which countries or regions, based on the countries or regions in which authors were located, contributed to journal publications in STEM education?
What were the patterns of single-author and multiple-author publications in STEM education?
What main topics had emerged in STEM education research based on the journal publications?
What research methods did authors tend to use in conducting STEM education research?
Based on the above discussion, we developed the methods for this literature review to follow careful sequential steps to identify journals first and then identify and select STEM education research articles published in these journals from January 2000 to the end of 2018. The methods should allow us to obtain a comprehensive overview about the status and trends of STEM education research based on a systematic analysis of related publications from a broad range of journals and over a longer period of time.
Identifying journals
We used the following three steps to search and identify journals for inclusion:
We assumed articles on research in STEM education have been published in journals that involve more than one traditional discipline. Thus, we used Google to search and identify all education journals with their titles containing either two, three, or all four disciplines of STEM. For example, we did Google search of all the different combinations of three areas of science, mathematics, technology Footnote 1 , and engineering as contained in a journal’s title. In addition, we also searched possible journals containing the word STEAM in the title.
Since STEM education may be viewed as encompassing discipline-based education research, articles on STEM education research may have been published in traditional discipline-based education journals, such as the Journal of Research in Science Teaching . However, there are too many such journals. Yale’s Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning has listed 16 journals that publish articles spanning across undergraduate STEM education disciplines (see https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/FacultyResources/STEMjournals ). Thus, we selected from the list some individual discipline-based education research journals, and also added a few more common ones such as the Journal of Engineering Education .
Since articles on research in STEM education have appeared in some general education research journals, especially those well-established ones. Thus, we identified and selected a few of those journals that we noticed some publications in STEM education research.
Following the above three steps, we identified 45 journals (see Table 1 ).
Identifying articles
In this review, we will not discuss or define the meaning of STEM education. We used the acronym STEM (or STEAM, or written as the phrase of “science, technology, engineering, and mathematics”) as a term in our search of publication titles and/or abstracts. To identify and select articles for review, we searched all items published in those 45 journals and selected only those articles that author(s) self-identified with the acronym STEM (or STEAM, or written as the phrase of “science, technology, engineering, and mathematics”) in the title and/or abstract. We excluded publications in the sections of practices, letters to editors, corrections, and (guest) editorials. Our search found 798 publications that authors self-identified as in STEM education, identified from 36 journals. The remaining 9 journals either did not have publications that met our search terms or published in another language other than English (see the two separate lists in Table 1 ).
Data analysis
To address research question 3, we analyzed authorship to examine which countries/regions contributed to STEM education research over the years. Because each publication may have either one or multiple authors, we used two different methods to analyze authorship nationality that have been recognized as valuable from our review of IJ-STEM publications (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ). The first method considers only the corresponding author’s (or the first author, if no specific indication is given about the corresponding author) nationality and his/her first institution affiliation, if multiple institution affiliations are listed. Method 2 considers every author of a publication, using the following formula (Howard, Cole, & Maxwell, 1987 ) to quantitatively assign and estimate each author’s contribution to a publication (and thus associated institution’s productivity), when multiple authors are included in a publication. As an example, each publication is given one credit point. For the publication co-authored by two, the first author would be given 0.6 and the second author 0.4 credit point. For an article contributed jointly by three authors, the three authors would be credited with scores of 0.47, 0.32, and 0.21, respectively.
After calculating all the scores for each author of each paper, we added all the credit scores together in terms of each author’s country/region. For brevity, we present only the top 10 countries/regions in terms of their total credit scores calculated using these two different methods, respectively.
To address research question 5, we used the same seven topic categories identified and used in our review of IJ-STEM publications (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ). We tested coding 100 articles first to ensure the feasibility. Through test-coding and discussions, we found seven topic categories could be used to examine and classify all 798 items.
K-12 teaching, teacher, and teacher education in STEM (including both pre-service and in-service teacher education)
Post-secondary teacher and teaching in STEM (including faculty development, etc.)
K-12 STEM learner, learning, and learning environment
Post-secondary STEM learner, learning, and learning environments (excluding pre-service teacher education)
Policy, curriculum, evaluation, and assessment in STEM (including literature review about a field in general)
Culture and social and gender issues in STEM education
History, epistemology, and perspectives about STEM and STEM education
To address research question 6, we coded all 798 publications in terms of (1) qualitative methods, (2) quantitative methods, (3) mixed methods, and (4) non-empirical studies (including theoretical or conceptual papers, and literature reviews). We assigned each publication to only one research topic and one method, following the process used in the IJ-STEM review (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ). When there was more than one topic or method that could have been used for a publication, a decision was made in choosing and assigning a topic or a method. The agreement between two coders for all 798 publications was 89.5%. When topic and method coding discrepancies occurred, a final decision was reached after discussion.
Results and discussion
In the following sections, we report findings as corresponding to each of the six research questions.
The status and trends of journal publications in STEM education research from 2000 to 2018
Figure 1 shows the number of publications per year. As Fig. 1 shows, the number of publications increased each year beginning in 2010. There are noticeable jumps from 2015 to 2016 and from 2017 to 2018. The result shows that research in STEM education had grown significantly since 2010, and the most recent large number of STEM education publications also suggests that STEM education research gained its own recognition by many different journals for publication as a hot and important topic area.
The distribution of STEM education publications over the years
Among the 798 articles, there were 549 articles with the word “STEM” (or STEAM, or written with the phrase of “science, technology, engineering, and mathematics”) included in the article’s title or both title and abstract and 249 articles without such identifiers included in the title but abstract only. The results suggest that many scholars tended to include STEM in the publications’ titles to highlight their research in or about STEM education. Figure 2 shows the number of publications per year where publications are distinguished depending on whether they used the term STEM in the title or only in the abstract. The number of publications in both categories had significant increases since 2010. Use of the acronym STEM in the title was growing at a faster rate than using the acronym only in the abstract.
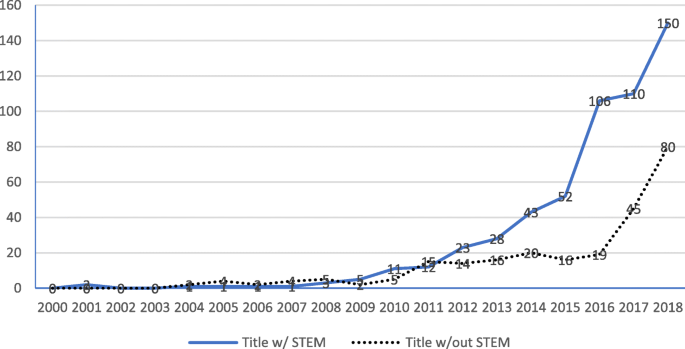
The trends of STEM education publications with vs. without STEM included in the title
Not all the publications that used the acronym STEM in the title and/or abstract reported on a study involving all four STEM areas. For each publication, we further examined the number of the four areas involved in the reported study.
Figure 3 presents the number of publications categorized by the number of the four areas involved in the study, breaking down the distribution of these 798 publications in terms of the content scope being focused on. Studies involving all four STEM areas are the most numerous with 488 (61.2%) publications, followed by involving one area (141, 17.7%), then studies involving both STEM and non-STEM (84, 10.5%), and finally studies involving two or three areas of STEM (72, 9%; 13, 1.6%; respectively). Publications that used the acronym STEAM in either the title or abstract were classified as involving both STEM and non-STEM. For example, both of the following publications were included in this category.
Dika and D’Amico ( 2016 ). “Early experiences and integration in the persistence of first-generation college students in STEM and non-STEM majors.” Journal of Research in Science Teaching , 53 (3), 368–383. (Note: this article focused on early experience in both STEM and Non-STEM majors.)
Sochacka, Guyotte, and Walther ( 2016 ). “Learning together: A collaborative autoethnographic exploration of STEAM (STEM+ the Arts) education.” Journal of Engineering Education , 105 (1), 15–42. (Note: this article focused on STEAM (both STEM and Arts).)
Publication distribution in terms of content scope being focused on. (Note: 1=single subject of STEM, 2=two subjects of STEM, 3=three subjects of STEM, 4=four subjects of STEM, 5=topics related to both STEM and non-STEM)
Figure 4 presents the number of publications per year in each of the five categories described earlier (category 1, one area of STEM; category 2, two areas of STEM; category 3, three areas of STEM; category 4, four areas of STEM; category 5, STEM and non-STEM). The category that had grown most rapidly since 2010 is the one involving all four areas. Recent growth in the number of publications in category 1 likely reflected growing interest of traditional individual disciplinary based educators in developing and sharing multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary scholarship in STEM education, as what was noted recently by Li and Schoenfeld ( 2019 ) with publications in IJ-STEM.
Publication distribution in terms of content scope being focused on over the years
Patterns of publications across different journals
Among the 36 journals that published STEM education articles, two are general education research journals (referred to as “subject-0”), 12 with their titles containing one discipline of STEM (“subject-1”), eight with journal’s titles covering two disciplines of STEM (“subject-2”), six covering three disciplines of STEM (“subject-3”), seven containing the word STEM (“subject-4”), and one in STEAM education (“subject-5”).
Table 2 shows that both subject-0 and subject-1 journals were usually mature journals with a long history, and they were all traditional subscription-based journals, except the Journal of Pre - College Engineering Education Research , a subject-1 journal established in 2011 that provided open access (OA). In comparison to subject-0 and subject-1 journals, subject-2 and subject-3 journals were relatively newer but still had quite many years of history on average. There are also some more journals in these two categories that provided OA. Subject-4 and subject-5 journals had a short history, and most provided OA. The results show that well-established journals had tended to focus on individual disciplines or education research in general. Multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary education journals were started some years later, followed by the recent establishment of several STEM or STEAM journals.
Table 2 also shows that subject-1, subject-2, and subject-4 journals published approximately a quarter each of the publications. The number of publications in subject-1 journals is interested, because we selected a relatively limited number of journals in this category. There are many other journals in the subject-1 category (as well as subject-0 journals) that we did not select, and thus it is very likely that we did not include some STEM education articles published in subject-0 or subject-1 journals that we did not include in our study.
Figure 5 shows the number of publications per year in each of the five categories described earlier (subject-0 through subject-5). The number of publications per year in subject-5 and subject-0 journals did not change much over the time period of the study. On the other hand, the number of publications per year in subject-4 (all 4 areas), subject-1 (single area), and subject-2 journals were all over 40 by the end of the study period. The number of publications per year in subject-3 journals increased but remained less than 30. At first sight, it may be a bit surprising that the number of publications in STEM education per year in subject-1 journals increased much faster than those in subject-2 journals over the past few years. However, as Table 2 indicates these journals had long been established with great reputations, and scholars would like to publish their research in such journals. In contrast to the trend in subject-1 journals, the trend in subject-4 journals suggests that STEM education journals collectively started to gain its own identity for publishing and sharing STEM education research.
STEM education publication distribution across different journal categories over the years. (Note: 0=subject-0; 1=subject-1; 2=subject-2; 3=subject-3; 4=subject-4; 5=subject-5)
Figure 6 shows the number of STEM education publications in each journal where the bars are color-coded (yellow, subject-0; light blue, subject-1; green, subject-2; purple, subject-3; dark blue, subject-4; and black, subject-5). There is no clear pattern shown in terms of the overall number of STEM education publications across categories or journals, but very much individual journal-based performance. The result indicates that the number of STEM education publications might heavily rely on the individual journal’s willingness and capability of attracting STEM education research work and thus suggests the potential value of examining individual journal’s performance.
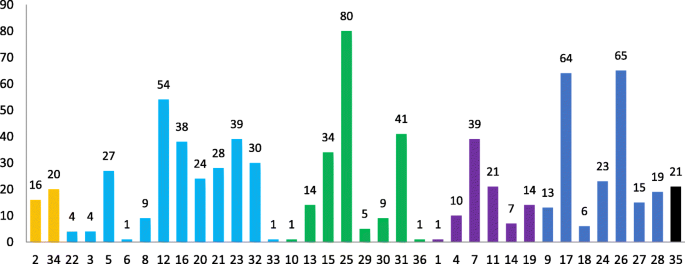
Publication distribution across all 36 individual journals across different categories with the same color-coded for journals in the same subject category
The top five journals in terms of the number of STEM education publications are Journal of Science Education and Technology (80 publications, journal number 25 in Fig. 6 ), Journal of STEM Education (65 publications, journal number 26), International Journal of STEM Education (64 publications, journal number 17), International Journal of Engineering Education (54 publications, journal number 12), and School Science and Mathematics (41 publications, journal number 31). Among these five journals, two journals are specifically on STEM education (J26, J17), two on two subjects of STEM (J25, J31), and one on one subject of STEM (J12).
Figure 7 shows the number of STEM education publications per year in each of these top five journals. As expected, based on earlier trends, the number of publications per year increased over the study period. The largest increase was in the International Journal of STEM Education (J17) that was established in 2014. As the other four journals were all established in or before 2000, J17’s short history further suggests its outstanding performance in attracting and publishing STEM education articles since 2014 (Li, 2018b ; Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ). The increase was consistent with the journal’s recognition as the first STEM education journal for inclusion in SSCI starting in 2019 (Li, 2019a ).
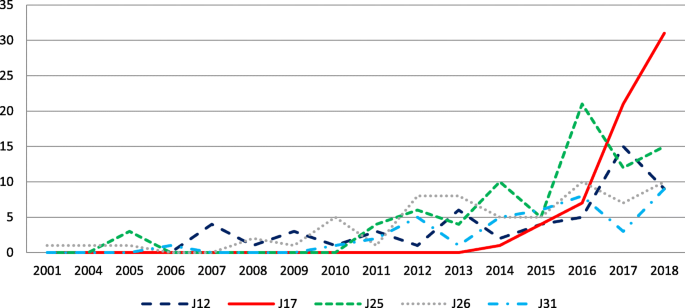
Publication distribution of selected five journals over the years. (Note: J12: International Journal of Engineering Education; J17: International Journal of STEM Education; J25: Journal of Science Education and Technology; J26: Journal of STEM Education; J31: School Science and Mathematics)
Top 10 countries/regions where scholars contributed journal publications in STEM education
Table 3 shows top countries/regions in terms of the number of publications, where the country/region was established by the authorship using the two different methods presented above. About 75% (depending on the method) of contributions were made by authors from the USA, followed by Australia, Canada, Taiwan, and UK. Only Africa as a continent was not represented among the top 10 countries/regions. The results are relatively consistent with patterns reported in the IJ-STEM study (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 )
Further examination of Table 3 reveals that the two methods provide not only fairly consistent results but also yield some differences. For example, Israel and Germany had more publication credit if only the corresponding author was considered, but South Korea and Turkey had more publication credit when co-authors were considered. The results in Table 3 show that each method has value when analyzing and comparing publications by country/region or institution based on authorship.
Recognizing that, as shown in Fig. 1 , the number of publications per year increased rapidly since 2010, Table 4 shows the number of publications by country/region over a 10-year period (2009–2018) and Table 5 shows the number of publications by country/region over a 5-year period (2014–2018). The ranks in Tables 3 , 4 , and 5 are fairly consistent, but that would be expected since the larger numbers of publications in STEM education had occurred in recent years. At the same time, it is interesting to note in Table 5 some changes over the recent several years with Malaysia, but not Israel, entering the top 10 list when either method was used to calculate author's credit.
Patterns of single-author and multiple-author publications in STEM education
Since STEM education differs from traditional individual disciplinary education, we are interested in determining how common joint co-authorship with collaborations was in STEM education articles. Figure 8 shows that joint co-authorship was very common among these 798 STEM education publications, with 83.7% publications with two or more co-authors. Publications with two, three, or at least five co-authors were highest, with 204, 181, and 157 publications, respectively.
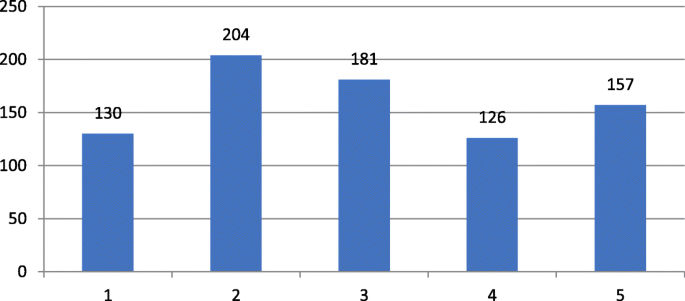
Number of publications with single or different joint authorship. (Note: 1=single author; 2=two co-authors; 3=three co-authors; 4=four co-authors; 5=five or more co-authors)
Figure 9 shows the number of publications per year using the joint authorship categories in Fig. 8 . Each category shows an increase consistent with the increase shown in Fig. 1 for all 798 publications. By the end of the time period, the number of publications with two, three, or at least five co-authors was the largest, which might suggest an increase in collaborations in STEM education research.
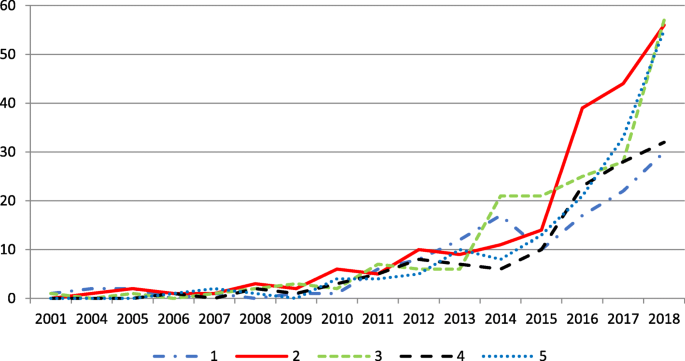
Publication distribution with single or different joint authorship over the years. (Note: 1=single author; 2=two co-authors; 3=three co-authors; 4=four co-authors; 5=five or more co-authors)
Co-authors can be from the same or different countries/regions. Figure 10 shows the number of publications per year by single authors (no collaboration), co-authors from the same country (collaboration in a country/region), and co-authors from different countries (collaboration across countries/regions). Each year the largest number of publications was by co-authors from the same country, and the number increased dramatically during the period of the study. Although the number of publications in the other two categories increased, the numbers of publications were noticeably fewer than the number of publications by co-authors from the same country.
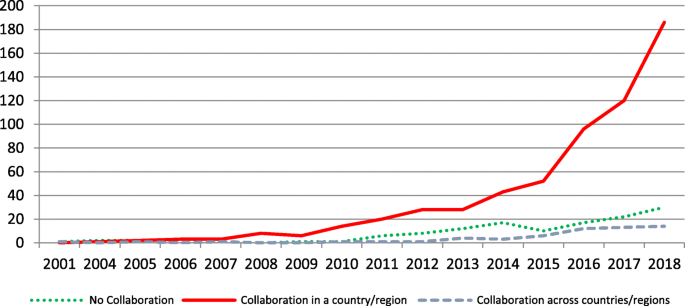
Publication distribution in authorship across different categories in terms of collaboration over the years
Published articles by research topics
Figure 11 shows the number of publications in each of the seven topic categories. The topic category of goals, policy, curriculum, evaluation, and assessment had almost half of publications (375, 47%). Literature reviews were included in this topic category, as providing an overview assessment of education and research development in a topic area or a field. Sample publications included in this category are listed as follows:
DeCoito ( 2016 ). “STEM education in Canada: A knowledge synthesis.” Canadian Journal of Science , Mathematics and Technology Education , 16 (2), 114–128. (Note: this article provides a national overview of STEM initiatives and programs, including success, criteria for effective programs and current research in STEM education.)
Ring-Whalen, Dare, Roehrig, Titu, and Crotty ( 2018 ). “From conception to curricula: The role of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics in integrated STEM units.” International Journal of Education in Mathematics Science and Technology , 6 (4), 343–362. (Note: this article investigates the conceptions of integrated STEM education held by in-service science teachers through the use of photo-elicitation interviews and examines how those conceptions were reflected in teacher-created integrated STEM curricula.)
Schwab et al. ( 2018 ). “A summer STEM outreach program run by graduate students: Successes, challenges, and recommendations for implementation.” Journal of Research in STEM Education , 4 (2), 117–129. (Note: the article details the organization and scope of the Foundation in Science and Mathematics Program and evaluates this program.)
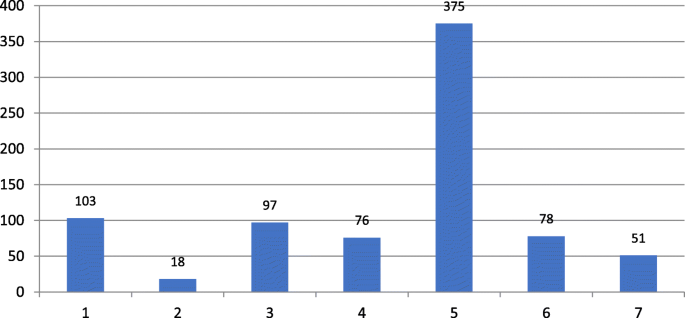
Frequencies of publications’ research topic distributions. (Note: 1=K-12 teaching, teacher and teacher education; 2=Post-secondary teacher and teaching; 3=K-12 STEM learner, learning, and learning environment; 4=Post-secondary STEM learner, learning, and learning environments; 5=Goals and policy, curriculum, evaluation, and assessment (including literature review); 6=Culture, social, and gender issues; 7=History, philosophy, Epistemology, and nature of STEM and STEM education)
The topic with the second most publications was “K-12 teaching, teacher and teacher education” (103, 12.9%), followed closely by “K-12 learner, learning, and learning environment” (97, 12.2%). The results likely suggest the research community had a broad interest in both teaching and learning in K-12 STEM education. The top three topics were the same in the IJ-STEM review (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ).
Figure 11 also shows there was a virtual tie between two topics with the fourth most cumulative publications, “post-secondary STEM learner & learning” (76, 9.5%) and “culture, social, and gender issues in STEM” (78, 9.8%), such as STEM identity, students’ career choices in STEM, and inclusion. This result is different from the IJ-STEM review (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ), where “post-secondary STEM teacher & teaching” and “post-secondary STEM learner & learning” were tied as the fourth most common topics. This difference is likely due to the scope of journals and the length of the time period being reviewed.
Figure 12 shows the number of publications per year in each topic category. As expected from the results in Fig. 11 the number of publications in topic category 5 (goals, policy, curriculum, evaluation, and assessment) was the largest each year. The numbers of publications in topic category 3 (K-12 learner, learning, and learning environment), 1 (K-12 teaching, teacher, and teacher education), 6 (culture, social, and gender issues in STEM), and 4 (post-secondary STEM learner and learning) were also increasing. Although Fig. 11 shows the number of publications in topic category 1 was slightly more than the number of publications in topic category 3 (see Fig. 11 ), the number of publications in topic category 3 was increasing more rapidly in recent years than its counterpart in topic category 1. This may suggest a more rapidly growing interest in K-12 STEM learner, learning, and learning environment. The numbers of publications in topic categories 2 and 7 were not increasing, but the number of publications in IJ-STEM in topic category 2 was notable (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ). It will be interesting to follow trends in the seven topic categories in the future.
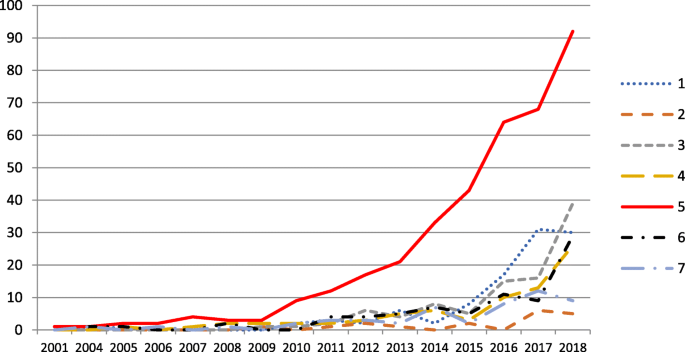
Publication distributions in terms of research topics over the years
Published articles by research methods
Figure 13 shows the number of publications per year by research methods in empirical studies. Publications with non-empirical studies are shown in a separate category. Although the number of publications in each of the four categories increased during the study period, there were many more publications presenting empirical studies than those without. For those with empirical studies, the number of publications using quantitative methods increased most rapidly in recent years, followed by qualitative and then mixed methods. Although there were quite many publications with non-empirical studies (e.g., theoretical or conceptual papers, literature reviews) during the study period, the increase of the number of publications in this category was noticeably less than empirical studies.
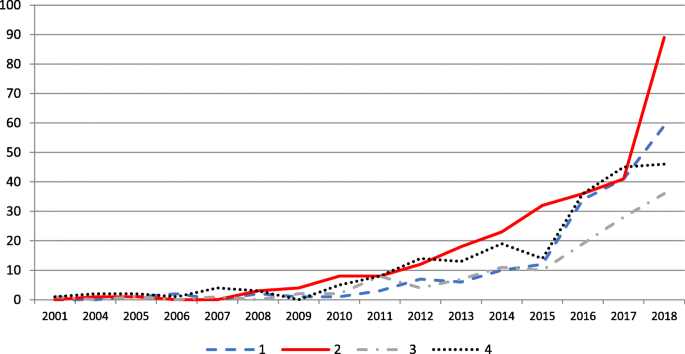
Publication distributions in terms of research methods over the years. (Note: 1=qualitative, 2=quantitative, 3=mixed, 4=Non-empirical)
Concluding remarks
The systematic analysis of publications that were considered to be in STEM education in 36 selected journals shows tremendous growth in scholarship in this field from 2000 to 2018, especially over the past 10 years. Our analysis indicates that STEM education research has been increasingly recognized as an important topic area and studies were being published across many different journals. Scholars still hold diverse perspectives about how research is designated as STEM education; however, authors have been increasingly distinguishing their articles with STEM, STEAM, or related words in the titles, abstracts, and lists of keywords during the past 10 years. Moreover, our systematic analysis shows a dramatic increase in the number of publications in STEM education journals in recent years, which indicates that these journals have been collectively developing their own professional identity. In addition, the International Journal of STEM Education has become the first STEM education journal to be accepted in SSCI in 2019 (Li, 2019a ). The achievement may mark an important milestone as STEM education journals develop their own identity for publishing and sharing STEM education research.
Consistent with our previous reviews (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ; Li, Wang, & Xiao, 2019 ), the vast majority of publications in STEM education research were contributed by authors from the USA, where STEM and STEAM education originated, followed by Australia, Canada, and Taiwan. At the same time, authors in some countries/regions in Asia were becoming very active in the field over the past several years. This trend is consistent with findings from the IJ-STEM review (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ). We certainly hope that STEM education scholarship continues its development across all five continents to support educational initiatives and programs in STEM worldwide.
Our analysis has shown that collaboration, as indicated by publications with multiple authors, has been very common among STEM education scholars, as that is often how STEM education distinguishes itself from the traditional individual disciplinary based education. Currently, most collaborations occurred among authors from the same country/region, although collaborations across cross-countries/regions were slowly increasing.
With the rapid changes in STEM education internationally (Li, 2019b ), it is often difficult for researchers to get an overall sense about possible hot topics in STEM education especially when STEM education publications appeared in a vast array of journals across different fields. Our systematic analysis of publications has shown that studies in the topic category of goals, policy, curriculum, evaluation, and assessment have been the most prevalent, by far. Our analysis also suggests that the research community had a broad interest in both teaching and learning in K-12 STEM education. These top three topic categories are the same as in the IJ-STEM review (Li, Froyd, & Wang, 2019 ). Work in STEM education will continue to evolve and it will be interesting to review the trends in another 5 years.
Encouraged by our recent IJ-STEM review, we began this review with an ambitious goal to provide an overview of the status and trends of STEM education research. In a way, this systematic review allowed us to achieve our initial goal with a larger scope of journal selection over a much longer period of publication time. At the same time, there are still limitations, such as the decision to limit the number of journals from which we would identify publications for analysis. We understand that there are many publications on STEM education research that were not included in our review. Also, we only identified publications in journals. Although this is one of the most important outlets for scholars to share their research work, future reviews could examine publications on STEM education research in other venues such as books, conference proceedings, and grant proposals.
Availability of data and materials
The data and materials used and analyzed for the report are publicly available at the various journal websites.
Journals containing the word "computers" or "ICT" appeared automatically when searching with the word "technology". Thus, the word of "computers" or "ICT" was taken as equivalent to "technology" if appeared in a journal's name.
Abbreviations
Information and Communications Technology
International Journal of STEM Education
Kindergarten–Grade 12
Science, Mathematics, Engineering, and Technology
Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics
Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics
Borrego, M., Foster, M. J., & Froyd, J. E. (2015). What is the state of the art of systematic review in engineering education? Journal of Engineering Education, 104 (2), 212–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/jee.20069 .
Article Google Scholar
Bray, A., & Tangney, B. (2017). Technology usage in mathematics education research – a systematic review of recent trends. Computers & Education, 114 , 255–273.
Brown, J. (2012). The current status of STEM education research. Journal of STEM Education: Innovations & Research, 13 (5), 7–11.
Google Scholar
Christenson, J. (2011). Ramaley coined STEM term now used nationwide . Winona Daily News Retrieved from http://www.winonadailynews.com/news/local/article_457afe3e-0db3-11e1-abe0-001cc4c03286.html Accessed on 16 Jan 2018.
Chute, E. (2009). STEM education is branching out . Pittsburgh Post-Gazette Feb 9, 2009. https://www.post-gazette.com/news/education/2009/02/10/STEM-education-is-branching-out/stories/200902100165 Accessed on 2 Jan 2020.
DeCoito, I. (2016). STEM education in Canada: A knowledge synthesis. Canadian Journal of Science, Mathematics and Technology Education, 16 (2), 114–128.
Dika, S. L., & D'Amico, M. M. (2016). Early experiences and integration in the persistence of first-generation college students in STEM and non-STEM majors. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 53 (3), 368–383.
English, L. D. (2016). STEM education K-12: Perspectives on integration. International Journal of STEM Education, 3 , 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s4059%204-016-0036-1 .
Erduran, S., Ozdem, Y., & Park, J.-Y. (2015). Research trends on argumentation in science education: A journal content analysis from 1998-2014. International Journal of STEM Education, 2 , 5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-015-0020-1 .
Gonzalez, H. B. & Kuenzi, J. J. (2012). Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) education: A primer. CRS report for congress, R42642, https://fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/R42642.pdf Accessed on 2 Jan 2020.
Henderson, C., Beach, A., & Finkelstein, N. (2011). Facilitating change in undergraduate STEM instructional practices: An analytic review of the literature. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 48 (8), 952–984.
Honey, M., Pearson, G., & Schweingruber, A. (2014). STEM integration in K-12 education: Status, prospects, and an agenda for research . Washington: National Academies Press.
Howard, G. S., Cole, D. A., & Maxwell, S. E. (1987). Research productivity in psychology based on publication in the journals of the American Psychological Association. American Psychologist, 42 (11), 975–986.
Johnson, C. C., Peters-Burton, E. E., & Moore, T. J. (2015). STEM roadmap: A framework for integration . London: Taylor & Francis.
Book Google Scholar
Kelley, T. R., & Knowles, J. G. (2016). A conceptual framework for integrated STEM education. International Journal of STEM Education, 3 , 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-016-0046-z .
Kilpatrick, J. (1992). A history of research in mathematics education. In D. A. Grouws (Ed.), Handbook of research on mathematics teaching and learning (pp. 3–38). New York: Macmillan.
Kim, A. Y., Sinatra, G. M., & Seyranian, V. (2018). Developing a STEM identity among young women: A social identity perspective. Review of Educational Research, 88 (4), 589–625.
Li, Y. (2014). International journal of STEM education – a platform to promote STEM education and research worldwide. International Journal of STEM Education, 1 , 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/2196-7822-1-1 .
Li, Y. (2018a). Journal for STEM education research – promoting the development of interdisciplinary research in STEM education. Journal for STEM Education Research, 1 (1–2), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41979-018-0009-z .
Li, Y. (2018b). Four years of development as a gathering place for international researchers and readers in STEM education. International Journal of STEM Education, 5 , 54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-018-0153-0 .
Li, Y. (2019a). Five years of development in pursuing excellence in quality and global impact to become the first journal in STEM education covered in SSCI. International Journal of STEM Education, 6 , 42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-019-0198-8 .
Li, Y. (2019b). STEM education research and development as a rapidly evolving and international field. 数学教育学报(Journal of Mathematics Education), 28 (3), 42–44.
Li, Y., Froyd, J. E., & Wang, K. (2019). Learning about research and readership development in STEM education: A systematic analysis of the journal’s publications from 2014 to 2018. International Journal of STEM Education, 6 , 19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-019-0176-1 .
Li, Y., & Schoenfeld, A. H. (2019). Problematizing teaching and learning mathematics as ‘given’ in STEM education. International Journal of STEM Education, 6 , 44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-019-0197-9 .
Li, Y., Wang, K., & Xiao, Y. (2019). Exploring the status and development trends of STEM education research: A review of research articles in selected journals published between 2000 and 2018. 数学教育学报(Journal of Mathematics Education), 28 (3), 45–52.
Lin, T.-J., Lin, T.-C., Potvin, P., & Tsai, C.-C. (2019). Research trends in science education from 2013 to 2017: A systematic content analysis of publications in selected journals. International Journal of Science Education, 41 (3), 367–387.
Margot, K. C., & Kettler, T. (2019). Teachers’ perception of STEM integration and education: A systematic literature review. International Journal of STEM Education, 6 , 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-018-0151-2 .
Minichiello, A., Hood, J. R., & Harkness, D. S. (2018). Bring user experience design to bear on STEM education: A narrative literature review. Journal for STEM Education Research, 1 (1–2), 7–33.
Minner, D. D., Levy, A. J., & Century, J. (2010). Inquiry-based science instruction – what is it and does it matter? Results from a research synthesis years 1984 to 2002. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 47 (4), 474–496.
Mizell, S., & Brown, S. (2016). The current status of STEM education research 2013-2015. Journal of STEM Education: Innovations & Research, 17 (4), 52–56.
National Research Council. (2012). Discipline-based education research: Understanding and improving learning in undergraduate science and engineering . Washington DC: National Academies Press.
National Science Foundation (1998). Information technology: Its impact on undergraduate education in science, mathematics, engineering, and technology. (NSF 98–82), April 18–20, 1996. http://www.nsf.gov/cgi-bin/getpub?nsf9882 Accessed 16 Jan 2018.
Raju, P. K., & Sankar, C. S. (2003). Editorial. Journal of STEM Education: Innovations & Research, 4 (3&4), 2.
Ring-Whalen, E., Dare, E., Roehrig, G., Titu, P., & Crotty, E. (2018). From conception to curricula: The role of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics in integrated STEM units. International Journal of Education in Mathematics, Science and Technology, 6 (4), 343–362.
Schreffler, J., Vasquez III, E., Chini, J., & James, W. (2019). Universal design for learning in postsecondary STEM education for students with disabilities: A systematic literature review. International Journal of STEM Education, 6 , 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-019-0161-8 .
Schwab, D. B., Cole, L. W., Desai, K. M., Hemann, J., Hummels, K. R., & Maltese, A. V. (2018). A summer STEM outreach program run by graduate students: Successes, challenges, and recommendations for implementation. Journal of Research in STEM Education, 4 (2), 117–129.
Sochacka, N. W., Guyotte, K. W., & Walther, J. (2016). Learning together: A collaborative autoethnographic exploration of STEAM (STEM+ the Arts) education. Journal of Engineering Education, 105 (1), 15–42.
Sokolowski, A., Li, Y., & Willson, V. (2015). The effects of using exploratory computerized environments in grades 1 to 8 mathematics: A meta-analysis of research. International Journal of STEM Education, 2 , 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-015-0022-z .
Thibaut, L., Ceuppens, S., De Loof, H., De Meester, J., Goovaerts, L., Struyf, A., Pauw, J. B., Dehaene, W., Deprez, J., De Cock, M., Hellinckx, L., Knipprath, H., Langie, G., Struyven, K., Van de Velde, D., Van Petegem, P., & Depaepe, F. (2018). Integrated STEM education: A systematic review of instructional practices in secondary education. European Journal of STEM Education, 3 (1), 2.
Tsai, C. C., & Wen, L. M. C. (2005). Research and trends in science education from 1998 to 2002: A content analysis of publication in selected journals. International Journal of Science Education, 27 (1), 3–14.
United States Congress House Committee on Science. (1998). The state of science, math, engineering, and technology (SMET) education in America, parts I-IV, including the results of the Third International Mathematics and Science Study (TIMSS): hearings before the Committee on Science, U.S. House of Representatives, One Hundred Fifth Congress, first session, July 23, September 24, October 8 and 29, 1997. Washington: U.S. G.P.O.
Vasquez, J., Sneider, C., & Comer, M. (2013). STEM lesson essentials, grades 3–8: Integrating science, technology, engineering, and mathematics . Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann.
Wu, S. P. W., & Rau, M. A. (2019). How students learn content in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) through drawing activities. Educational Psychology Review . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-019-09467-3 .
Xu, M., Williams, P. J., Gu, J., & Zhang, H. (2019). Hotspots and trends of technology education in the International Journal of Technology and Design Education: 2000-2018. International Journal of Technology and Design Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-019-09508-6 .
Download references
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, 77843-4232, USA
Yeping Li & Yu Xiao
Nicholls State University, Thibodaux, LA, 70310, USA
Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 43210, USA
Jeffrey E. Froyd
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
YL conceptualized the study and drafted the manuscript. KW and YX contributed with data collection, coding, and analyses. JEF reviewed drafts and contributed to manuscript revisions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yeping Li .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Li, Y., Wang, K., Xiao, Y. et al. Research and trends in STEM education: a systematic review of journal publications. IJ STEM Ed 7 , 11 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00207-6
Download citation
Received : 10 February 2020
Accepted : 12 February 2020
Published : 10 March 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-020-00207-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Journal publication
- Literature review
- STEM education research
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
More than half of Americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out

A majority of Americans say they are closely following news about the 2024 U.S. presidential election, a slightly higher share than in April 2020. At the same time, many people already say they are worn out by so much coverage of the campaign and candidates, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted this April.
To examine Americans’ habits and attitudes toward political and election news and information, Pew Research Center surveyed 8,709 U.S. adults from April 8 to 14, 2024.
Everyone who completed the survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The surveys are weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts, its primary funder. This is the latest analysis in Pew Research Center’s ongoing investigation of the state of news, information and journalism in the digital age, a research program funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts, with generous support from the John S. and James L. Knight Foundation.
How closely Americans follow election news
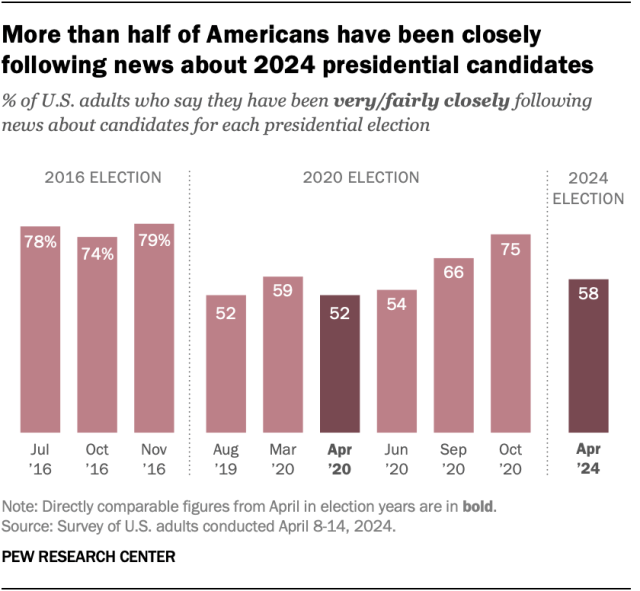
More than half of Americans (58%) say they are following news about candidates for the 2024 presidential election very or fairly closely. Another 28% say they aren’t following it too closely, and 13% aren’t following it closely at all.
The share of Americans who are closely following election news is slightly higher now than it was in April 2020 (52%). In October 2020, however, that share increased to 75%.
This year, Republicans and independents who lean toward the Republican Party are slightly more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say they are closely following election news (64% vs. 58%).
As in past presidential elections, older adults are more likely than younger adults to say they are closely following news about the candidates. Roughly eight-in-ten U.S. adults ages 65 and older (82%) currently say this, compared with 68% of those ages 50 to 64, 48% of those ages 30 to 49, and only 34% of those ages 18 to 29.
Fatigue over election coverage
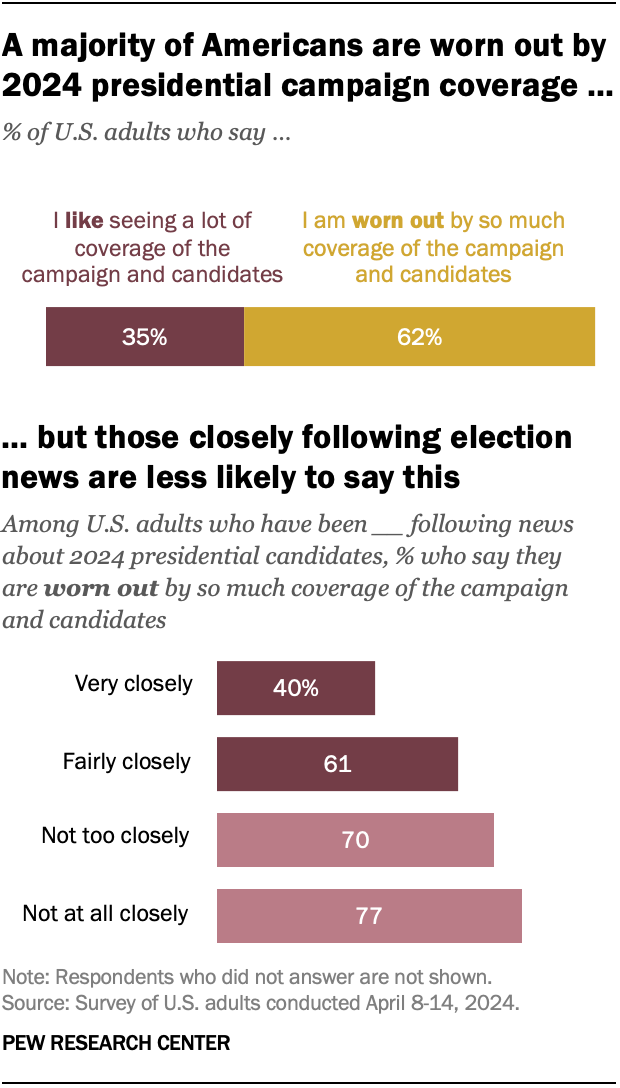
Although many Americans are following news about the 2024 presidential candidates, they are also experiencing fatigue over election coverage. About six-in-ten U.S. adults (62%) already say they are worn out by so much coverage of the campaign and candidates, while 35% say they like seeing a lot of this coverage.
This is similar to the share of Americans who said they felt worn out at later points in the last two presidential election years. In June and July 2016 , 59% of Americans said they felt worn out, and in October 2020 , 61% felt this way.
Americans who are following election news closely are less likely than those who aren’t to be worn out by election coverage. Four-in-ten Americans who say they follow news about candidates very closely say they are worn out by so much coverage, compared with 77% of those who say they don’t follow it closely at all.
Republicans are slightly less likely than Democrats to say they are worn out by election coverage (58% vs. 66%). This gap is driven by conservative Republicans (55%), who are less likely than moderate or liberal Republicans (65%) to feel worn out.
How Americans come across election news
Americans are more likely to say they mostly get political news because they happen to come across it (57%) than because they are looking for it (42%).
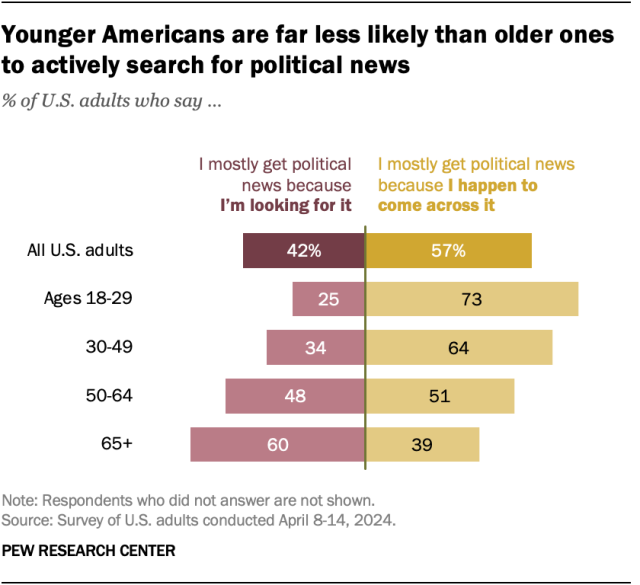
However, there are striking differences on this question by age. Just a quarter of Americans ages 18 to 29 say they mostly get political news because they are looking for it, compared with 60% of those 65 and older – a gap of 35 percentage points.
Those who say they closely follow news about the 2024 presidential election are also far more likely to actively seek out political news. About six-in-ten U.S. adults who closely follow election news (58%) say they mostly get political news this way, compared with 18% of those who are not closely following election news.
Republicans and Democrats are equally likely to say they mostly get political news because they look for it (44% vs. 43%). However, independents who do not lean toward either party (21%) are about half as likely to say this.
Sources of election news
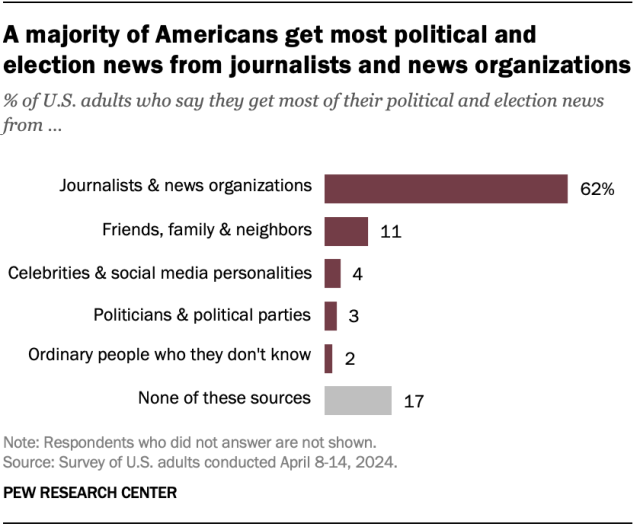
We also asked what type of sources Americans get most of their political and election news from. A majority of U.S. adults (62%) say they get most of this news from journalists and news organizations. (The question did not ask how people access that news , such as through TV, print, news websites or social media.)
Around one-in-ten Americans (11%) say they get most political and election news from friends, family and neighbors. Smaller shares say they get most of this news from celebrities and social media personalities (4%), politicians and political parties (3%), and ordinary people they don’t know (2%). An additional 17% say they don’t get most of their political or election news from any of these sources.
There are a few differences in election news sources by Americans’ age and political party:
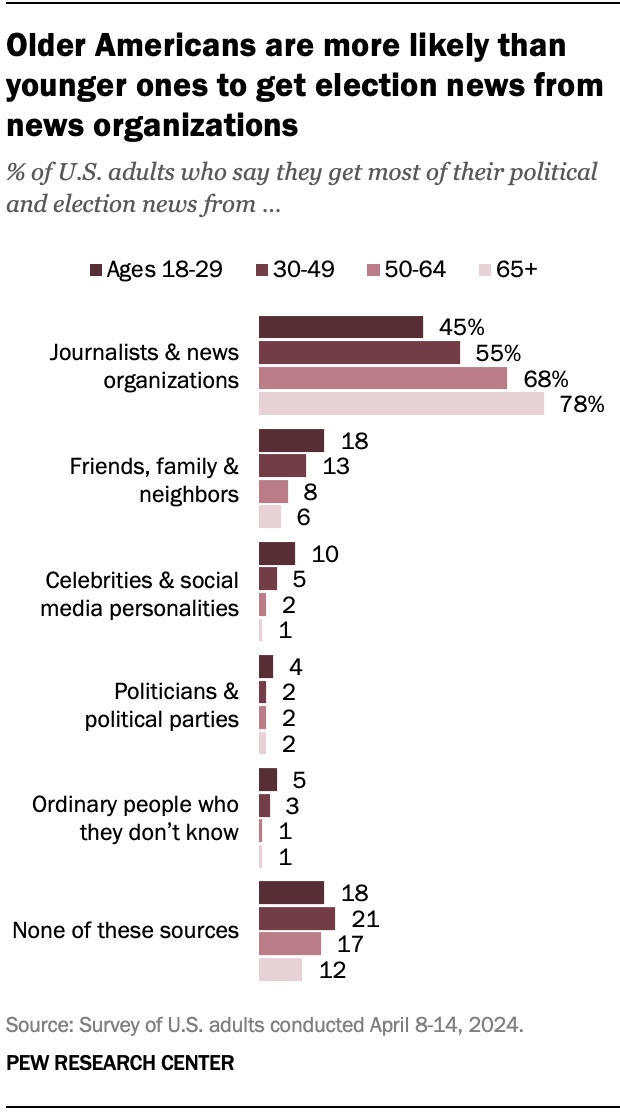
- Older Americans are far more likely than younger ones to say they get most political and election news from journalists and news organizations. Around three-quarters of Americans ages 65 and older (78%) say this, compared with 68% of those ages 50 to 64, 55% of those 30 to 49, and 45% of those 18 to 29.
- Adults under 30 are significantly more likely than those 65 and older to say they get most of this news from celebrities and social media personalities (10% vs. 1%). They are also more likely to get this news from friends, family and neighbors (18% vs. 6%).
- Democrats are slightly more likely than Republicans to say they get most political and election news from journalists and news organizations (69% vs. 59%).
- Republicans are slightly more likely than Democrats to say they don’t get most political or election news from any of these sources (20% vs. 12%).
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology . Research Assistant Emily Tomasik contributed to this analysis.
- Election 2024
- Election News
- News Coverage
- Politics & Media
Kirsten Eddy is a senior researcher focusing on news and information at Pew Research Center .
Two-thirds of U.S. adults say they’ve seen their own news sources report facts meant to favor one side
A growing share of voters say it’s important to them to hear from the trump and biden campaigns, americans are following news about presidential candidates much less closely than covid-19 news, black and white democrats differ in their media diets, assessments of primaries, 5 key findings from our latest election news pathways survey, from impeachment to the democratic race, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Science and Technology Directorate
- IRD Strategic Plan Prepares DHS for Future Homeland Security Challenges
News Release: Innovation, Research and Development Strategic Plan Prepares DHS for Future Homeland Security Challenges
For immediate release s&t public affairs , 202-286-9047.
Plan will prepare DHS to meet emerging technological needs and maximize strategic impact.
WASHINGTON - The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) released the first-ever department-wide Innovation, Research and Development (IRD) Strategic Plan , articulating key investment goals over the next seven fiscal years. Developed at the direction of Secretary Alejandro N. Mayorkas, the Strategic Plan serves as a blueprint for DHS to keep pace with technology by leveraging research and development to address homeland security challenges.
“This visionary roadmap, informed by scientific efforts, will empower DHS and its components to reduce risks to the homeland through optimized innovation, research and development investments,” said Dr. Dimitri Kusnezov, DHS Under Secretary for Science and Technology. “The technologies resulting from our IRD investments play a critical role in equipping the Department’s front-line operators with necessary tools to outpace our adversaries and enhance our preparedness and response capabilities.”
In 2022, Secretary Mayorkas tasked the DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) with examining DHS’s execution of research and development (R&D), including through developing a coordinated strategy focused on areas for long-term Departmental research. The resulting IRD Strategic Plan will help the Department and its partners make coordinated, integrated investments. In addition to capturing current IRD efforts already underway – compiling data from every DHS component and office – it provides an overview of complementary efforts led by federal, state, local, tribal, territorial, nongovernmental and private sector entities.
From this analysis of common research fields, the plan highlights eight Strategic Priority Research Areas (SPRAs) and future capabilities that DHS needs across its missions. The SPRAs will enhance the coordination of R&D across DHS while giving a demand signal for industry, interagency, academic, and international communities about future partnership opportunities. The Strategic Priority Research Areas for Fiscal Years 2024-2030 are:
- Advanced Sensing – next-generation sensor capabilities to provide enhanced detection performance against a broad spectrum of threats.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Autonomous Systems – automated technologies to provide predictions, recommendations, or decisions across a wide variety of operating environments, including means to deal with adversarial AI.
- Biotechnology – augmented capabilities to predict, detect, and defend against current and emerging bioagents and biotechnologies of concern.
- Climate Change – technologies to strengthen climate adaptation/resilience, improve equity, protect critical infrastructure, and reduce carbon emissions.
- Communications and Networking – enhanced communications and networking capabilities, while maintaining security and resiliency.
- Cybersecurity – enhanced resiliency, protection, and operational assurance across data, software, hardware, and communications networks.
- Data Integration, Analytics, Modeling and Simulation – enhanced, integrated data ecosystems, analytics, and modeling to enable better and more accurate data-driven insights, predictions, and decisions.
- Digital Identity and Trust – enhanced capabilities to establish and verify both individuals’ identities and the validity, integrity, and privacy of associated data.
In collaboration with stakeholders from across DHS, S&T is advancing implementation of the Strategic Plan by developing IRD investment roadmaps for each SPRA. These roadmaps will inform the Department’s budget process for FY 2027 and beyond.
More information about the IRD Strategic Plan and its priorities can be found at DHS IRD Strategic Plan FY24-30 | Homeland Security .
- Science and Technology
- Strategic Plan
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Scientists identify mechanism behind drug resistance in malaria parasite
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Peter Dedon
- Antimicrobial Resistance Interdisciplinary Research Group
- Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART)
- Department of Biological Engineering
Related Topics
- Drug resistance
- Antibiotics
- Biological engineering
- Drug development
- International initiatives
- Collaboration
Related Articles

Satellite-based method measures carbon in peat bogs

Newly discovered bacterial communication system aids antimicrobial resistance

SMART launches research group to advance AI, automation, and the future of work

A novel combination therapy counters antibiotic-resistant Mycobacterium abscessus infections
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

Noubar Afeyan PhD ’87 gives new MIT graduates a special assignment
Read full story →

President Sally Kornbluth’s charge to the Class of 2024

Commencement address by Noubar Afeyan PhD ’87

Microscopic defects in ice influence how massive glaciers flow, study shows

Getting to systemic sustainability

New MIT-LUMA Lab created to address climate challenges in the Mediterranean region
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Medium and mighty: Intermediate-mass black holes can survive in globular clusters
Joint research led by Michiko Fujii of the University of Tokyo demonstrated a possible formation mechanism of intermediate-mass black holes in globular clusters, star clusters that could contain tens of thousands or even millions of tightly packed stars. The first ever star-by-star massive cluster-formation simulations revealed that sufficiently dense molecular clouds, the "birthing nests" of star clusters, can give birth to very massive stars that evolve into intermediate-mass black holes. The findings were published in the journal Science .
"Previous observations have suggested that some massive star clusters (globular clusters) host an intermediate-mass black hole (IMBH)," Fujii explains the motivation for the research project. "An IMBH is a black hole with a mass of 100-10000 solar masses. So far, there has been no strong theoretical evidence to show the existence of IMBH with 1000-10, 10.1126/science.adi4211 000 solar masses compared to less massive (stellar mass) and more massive (supermassive) ones."
Birthing nests might conjure up images of warmth and tranquility. Not so with stars. Globular star clusters form in turmoil. The differences in density first cause stars to collide and merge. As the stars continue to merge and grow, the gravitational forces grow with them. The repeated stellar collisions in the dense, central region of globular clusters are called runaway collisions. They can lead to the birth of very massive stars with more than 1000 solar masses. These stars could potentially evolve into IMBHs. However, previous simulations of already-formed clusters suggested that stellar winds blow away most of their mass, leaving them too small. To investigate whether IMBHs could "survive," researchers needed to simulate a cluster while it was still forming.
"Star cluster formation simulations were challenging because of the simulation cost," Fujii says. "We, for the first time, successfully performed numerical simulations of globular cluster formation, modeling individual stars. By resolving individual stars with a realistic mass for each, we could reconstruct the collisions of stars in a tightly packed environment. For these simulations, we have developed a novel simulation code, in which we could integrate millions of stars with high accuracy."
In the simulation, the runaway collisions indeed led to the formation of very massive stars that evolved into intermediate-mass black holes. The researchers also found that the mass ratio between the cluster and the IMBH matched that of the observations that originally motivated the project.
"Our final goal is to simulate entire galaxies by resolving individual stars," Fujii points to future research. "It is still difficult to simulate Milky Way-size galaxies by resolving individual stars using currently available supercomputers. However, it would be possible to simulate smaller galaxies such as dwarf galaxies. We also want to target the first clusters, star clusters formed in the early universe. First clusters are also places where IMBHs can be born."
- Black Holes
- Astrophysics
- Extrasolar Planets
- Solar Flare
- Star cluster
- Open cluster
- Globular cluster
- Blue supergiant star
Story Source:
Materials provided by School of Science, The University of Tokyo . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Michiko S. Fujii, Long Wang, Ataru Tanikawa, Yutaka Hirai, Takayuki R. Saitoh. Simulations predict intermediate-mass black hole formation in globular clusters . Science , 2024; DOI: 10.1126/science.adi4211
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Food Groups Based On Level of Processing
- Computer Vision, Machine Learning Aid Driving
- Most Distant Known Galaxy
- A New Dinosaur from Zimbabwe
- The Case of the Missing Black Holes
- Menstrual Periods Arriving Earlier
- Adjusting Sunglasses for Your Windows
- Novel Gene-Editing Tool Created
- How Hummingbirds Hover With Such Accuracy
- Complete X and Y Chromosomes of Great Apes
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
200+ Research Title Ideas To Explore In 2024. Choosing a compelling research title is a critical step in the research process, as it serves as the gateway to capturing the attention of readers and potential collaborators. A well-crafted research title not only encapsulates the essence of your study but also entices readers to delve deeper into ...
Writing effective headings. Although similar, headings are not the same as titles. Headings head paragraphs and help structure a document. Effective headings make your paper easily scannable. Common high level headings in dissertations and research papers are "Methods", "Research results", and "Discussion". Lower level headings are ...
I analyzed a random sample of 105,975 full-text research papers, uploaded to PubMed Central between the years 2016 and 2021, in order to explore common ways to start a research title. I used the BioC API to download the data (see the References section below). Common ways to start a title The most common 3-word phrases to start a title
Political Studies 63 (August 2015): 626-641. With these examples in mind, think about what type of subtitle reflects the overall approach to your study. ... Choosing the Proper Research Paper Titles. AplusReports.com, 2007-2012; Eva, Kevin W. "Titles, Abstracts, and Authors." In How to Write a Paper. George M. Hall, editor. 5th edition ...
Shorten the text to make it more concise, while still remaining descriptive. Repeat this process until you have a title of fewer than 15 words. 2. A good title is easily searchable. Most readers ...
Good titles help readers find your research, and decide whether to keep reading. Search engines use titles to retrieve relevant articles based on users' keyword searches. Once readers find your article, they'll use the title as the first filter to decide whether your research is what they're looking for. A strong and specific title is the ...
In addition to the above process, keep the following main tips in mind when writing an effective research paper title: Write your paper and abstract first, then work on your title. This will make the process much easier than trying to nail a title down without a full, finished paper to start from. Keep your title short!
An effective title captures all aspects of the research-the subject, methods, results, and novelty. As is customary with most types of writing, research writing is done in the stages of outline, draft, and final. Thus, a title may not always be determined at the beginning of a study and often evolves as the study progresses.
Soler (2007) identified four different types in an analysis of 570 titles in the biological and social. sciences: nominal group, full sentence, compound, and question, and Wang and Bai (2007 ...
A good title is a "concise statement of the main topic of the research and should identify the variables or theoretical issues under investigation and the relationship between them" (American Psychological Association, 2020, p. 31); thus, writers may spend an "inordinate amount of time, discussion and mental effort" (Swales, 1990, p. 222) on making their titles appropriate and attractive.
Step 2: Identify research study keywords. Now that you have answers to your research questions, find the most important parts of these responses and make these your study keywords. Note that you should only choose the most important terms for your keywords-journals usually request anywhere from 3 to 8 keywords maximum. One-sentence answer ...
Avoid abbreviations or jargon in your title.3, 4, 9 People from other fields whose research intersects with yours might cite you if they can find your article, but if you use abbreviations or jargon specific to your field, their searches won't uncover your article. Some authors think attracting attention with humor or puns is a good idea, but that practice is actually counterproductive.3, 4 ...
Make sure your research title describes (a) the topic, (b) the method, (c) the sample, and (d) the results of your study. You can use the following formula: [ Result ]: A [ method] study of [ topic] among [ sample] Example: Meditation makes nurses perform better: a qualitative study of mindfulness meditation among German nursing students. Avoid ...
Abstract. Title is an important part of the article. It condenses article content in a few words and captures readers' attention. A good title for a research article is the one which, on its own ...
While the APA suggests limiting titles to 12 words, research has shown that title length has been steadily increasing and often go over that limit, particularly in psychological journals (Hallock & Dillner, 2016; Lewison & Hartley, 2005; Whissell, 2012). Our study, in conjunction with past studies, suggests that longer titles are preferred and ...
Here are some general tips and examples to help inspire you: 1. Start with a working title while you're researching and drafting, and refine it once your project is complete. 2. Make sure your title is specific, focused, and relevant to your research. 3. Use clear and straightforward language, avoiding jargon and acronyms.
Nagano (2015) and Milojevic (2017) ... Overall, the relative lack of research into titles may lead us to suppose that practices are homogeneous across the academy, but what research there is shows different interests and foci with titles differentiated by topic, journal and discipline. This is because, we assume, titles aim to both attract and ...
Titles are a key part of every academic genre and are particularly important in research papers. Today, online searches are overwhelmingly based on articles rather than journals which means that writers must, more than ever, make their titles both informative and appealing to attract readers who may go on to read, cite and make use of their research.
Qualitative Research Topics. Qualitative Research Topics are as follows: Understanding the lived experiences of first-generation college students. Exploring the impact of social media on self-esteem among adolescents. Investigating the effects of mindfulness meditation on stress reduction. Analyzing the perceptions of employees regarding ...
Introduction. This article deals with drafting a suitable "title" and an appropriate "abstract" for an original research paper. Because the "title" and the "abstract" are the "initial impressions" or the "face" of a research article, they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, meticulously, and consume time and energy.[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] Often, these ...
Research Paper Title. Research Paper Title is the name or heading that summarizes the main theme or topic of a research paper.It serves as the first point of contact between the reader and the paper, providing an initial impression of the content, purpose, and scope of the research.A well-crafted research paper title should be concise, informative, and engaging, accurately reflecting the key ...
113 Great Research Paper Topics. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily ...
With the rapid increase in the number of scholarly publications on STEM education in recent years, reviews of the status and trends in STEM education research internationally support the development of the field. For this review, we conducted a systematic analysis of 798 articles in STEM education published between 2000 and the end of 2018 in 36 journals to get an overview about developments ...
Li's co-authors include Ruonan Han, an associate professor in EECS, leader of the Terahertz Integrated Electronics Group, and member of the Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE); senior author Dirk Englund, professor of EECS, principal investigator of the Quantum Photonics and Artificial Intelligence Group and of RLE; as well as others at ...
May 30, 2024. Israeli Views of the Israel-Hamas War. 1. Views of the Israel-Hamas war. By Laura Silver and Maria Smerkovich. At the time of the survey in March and early April, Israelis voiced differing views of the war. Reactions to the military response against Hamas were generally mixed, as were attitudes toward the principal decision-makers ...
A majority of Americans say they are closely following news about the 2024 U.S. presidential election, a slightly higher share than in April 2020. At the same time, many people already say they are worn out by so much coverage of the campaign and candidates, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted this April.
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE S&T Public Affairs, 202-286-9047. Plan will prepare DHS to meet emerging technological needs and maximize strategic impact. WASHINGTON - The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) released the first-ever department-wide Innovation, Research and Development (IRD) Strategic Plan, articulating key investment goals over the next seven fiscal years.
In a paper titled "tRNA modification reprogramming contributes to artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum", published in the journal Nature Microbiology, researchers from SMART's Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) interdisciplinary research group documented their discovery: A change in a single tRNA, a small RNA molecule that is involved in translating genetic information from RNA to ...
New research demonstrated a possible formation mechanism of intermediate-mass black holes in globular clusters, star clusters that could contain tens of thousands or even millions of tightly ...
Susan D. McMahon, PhD, via email. Russell Dorn, DePaul University Media Relations, via email. Research by APA reveals a post-pandemic surge in violence against pre-K to 12th-grade teachers, driving a rise in intentions to resign or transfer, highlighting a critical need for national interventions to ensure the well-being of educators and school ...